Items
topic_interest is exactly
research
-
 2021-04-18
2021-04-18Edinburgh and Northumberland, "Post Pandemic" Historical Tourism
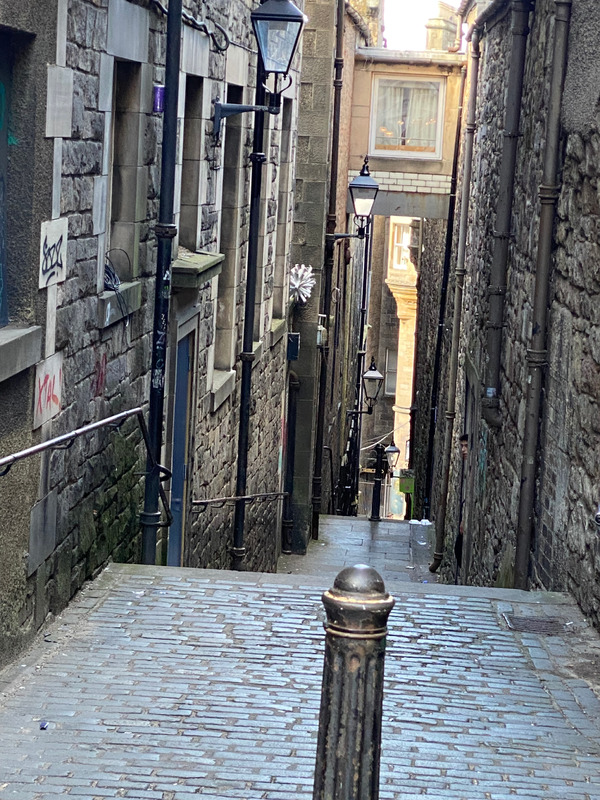
I had been dreaming of this trip since 1996 when I went to England on a high school theatre and literature trip and fell in love with the UK. Specifically, I fell in love with Scotland and its history, becoming a British History enthusiast. In August, 2021, I completed my BA in History at ASU, then changed careers from Film/tv costuming to a special education teaching position. During the peak age of Covid-19, I worked full time, completed full time undergraduate studies, interned in politics and not-for-profit law, and started over in a new career and life in a new state. All of 2020-2021 was a non-stop adrenaline rush of constantly moving, getting Covid, and burning out mentally along the way. In 2021, I was halfway through a teaching contract and gravely unhappy, longing to just... escape. I kept dreaming of one photo of Edinburgh that was on my vision board. The picture, from Pinterest, was of a narrow Close in Old Town, Edinburgh, the historic "original" city that squeezed so much history and magic in about a mile. Old Edinburgh held tens of thousands of people in one square mile with their Closes serving as narrow alleyways between buildings of both stone and wood, both affluent and poor societal classes. After creating this vision board, I started working a ridiculous amount of overtime in the school's residences for special needs students and saving money. I was used to already working over 60 hours a week, so I didn't see the problem yet. The short staffing crisis of special education staff provided the opportunity to earn $40/ hour plus $1000 monthly bonus for anyone willing to work and be okay with less support for challenging behavior or emergency resources. I was willing to work hard to be free for just a short time over the Easter/Passover School break. Flight and accommodation prices were incredibly low at the start of 2021, encouraging tourists to travel. British Airways and other airlines offered incredible fares! These discounts still enabled me to book more affordable fare into 2023. My flight from Boston to Edinburgh was just over $400, with 7 nights stay in two 4 and 5 star hotels plus one castle for a total of less than $1000. My dream trip was planned to every detail and paid in advance or booked for free with historical memberships. The pandemic and rising popularity of Airbnb and Verbo created the perfect discounts for hotels and upgrades to better suites. Pre-pandemic, I got bed bugs from an Airbnb and had a nightmare of an experience, so it was out of the question for accomodation moving forward. While in planning stages, I booked historical tours and entry into sites like Edinburgh Castle, Mary Kings Close, Ghost Tours of the Vaults, Sterling Castle, then in England, Alnwick Castle and Chillingham Castle's paranormal investigation. I already had memberships to multiple British historical and public sites like the Alnwick Gardens (site of the famous Poison Garden) and Historical Scotland. From Edinburgh Castle to Chillingham Castle, I finally got to see the gallows, dungeons, and artifacts that were in my undergraduate classes. Finances and waiting for a travel companion to finally find "the time" to go held me back from going previously, but I was there, alone, at this particular time for a reason. I got to hold Witches Collars and touch an Iron Maiden that tortured so many innocent "witches". I sat in castle common areas alone with a glass of Whisky and venison sausage while hunting ghosts. Museum staff showed me witches charms and introduced me to folklore that secretly told tales of history in starkly lit archival research rooms. It was this trip that solidified by decision to continue onto graduate studies in history at ASU. It was this trip that made me question, "Why are we so fascinated by death and folklore?" It would be remiss to mention that during my historical tourism of Edinburgh and the Scottish-English Borderlands, the stories of historically significant pandemics and major moments of medical and scientific struggle or discovery were always present- It was..."everything, everywhere, all at once", if you will. The comparisons between Black Death to Cholera to Spanish Flu were ever-present while exploring Mary Kings Close, places of Surgical and Medical History interest, The Vaults, the Grass Market Gallows. I stepped into a cramped spaces that were once the homes of a families who all died of The Plague. White rags hung out the windows of these tourist destinations to remind visitors that it was the way leather beak masked Plague Doctors identified the infected and quarantined. "Haunted" Vaults served as reminders to modern tourists