Items
topic_interest is exactly
study
-
 2022-07-15
2022-07-15Menstrual changes after Covid vaccines may be far more common than previously known
This is a news story from NBC News by Sarah Sloat. Since vaccines have been administered for the last year, new information has come out on how they effect the human body. The journal, Science Advances, found 42% of women with regular menstrual cycles bled more heavily after vaccination. 44% said no change occurred, while 14% reported lighter periods. There is no mention on if this side effect has any effect on fertility. -
 2022-07-05
2022-07-05Yearly BMI changes of children found to be higher during the COVID-19 pandemic
This is a news story from News Medical Life Sciences by Bhavana Kunkalikar. In a study published by the Pediatrics journal, researchers looked at the BMI variations during the COVID-19 pandemic. The study found that compared to the baseline measurements used pre-pandemic, the pandemic showed an increase in BMI that was .24 higher than the baseline. Higher rates of BMI increased in already obese children compared to children of a healthy weight. This article does not mention the social factors that would have contributed to weight gain during the pandemic, but not being able to socialize as often probably was a large contributor. From my own personal experience, I notice some people that I knew prior to the pandemic, and noticed that they put on some weight after the pandemic. Granted, this was what I noticed in adults I knew, not kids. Regardless, I believe that even if someone were to eat the same way they did pre-pandemic, but not exercise like they used to during the pandemic, they are bound to put on a bit of weight from lack of activity. Hopefully, with things being less restricted in some places, it will allow people to do things they did pre-pandemic more often and get back to healthier weights. -
 2022-06-09
2022-06-09Sharing source-backed information can help reduce COVID-19 misinformation online
This is a news story from Penn State University by Jessica Hallman. A recent study has shown that user corrections given back and forth on social media has helped reduce the spread of misinformation. Through sharing source-backed information, people were able to pick out fake news easier. -
 2022-06-11
2022-06-11Adolescents eating less ultra-processed food during COVID-19 pandemic
This is a news story from Healio by Michael Monostra. During the COVID pandemic, adolescents are eating less processed food. "In an interim analysis of the Processed Intake Evaluation (PIE) study of 452 adolescents and young adults presented at ENDO 2022, participants reported eating less ultra-processed food during the first 2 years of the pandemic in 2020 and 2021 compared with prior to 2020. Ultra-processed food consumption dropped further in 2022 when COVID-19 restrictions eased." -
 2022-05-22
2022-05-22People in counties backed by Trump were twice as likely to die from COVID: Study
This is an Instagram post by coach.fun.2. The study is not linked in the description, but I did find the article the title is referencing. The story come from the Huffington Post. It says that political affiliation is linked to vaccination rates, which some claim are what is making the difference between living and dying from COVID. Wealth and access to certain care are also taken into account. The study was from Brown and the study claims that states that went heavily for Trump had more cases of COVID deaths. -
 2022-05-10
2022-05-10High Rates of COVID Vaccination Among Adults With Autism
This is a news story from Health Day. Adults with autism have been shown to have higher rates of vaccination according to a new study. Those with autism are more at-risk for severe illness if they contract the disease, say researchers. To get the data, researchers sent online surveys to 431 autistic adults in Pennsylvania. They showed that about 78% of survey respondents said they had received or intended to get a COVID-19 vaccine, and more than 55% said that they had received at least one dose. In comparison, 42% of the overall adult population in Pennsylvania had received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine as of the median response date for the survey (April 2, 2021), according to the study. The findings were published in the journal Vaccine. -
 2022-05-12
2022-05-12Covid-19 narrows long-standing Latino mortality advantage, study finds