that the poor and disenfranchised once stayed here. If you want to go anywhere in the world to see a pandemic being held with an engrained fear and solemn respect for medical research, it's Scotland. In England, Chillingham Castle and Alnwick Castle allow visitors close proximity to places where prisoners carved each imprisoned day before their deaths into the walls. In Edinbugh, if it isn't a Harry Potter tour, it is a ghost tour. These ghosts are explored with light-hearted entertainment or found during paranormal investigations with high-tech gizmos and Ouiji Boards in this new age when we don't want to talk about how many people died of Covid-19 or a lack of health resources, but pre-modern history when people don't currently hold memory of the dead... One late morning, I went to a pub on the Royal Mile for a proper Scottish breakfast of sausages, haggis, bacon, eggs, tomato, and toast... and a pint. Bagpipes echoed in the air, passers-by spoke different languages and carried their cameras and I (Heart) Scotland t shirts and Whisky. As I sat outside, just taking everything in, a group of domestic tourists sat at my table. We laughed because we were all uncertain of "Mask? no Mask? What does 'optional Mask mean?' Were we bad people for NOT wearing a mask inside the pub to get another beer?" "Is it appropriate to sit so 'close'?" That particular day was the lifting of the Scottish masks in public places mandate. My mates-for-the-day spoke of their quarantines and experiences with Covid-19 and quarantine with both humor and sombre memories. The photo attached to this story was from this day where masks were no longer a must. It is also the same scene from my vision board. On my camera and iPhone camera reels, before this moment and after are dozens of photos of castle chambers, countryside fog, tourist photo ops of High Tea or plain ol Costa Coffee at [Insert Tourist Destination]. My photos are visited with gratitude and inspiration. Not only do I have a renewed desire to travel, but I have a spark of motivation to keep learning. I would never have been able to afford this trip at the level of luxury and privilege I experienced it without the Covid-19 pandemic's aftermath of needed promotional discounts. Misery was everywhere, yes, but joy and purpose were found for me. I hope there were others that experienced incredible change and revelation during this time. -
 2022-07-06T10:19
2022-07-06T10:19Adulting On Lockdown
I was 17 and a freshman in college when lockdown started. At the beginning of the year, COVID was just a blip on the news; the first time I'd heard of it, my mother was sharing an article on how the flu was deadlier and telling me I should get vaccinated. That February I got my first flu vaccine. A month later, I was packing up my dorm in a day and getting sent home. We went to McDonald's for lunch as fuel for the two-hour drive back to my small hometown. I wouldn't step foot in another business for a year. I spent the fall of my sophomore year away from all my newfound friends, too scared to risk infection on campus and too disappointed with the idea of spending the semester locked in a dorm room. I didn't return until the spring, now a legal adult. It would take another year for the mask mandate to be lifted; by then I'd been accepted into my school's Masters program and had moved out of my parent's place permanently. I haven't hit my 20s yet and the world still seems to be falling apart. A new variant, another mass shooting, the world burning... it's hard to believe it's ever going to end. But I keep working. Right now I'm doing research on the parallel's between Marvel's "Blip" and COVID. People ask me how I got a grant to do that, but to me it's the only way to make sense of the event that's marked my whole adult life. Superheroes make sense. They at least had control over their plague. -
 2022-06-25
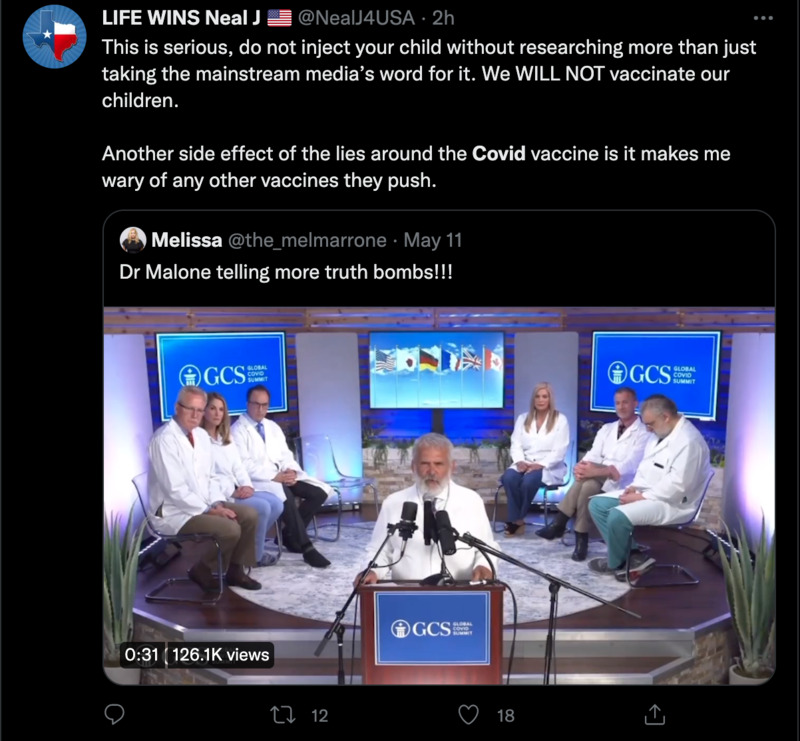
2022-06-25Do not inject your child without research
This is a tweet from NealJ4USA. This person has decided not to vaccinate their children after having done some research on the subject. Due to distrust in the COVID vaccine, it is also making this person feel more hesitant about any other vaccines that end up getting pushed. -
 2022-05-03
2022-05-03Nose Spray Vaccines Could Quash COVID Virus Variants
This is a news story from The Scientific American by Marla Broadfoot. With the effectiveness of vaccines waning due to new variants coming about, scientists have been coming up with new ways to combat the virus. Scientists are thinking of developing a nose spray vaccine that attacks the virus at the source. It is believed that a vaccine delivered this method could trigger mucosal immunity. Nasal vaccines have been shown in the past to be more effective than traditional administration of vaccines. There is risk in this, however, because there still needs to be more research done on mucosal immunity. The advantage is that this vaccine does not rely on syringes or needles, so it has the possibility of reaching more people. -
 2021-07-01
2021-07-01Pets can catch Covid from owners, study suggests
Swabs were taken from 310 pets in 196 households where a human infection had been detected. Six cats and seven dogs returned a positive PCR result, while 54 animals tested positive for virus antibodies. "If you have Covid, you should avoid contact with your cat or dog, just as you would do with other people," Dr Els Broens, from Utrecht University, said. The researchers say the most likely route of virus transmission is from human to animal, rather than the other way round. "We can't say there is a 0% risk of owners catching Covid from their pets," Veterinary Microbiological Diagnostic Centre Dr Broens said. "At the moment, the pandemic is still being driven by human-to-human infections, so we just wouldn't detect it." -
 2021-08-10
2021-08-10COVID meme
I think what makes Covid memes so funny is that they are sometimes based on truth... -
 2021-04-09
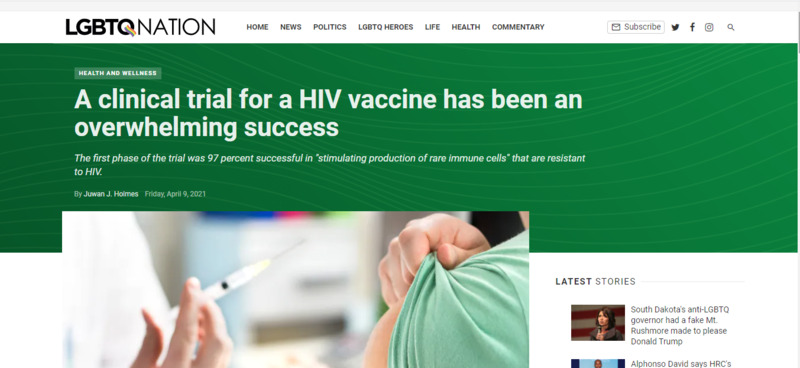
2021-04-09Clinical Trials for HIV Vaccine has been Overwhelming Success due to the help of COVID-19 Vaccine
Clinical trials for HIV vaccines have been overwhelmingly successful with a 97% success rate at stimulating the production of rare immune cells which could lead to vaccines in the future. The COVID-19 vaccine has led to the increased development of m-RNA dosed vaccine which is also found in many other vaccines. By producing the COVID-19 vaccine has led to much more funding and research into the mRNA vaccine field which will bring about new changes in medicine in the future. -
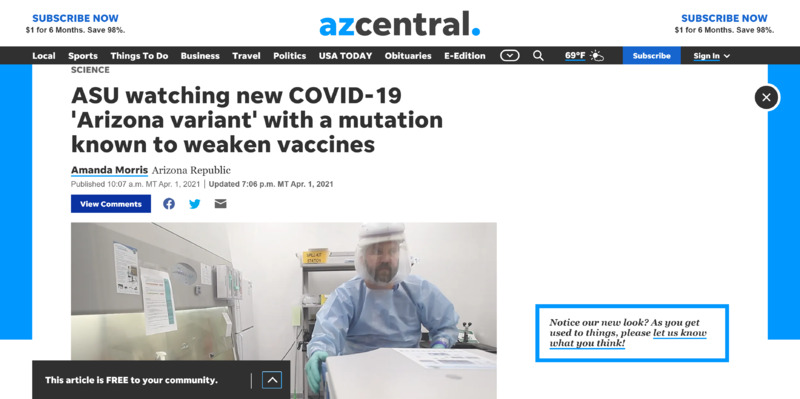 2021-04-01
2021-04-01News Article: ASU watching new COVID-19 'Arizona variant' with a mutation known to weaken vaccines
By Amanda Morris of the Arizona Republic: Arizona State University researchers have found a home-grown variant of the coronavirus emerging in Arizona that they say should be monitored closely because it carries a mutation known for weakening vaccines. In a non-peer reviewed study that published Sunday, researchers said they have detected 17 cases of the new variant since February, 15 of which were in Arizona. The other two cases were found in Houston in late February and New Mexico in early March, suggesting that the variant has begun to spread. "My hope is that we do not see more of these cases. The whole point of surveillance is to keep this from spreading," said Dr. Efrem Lim, an ASU virologist and assistant professor. The variant is known as the B.1.243.1 variant, and descends from a common lineage of the virus called B.1.243, which nationally makes up about 2.5% of all cases, according to David Engelthaler, director of the Translational Genomics Research Institute's infectious disease division in Flagstaff. "It's not dominant. But, there's a fair amount of that lineage that has been able to hang around," Engelthaler said. "It seems to have picked up this E484K mutation, what we call the 'eek!'" This E484K mutation has also been seen in the variants first detected in South Africa and Brazil, as well as one new variant recently discovered in New York. Numerous studies have shown that this mutation — located in the spike of the virus — lowers antibody responses to the virus and could weaken vaccines. Antibodies are one of the body's tool to recognize and fight the virus. The E484K mutation has been shown to weaken antibody responses. One study from Seattle showed that it caused the neutralizing effects of antibodies to decrease by tenfold, and numerous other studies have shown similar results. American vaccine development company Novavax reported that its COVID-19 vaccine was 96.4% effective against the original coronavirus strain and 86.3% effective against the U.K. variant, but was far less effective in South Africa, where the South Africa variant carrying this mutation is dominant. In the South Africa trials, the vaccine was shown to be 48.6% effective overall, and 55.4% effective in HIV-negative individuals. Moderna announced a sixfold reduction in antibody responses from its vaccine against the South Africa variant, and Pfizer observed a drop in vaccine-induced antibody responses against the South Africa variant. The Johnson & Johnson vaccine is reported to be 64% effective against moderate to severe COVID-19 in trials in South Africa vs. 72% effective in U.S. trials. Though the E484K mutation appears to reduce antibody response and possibly reduce vaccine efficacy, Lim stressed that vaccines still work well and said people should get their vaccines as planned. Scientists are monitoring mutations in the spike