This is a news story from NBC News by Nicole Acevedo. Latinos have been shown to have lower mortality rates compared to non-Hispanic whites, where they live an average of three extra years. This changed with the virus. In a study published by the Lerner Center for Public Health Promotion, COVID-19 has been shown to kill Latinos 65 or older at 2.1 times the rate of whites in 2020. This number decreased slightly in 2021, which was at 1.6 times the rate of whites. So far this year, it has been at 1.2 times the rate of death. In total, COVID has killed 124,000 Latinos since the start of the pandemic in the United States, which accounts for 17% of deaths. The reason the Latino death rate is high is debated, but some say it is because Latinos in the United States are less likely to have access to quality healthcare or have jobs that would expose them to the virus more often. -
 2022-04-28
2022-04-28There might finally be a good use for all those disposable masks
This is a news story from Mic by AJ Dellinger. A new study published in Material Letters has found that disposable masks could be used to help strengthen concrete. The concrete has tested out as 47% stronger than concrete than did not contain traces of masks. The reason it is stronger is due to the microfibers found in masks. Microfibers used in building materials have shown to reduce the amount fo cracks and shrinkage, which can happen within the first 28 days of laying concrete. Using disposable masks in concrete can help reduce mask pollution while making the concrete itself more durable. -
 2022-04-15
2022-04-15Why the COVID-19 Pandemic Has Disproportionately Impacted BIPOC and Women With Autism
This is a news story from Now This News by Talia Smith. The author says that over the course of the pandemic, BIPOC and autistic women have been disproportionately affected. BIPOC parents who were not able to work remotely struggled to support their autistic children. One study led by the NIH analyzing the impact of the pandemic on BIPOC and low-income populations shows that families with a child living with autism witnessed an increase in sleep issues and behavioral problems, in addition to increased conflict between children and adults and the use of more severe disciplinary methods. In a study published in “Molecular Autism,” researchers revealed that for adults with autism, the pandemic brought relief from certain stressors like “sensory overload” and ultimately led to an “increase in solidarity.” -
 2022-04-21
2022-04-21Study shows women with 'Long COVID' have more symptoms than men
This is a news story from the Hindustan Times. There has been a study showing that women tend to be affected more by 'Long COVID' symptoms than men do. The research was published in the Journal of Women's Health. In the study, women are more likely to have fatigue, difficulty swallowing, and chest pain after a COVID infection compared to men. -
 2022-04-05
2022-04-05US obesity rates increased during COVID pandemic, doctors weigh in
This is a text story from WITN by Justin Lundy. This is a news story on the increase in obesity rates since COVID started. In a study published by the American Journal of Preventative Medicine, the average BMI in US adults increased by 0.6% between March 2020 and March 2021. This increase happened even as exercise participation rates increased by 4.4%. -
 2022-04-11
2022-04-11A New Stanford Study
This is an Instagram post by newsrescue, which is a news site that claims to bust "fake news." The study that this news story is referring to is one on spike proteins, which found that the vaccinated and unvaccinated had roughly the same amount of spike proteins in their blood. This news story is designed to show that the vaccines may not be as effective as they are claimed to be. -
 2022-01-27
2022-01-27Populist nations fared much worse during Covid outbreak, new research says
This is a news story from CNBC, written by Chloe Taylor. This is a story about a study that came out about how well populist nations fared under COVID-19 compared to other nations around the world. More than 40 countries were included in this study, with the US, UK, and India being considered populist nations at the time that this was conducted. In 2020, the study claims that excess deaths were more than twice as high for populist ran governments. For comparison, the countries that were not considered populist in this study include Canada, Sweden, and Japan. For every 100 COVID related deaths, non-populist countries had an additional 8 deaths. In populist led countries, it was an additional 18 deaths for every 100 deaths. The study attributes this to higher citizen mobility that was allowed in populist nations, leading to more spread of the virus. It also claims that populist governments downplayed the severity of the virus itself, giving people the impression that things were safer than they actually were. -