of the novel coronavirus. Community spread is a concern Though the new Arizona variant carries this mutation, it's still possible for the variant to fizzle out and stop spreading. Lim said researchers have found two other cases where viruses within the B.1.243 lineage independently picked up the E484K mutation, but did not spread. "In both cases, they never led to more transmissions," Lim said. Engelthaler has also tracked other lineages where the E484K mutation showed up, but those strains fizzled out. Overall, researchers have detected over 60 samples containing the E484K mutation statewide, according to TGen's Arizona COVID-19 sequencing dashboard. In order to continue spread, Engelthaler said variants need to be very "fit." "This mutation has popped up on multiple instances and then just goes away," he said. "This one mutation by itself doesn't give the virus superpowers." "It’s definitely a mutation of concern but time will tell if it will be a variant of concern," he added. If the mutation shows up in a more fit version of the virus, then Engelthaler said it becomes more of a concern. The new variant in Arizona is different than past cases because it has already spread from one person to another and could spread further, according to Lim. He said "one-off" mutations here and there are normal, but that the bigger question is about the transmission levels of this variant. A variant's ability to spread to others is also dependent on human behavior, Lim said. If people follow public health guidelines, they are less likely to spread variants to others. In total, Lim said the new Arizona variant has 11 mutations, which is "quite a bit more" than normal virus variations. These 11 mutations could be helping the virus survive or spread and could also act as a "fingerprint" to help researchers identify the new variant, Lim said. Another one of the 11 mutations is located in the spike that the virus uses to attach to and infect cells. Engelthaler said that because of the importance of the spike, any mutations in that area could affect things like how fast the virus spreads or how severe the related illness is. Both Lim and Engelthaler said it's too soon to tell whether the other mutations in this variant have any effect. Overall, this variant still seems to account for a very low percentage of overall cases in the state, according to Dr. Joshua LaBaer, the executive director of ASU's Biodesign Institute. ASU researchers wrote that it's still possible there are more undetected cases of the variant since there are limited efforts to genetically monitor the virus nationwide. In Arizona, roughly 1.3% of cases overall have been genetically sequenced, or analyzed, according to TGen's Arizona COVID-19 sequencing dashboard. In February and March, over 3% of cases were sequenced, higher than national rates of sequencing, which were below 1% in January. ASU is working with the Arizona Department of Health Services to monitor the new variant and hopefully prevent further spread through contact tracing and other public health measures, Lim said. California and UK variant cases rise Currently the Arizona variant is only considered a "variant of interest" and not a "variant of concern." These are different categories outlined by the CDC and used to assess the risk level of each variant. The CDC defines "variants of interest" as those that are associated with potential changes, whereas "variants of concern" have evidence showing actual changes such as increased transmission, more severe disease or antibody evasion. There are five variants of concern, which include variants first identified in the United Kingdom, South Africa, Brazil and California. Two variants from California were elevated from variant of interest to variant of concern this month and have rapidly spread in Arizona. "They're closely related to each other and have definitely been documented with increased transmissibility and some impact on some antibody treatment," Engelthaler said. In November 2020, both the California variants accounted for only 0.73% of Arizona's genetically sequenced samples. By March, they accounted for 31.64% of samples and are predominant variants statewide. One non-peer reviewed study from the University of California San Francisco showed weaker antibody responses against the California variants. Because of concerns that monoclonal antibody treatments may be less effective against these two variants, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services announced two weeks ago that it would limit the distribution of one treatment to states with high levels of the California variant, including Arizona. The California Department of Public Health also recommended that the state stop distributing the treatment, which is made by American pharmaceutical company Eli & Lily. In a health alert, the department said this treatment was unlikely to be active against the California variants. The U.K. variant, which is highly contagious, has also been spreading statewide ever since it was first detected in late January. In March the U.K. variant accounted for 4.72% of genetically analyzed samples. Currently, Engelthaler said Arizona has over 100 cases of the U.K. variant and over 1,000 cases of the California variants. Arizona also detected its first cases of the South Africa variant last week. So far, Lim said that all of the variants of concern are manageable and have not risen to the level of "variant of high consequence," which the CDC defines as variants that are shown to significantly reduce the effectiveness of prevention and medical measures. "The risk is whether one of these current variants of concern acquire additional mutations that push it up to the next level," Lim said. To prevent further mutations, LaBaer said it's important to prevent spread of the virus by continuing to follow health guidelines and getting vaccinated. The more the community can prevent the spread of the virus, the less mutations will occur, he said. "We're kind of in this race right now between the developed dominance of these much more infectious variants that are now spreading throughout the country and getting people vaccinated," LaBaer said. "At the moment, I'm a little worried that the spread of this virus is so fast that that may outpace our ability to get vaccines in arms." He said it was theoretically possible that new variants could escape the vaccines, meaning that the public would move backward away from reaching herd immunity. But Lim said the vaccines can easily be updated to protect against new variants. Pharmaceutical companies like Pfizer and Moderna are already working on developing updated booster shots. In the meantime, researchers will continue to monitor the Arizona variant to see if it spreads further. Engelthaler said he expects the most fit variants of the virus to become more dominant statewide as people continue to get vaccinated and stamp out less successful strains. "There's a bit of a race here with the virus — a survival of the fittest race," Engelthaler said. "But what we don't want is to raise too much concern that things are going in the wrong direction...what we're doing is closely watching the evolution of a virus like we never have before. It's good that we have this capability, it's more important to put it into context." Amanda Morris covers all things bioscience, which includes health care, technology, new research and the environment. Send her tips, story ideas, or dog memes at amorris@gannett.com and follow her on Twitter @amandamomorris for the latest bioscience updates. Independent coverage of bioscience in Arizona is supported by a grant from the Flinn Foundation. -
 2021-03-12
2021-03-12Long-term Vaccine Effect Research Project
This article is about the Healthcare Worker Exposure Response and Outcomes (HERO) research project. They are trying to understand the long-term effects of the Covid-19 vaccine. The population that they are using is first-responders, who were among the first group to receive the vaccine in most states. The project plans to conduct periodic surveys over a 2 year period. Since this vaccine was produced in record time, and especially the lack of available data to the long term effects, it is an important project. The project also surveys the first responders regarding their mental health during the pandemic. It includes fire fighters, EMS providers, and law enforcement. -
 2020-04
2020-04The Historical Research Project
Specifically, the Covid-19 pandemic inadvertently prevented me from my continued work in the Research Department at the Denver Public Library, as well as my volunteer work with the School Tours program at the History Colorado Center. However, it has given me an opportunity to conduct a history research project of my own choosing. I have had an ongoing interest in a writing project on the Domesday Book, which was a survey conducted in medieval England in AD 1085-1088. The repeated news stories on fellow Americans and citizens from around the world choosing to become interested in artwork and/or other projects while presented with an abundance of personal time due to Covid-19 restrictions has inspired me to begin this project. I was able to obtain a copy of an English translation of the Domesday Book and, though my graduate level academic work has not been postponed in any way, I have found time to begin this work. I will always remember that I began this passionate project because of the Covid-19 lockdown and restrictions, it will occupy my time far beyond Covid-19. -
 2020-04-17
2020-04-17COVID-19 and Social Justice