 2022-03-31
2022-03-31'A Cry for Help': More than a Third of High Schoolers Report Poor Mental Health During COVID, CDC Study Finds
This is a story from USA Today by Adrianna Rodriguez. This is about the mental health in teens during the pandemic and how it has affected them. The CDC study that is cited says that 44% of high schoolers reported feeling persistently sad or helpless during 2021. Over half of the students surveyed were reported to have experienced emotional abuse from a parent, with 11% saying they have experienced physical abuse. Nearly 30% of students reported a parent or another adult in their house had lost a job. In a demographics breakdown, LGBT students reported more suicide attempts and poorer mental health than their counterparts. One third of students say that they have experienced racism. This article is meant to help show the impact COVID has had on people and the way lockdowns have impacted high schoolers specifically. -
 2021-10-01
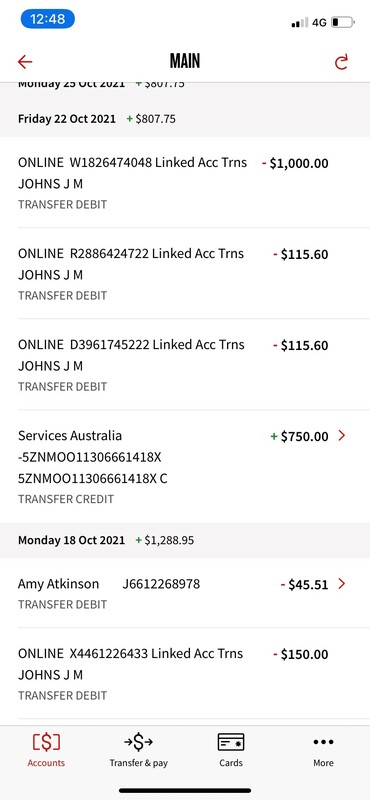
2021-10-01(HIST30060) Disaster Payment: "Getting Payed to Study"
HIST30060. The COVID-19 Disaster Payment, given to workers unable to earn income due to COVID-19 state or territory health order, was given to construction workers during the two-week construction shutdown in Victoria. Traffic control in the construction sector has been my casual job alongside university for the past three years. The recent construction shutdown, however, allowed me to receive the $750 a week from the Disaster Payment without working at all. My housemates and I called this “getting paid to study”. This was especially true in the lead up to exams were we spent the majority of time at home with very little excuse to do anything other than “hit the books”. -
2021-10-01
Disaster Payment: "Getting Paid to Study"
The COVID-19 Disaster Payment, given to workers unable to earn income due to COVID-19 state or territory health order, was given to construction workers during the two-week construction shutdown in Victoria. Traffic control in the construction sector has been my casual job alongside university for the past three years. The recent construction shutdown, however, allowed me to receive the $750 a week from the Disaster Payment without working at all. My housemates and I called this “getting paid to study”. This was especially true in the lead up to exams were we spent the majority of time at home with very little excuse to do anything other than “hit the books”. -
 2020-04-17
2020-04-17COVID-19 and Social Justice
From the article: The COVID-19 pandemic is a health and mental health crisis, to be sure. But it is also a crisis of social injustice, inequitably affecting vulnerable and marginalized populations that include, among others, individuals who earn low incomes, or are incarcerated, homeless, in foster care, over 65 (especially those in long-term care facilities), people of color, or undocumented. Social work practitioners, educators, and policy makers are working to address the needs of these populations despite the unpredictability of the virus’s secondary impact on systems. -
 2020-10-15
2020-10-15Have Blood Type O+ ? You May Be At a Lower Risk of Covid-19!!
Researchers are claiming that Covid-19 might not be as vulnerable to one blood type. To arrive at these findings, Danish researchers conducted a study on 7,422 sample people who tested positive for Covid-19. They found out that only 38.4% were blood type O, whereas 44% of people with the blood group A had tested positive. -
 2020-08-06
2020-08-06Even Asymptomatic People Carry the Coronavirus in High Amounts
This article discusses the findings of a report recently published in the Journal of American Medical Association explaining that asymptomatic carriers of Covid-19 carry as much virus in their nose and mouth as those with symptoms for about the same length of time. While previously the knowledge on asymptomatic spread was more anecdotal this study offers more direct evidence.