From the article: The COVID-19 pandemic is a health and mental health crisis, to be sure. But it is also a crisis of social injustice, inequitably affecting vulnerable and marginalized populations that include, among others, individuals who earn low incomes, or are incarcerated, homeless, in foster care, over 65 (especially those in long-term care facilities), people of color, or undocumented. Social work practitioners, educators, and policy makers are working to address the needs of these populations despite the unpredictability of the virus’s secondary impact on systems. -
 2020-06-09
2020-06-09Why Social Justice Is Central to Treating COVID-19
From article: Racism and classism create conditions where people of color, those living in poverty, and other marginalized groups have limited access to resources that affect health -
 2020-07-04
2020-07-04Suivre la trace du coronavirus dans les égouts
In anticipation of a second wave of COVID-19, Canadian scientists are currently working to set up a detection system based on organic waste that ends up in sewers. -
 2020-04-08
2020-04-08Sunnybrook is re-processing N95 masks, should the need for use arise
Sunnybrook Hospital began researching how to sterilize masks in April 2020 as the PPE shortages had become so severe. In the video, Dr. Jerome Leis explains the research. -
 2020-11-06
2020-11-06Nasal spray prevents COVID-19 infection in test animals, new study finds
A nasal spray aimed at temporarily preventing COVID-19 infections was tested on ferrets with positive results. -
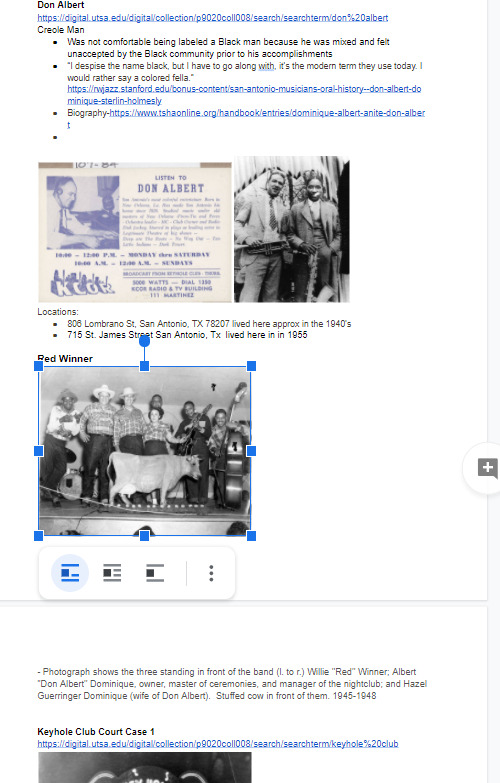 2020-11-13
2020-11-13Full-Virtual Work in the Middle of a Pandemic
This document was created and shared by myself and some coworkers in the History department at my university, St. Mary's. This document was the result of a project we were all assigned to work together on regarding researching the African-American community in West San Antonio, Texas. The work was not easy. Being separated from each other meant coordination and collaboration were very difficult, and actually accomplishing much in the way of actual work was slow going, with few of us actually being able to work together at the times the others were available. Not helping in any way was the fact that working remotely left us with almost no oversight from our supervisor, who was also in charge of several other projects in the department. Our research also took many different forms before settling on the one it ended up in, and it suffered most greatly from most of the workers assigned not being in the city we needed to be in, not having access to any traditional resources like proper records or non-digital resources that might have gone into the detail that we needed, and of course being unable to properly help each other. Despite this however, when we finally were able to coordinate a time to collaborate and work together, we surprisingly were able to unearth the aspect shown here, the resurrection of the Keyhole Club by noted Jazz musician Don Albert, famous for being a fully racially integrated nightclub during a time when such a thing was unheard of, and was challenged. Despite some serious challenges of our own, my coworkers and I were able to emerge successful after all and provide some much-needed information to the assignment. -
 2020-11-18
2020-11-18"The End of the Pandemic Is Now in Sight" - The Atlantic Monthly
With the development of two viable COVID-19 vaccines, it appears that the end of the pandemic appears to be at hand in the near future. In an article for the Atlantic Monthly magazine, journalist Sarah Zhang explains how these viable vaccines were developed using new technologies and how the resolution of the pandemic is now more dependent on policy choices made by political leaders, namely the President of the United States. During the initial months of the COVID-19 pandemic, medical professionals, epidemiologists, and vaccinologists were in the dark about the symptoms, treatability, and curability of the disease. After months of intense hands-on experience and in-depth genomic research, the companies Pfizer and Moderna have developed viable vaccine candidates. But these vaccines are different from typical vaccines: they are mRNA vaccines. This means that they work by injecting mRNA which encodes viral proteins, rather than injecting a weakened or dead SARS-CoV-2 virus. mRNA vaccines, according to Zhang, were once thought to be potentially unviable, but the positive preliminary results of the Pfizer and Moderna mRNA vaccines may mark the beginning of a new era of vaccine research and development. In the future, Zhang says, mRNA vaccines may be developed for the Zika virus or for personalized forms of cancer. However, a major drawback of mRNA vaccines is their fragility, as they require extremely cold temperatures to be preserved. Now that these vaccines may be available for public use in the near future, it is up to the United States' political leadership to formulate policies to promote the vaccination of the populace and the mitigation of COVID-19 infections during the winter. According to Zhang, "Every infection we prevent now—through masking and social distancing—is an infection that can, eventually, be prevented forever through vaccines." -
 2020-10-15
2020-10-15Have Blood Type O+ ? You May Be At a Lower Risk of Covid-19!!
Researchers are claiming that Covid-19 might not be as vulnerable to one blood type. To arrive at these findings, Danish researchers conducted a study on 7,422 sample people who tested positive for Covid-19. They found out that only 38.4% were blood type O, whereas 44% of people with the blood group A had tested positive. -
 2020-03-03
2020-03-03Survival of SARS-CoV-2 and influenza virus on the human skin: Importance of hand hygiene in COVID-19
This is a manuscript published recently in Japan regarding the survival time of COVID-19 virus (SARS-CoV-2) and the influenza A virus (IAV). Overall, the results showed that SARS-CoV-2 and IAV were inactivated more rapidly on skin surfaces than on other surfaces such as stainless steel/glass/plastic. However, the survival time of SARS-CoV-2 was significantly longer for than for IAV. Moreover, both SARS-CoV-2 and IAV in the mucus/medium on human skin were completely inactivated within 15 s by ethanol treatment. This showed that the COVID-19 virus we are facing now survives longer on our skin than influenza A virus, and thus it could spread much easier. Also, this paper shows the importance of sanitization, and how ethanol is one method that is useful in helping the virus to not be spread. -
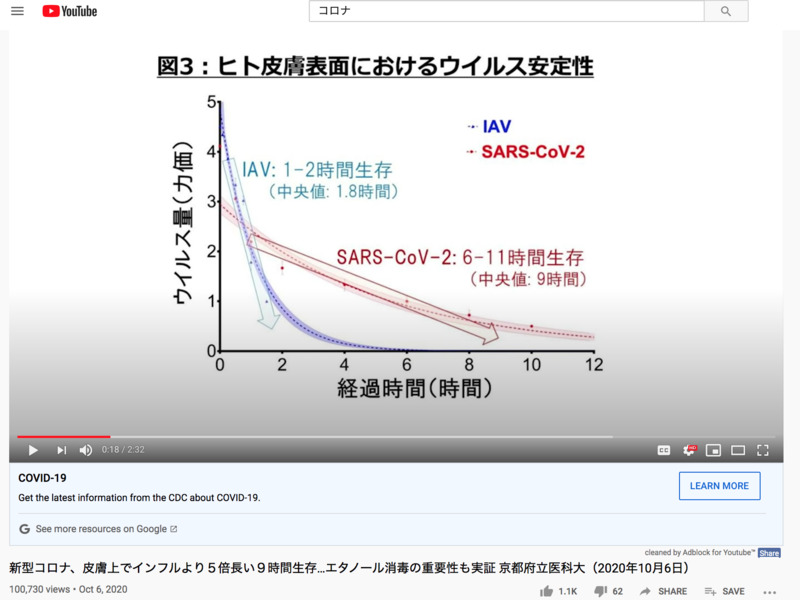 2020-10-06
2020-10-06新型コロナ、皮膚上でインフルより5倍長い9時間生存…エタノール消毒の重要性も実証 京都府立医科大(2020年10月6日)- New corona survives 9 hours on the skin, 5 times longer than influenza … Demonstrates the importance of ethanol disinfection Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine (October 6, 2020)
京都府立医科大学の研究チームは、 新型コロナウイルスが、インフルエンザウイルスに比べて ヒトの皮膚上で長期間生存することを明らかにしたと発表しました。 こちらは ヒトの皮膚表面でのウイルス量が時間とともにどう変化するかを示したグラフで、 赤が新型コロナウイルスを、青がインフルエンザA型ウイルスを表しています。 研究チームによりますと、 新型コロナウイルスは皮膚上で9時間程度生存することが明らかになり、 これはインフルエンザウイルスよりもおよそ5倍長いということです。 京都府立医科大・廣瀬亮平助教 「ウイルスが付いているものを手で触って、 その後喉や口や目の辺を触ると、それによって感染するので、 手の上で長生きをするということは、 そういう機会が増えてしまうということでいくと、 感染リスクが上がると考えたほうがいいのではないかと思っている。」 一方、研究チームは、 濃度80%のエタノールによる消毒効果についても評価を行いました。 それによれば、15秒間の消毒でウイルスが完全に不活化され、 「新型コロナウイルスに対する手指消毒の重要性を実証した」 としています。 京都府立医科大・廣瀬亮平助教 「エタノール消毒薬を使用すれば、 (ウイルスが皮膚上で)長生きするとはいえ、 過度に心配する必要はないのではないかと思っている。 ただ、長い時間生存するということは、裏を返すと、 やはり感染のきっかけが把握しづらい。 例えば手に1時間しか付いていないということであれば、 感染のきっかけ、他者に移すきっかけとかも認識できる可能性があるが、 やはり7,8,9時間と長い時間手に感染性のウイルスが残っていて、 どこを触ったかもわからないとか、どこからもらったかわからないという 状態になってしまう可能性がある。 最近、感染した人への風当たりが厳しい部分もあるが、 接触感染という観点から行くと、 なかなか個人の努力だけでは厳しいかなというところがあるので、 そこに関しては周りの方も優しい目で見てほしいと思う。」 ※引用元 ●論文:Clinical Infectious Diseases Ryohei Hirose et al., (2020) Survival of SARS-CoV-2 and influenza virus on the human skin: Importance of hand hygiene in COVID-19 https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-... ●プレスリリース:京都府立医科大のHP ヒトの皮膚上に存在する新型コロナウイルスの生存期間を解明 https://www.kpu-m.ac.jp/doc/news/2020... The research team at Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine discovered that the new coronavirus, compared to influenza virus, survives for a longer time on human skin. This is (graph shown on the screenshot) a graph showing how the amount of virus that is viral on the human skin surface changes over time. Red represents the new coronavirus and blue represents influenza A virus. According to the research team, it was revealed that the new coronavirus survives on the skin for about 9 hours. This is about five times longer than the influenza A virus. Assistant Professor Ryohei Hirose, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine stated "By touching something with a virus with your hand, then touching your throat, mouth, or eyes, you will be infected by it. The evidence that the virus lives long on your hands means the higher you will be exposed to the virus and thus I think it's better to think that the risk of infection will increase. " Meanwhile, the research team also evaluated the disinfecting effect of ethanol with a concentration of 80%. According to the research, the virus was completely inactivated by disinfecting with the 80% ethanol for 15 seconds and it "demonstrated the importance of hand sanitizer for the new coronavirus". Assistant Professor Ryohei Hirose, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine stated "If you use an ethanol disinfectant, Although the virus lives longer (on the skin), I don't think we need to worry too much. However, the fact that the virus survives longer means it is hard to figure out how an individual got infected. For example, if you the virus was on your hand for only an hour, It may be possible to track down the cause of infection and the cause of transfer to another person, but the infectious virus can remain on the hand for 7, 8 and 9 hours, and it is hard to tell what you touched that had the virus and where you got the virus from. Recently, there are negative views on people how got the virus, but looking from the point of view of infection via contact, it is difficult for an individual to put in the effort only, and I would like people to be more kind to them.” -
 2020-10-08
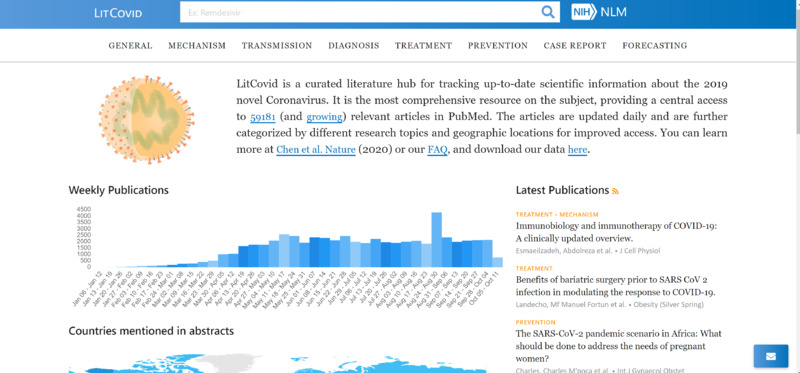
2020-10-08LitCovid- open access database to new and peer reviewed literature
LitCovid is a website created by the NIH to provide free access to all academic papers and studies published to PubMed about COVID-19. The database makes it easy to search for specific types of studies, and is broken down into different categories (such as mechanism, transmission, prevention, and forecasting). It is quite jargon-heavy since it is a collection of academic papers, but can be really useful for learning more about the disease. -
 2020-07-02
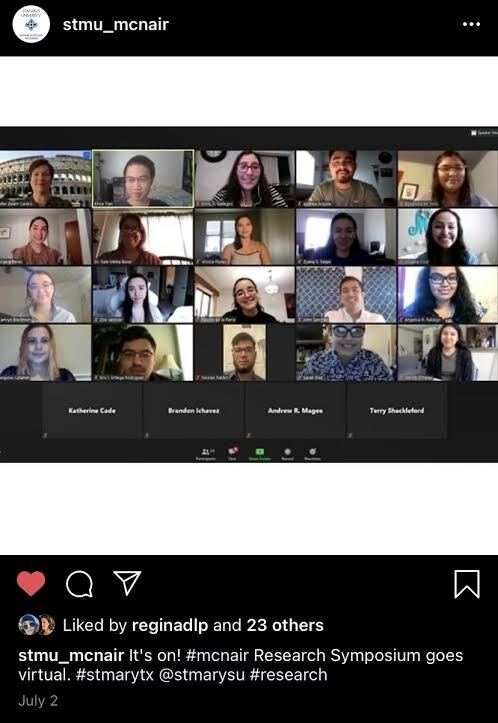
2020-07-02Summer College Programming During the Pandemic
The post is a screenshot from the annual McNair Scholars Program Research Symposium from the summer. The screenshot captures students and faculty from the program before they began their presentations over zoom. The McNair Scholars program prepares underrepresented students for graduate school. Students have a faculty mentor who advises them on a research project during the summer, where they write a paper, prepare for graduate school applications, and then later present the research at the annual research symposium. Usually, the program takes place on the St. Mary’s University campus, and students are provided campus resources such as housing and meal plans. They can meet with faculty and peers in person. Due to COVID-19, the program had to be completely virtual; every program meeting utilized zoom. The McNair Scholars summer research program is one example of college activities that had to adapt to the changing world with COVID-19. Although students were still able to meet virtually and present research, there were limitations to not being on campus, such as what research you could conduct and the resources and accessibility of having workspaces on campuses as many students were working at home. The picture also represents the new normal of large gatherings, especially for academic spaces. All of our classes resemble this image now. -
 2020-08
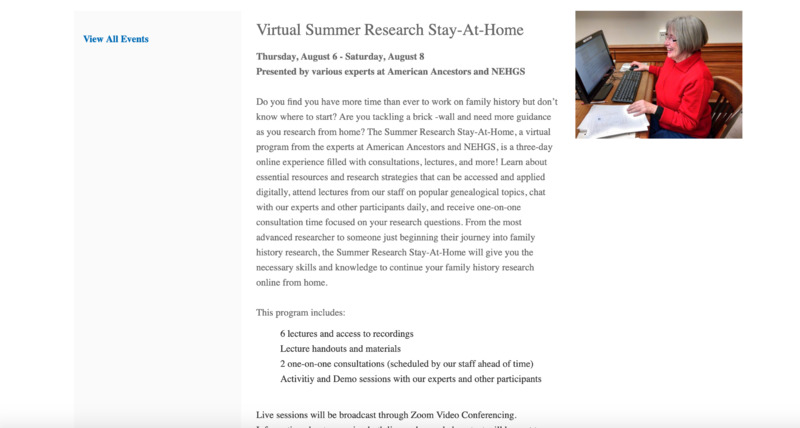
2020-08Virtual Summer Research Stay-At-Home
This screenshot explains a virtual event hosted by American Ancestors and the New England Historic Genealogical Society. This event is an example of how researchers are adapting to the pandemic. With the building closed, the New England Historic Genealogical Society is hosting a program to encourage researchers to access digitized material and continue researching during the pandemic -
 2020-07-24
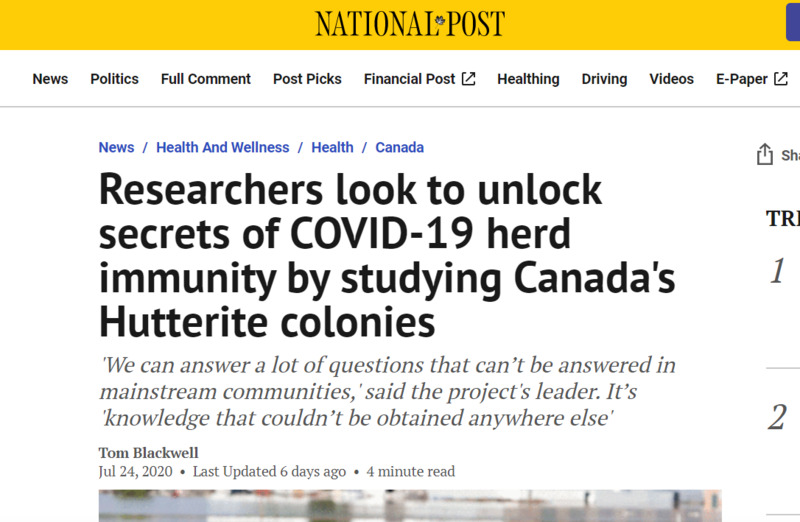
2020-07-24Researchers look to unlock secrets of COVID-19 herd immunity by studying Canada's Hutterite colonies
"'We can answer a lot of questions (in Hutterite colonies) that can’t be answered in mainstream communities,' said Dr. Mark Loeb, a McMaster infectious disease professor who’s heading the project. It’s 'knowledge that couldn’t be obtained anywhere else.'" "The safety council chastised some members for visiting doctors without warning them they were sick, not observing social distancing and travelling outside their colony when it was not essential. Saskatchewan Premier Scott Moe said Wednesday the province may impose restrictions on travel to and from the colonies to curb spread of the coronavirus. But Moe also argued against stigmatizing the Hutterites, who have seen businesses indiscriminately barring members of the communities." -
 2020-06-24
2020-06-24Congresswoman DeGette Press Release, Funding for Covid research, bipartisan
Excerpt from press release: WASHINGTON, D.C. – While coronavirus-related research is now in overdrive, most other research has been slowed down or stopped altogether due to pandemic-induced closures of campuses and laboratories. Now, tens of thousands of graduate students, postdocs, principal investigators and other technical support staff are at risk of losing their employment and their work without federal relief. Additionally, with this research stopped, America may lose the benefits that come with new technologies and scientific insights. -
 2020-05-13
2020-05-13The Sounds of a Health Pandemic
Music Professor examines the media's use of sound and music to portray the health pandemic
