Items
Tag is exactly
disparity
-
 2020-12-10
2020-12-10Analysis of Racial Disparity in COVID by CDC
CDC page outlining racial disparity in the transmission and treatment of COVID-19. There are explanations given for the discrepancies pertaining to economic disparity as well. This illustrates the knowledge of the discrepancies in the transmission of COVID-19 across different racial backgrounds and social classes and possible solutions. -
 11/30/2020
11/30/2020Dang Yang Oral History, 2020/11/30
Dang Yang is the Director for the Office of Multicultural Affairs at UW Eau Claire. He identifies as a Hmong American that was born and raised in the Midwest of the United States. Dang discusses how the COVID-19 pandemic affected his personal life as well as his professional life. In this discussion he emphasizes the challenges of operating an office at a higher learning institution as well as the issues of racism that came about with the onset of the Coronavirus and isolated racially charged events that happened during the pandemic. He focuses on equity in his discussion. -
 2020-12-22
2020-12-22The Virus Is Showing Black People What They Knew All Along
In this article, author Patrice Peck discusses how black Americans are dying of COVID-19 at 1.7 times the rate of whites. In her words "19,000 Black people would still be alive if not for systemic racism." -
 2021-07-21
2021-07-21Latest Data on COVID-19 Vaccinations by Race/Ethnicity
This is an analysis of equity in vaccine distribution. The data shows a disparity between whites and Asians (whose vaccination rates were equal to or higher than their case counts) and black, Latino, Native American, and Native Hawaiians (whose vaccination rates were generally lower than their case counts). In recent weeks, however, these numbers seem to be improving. -
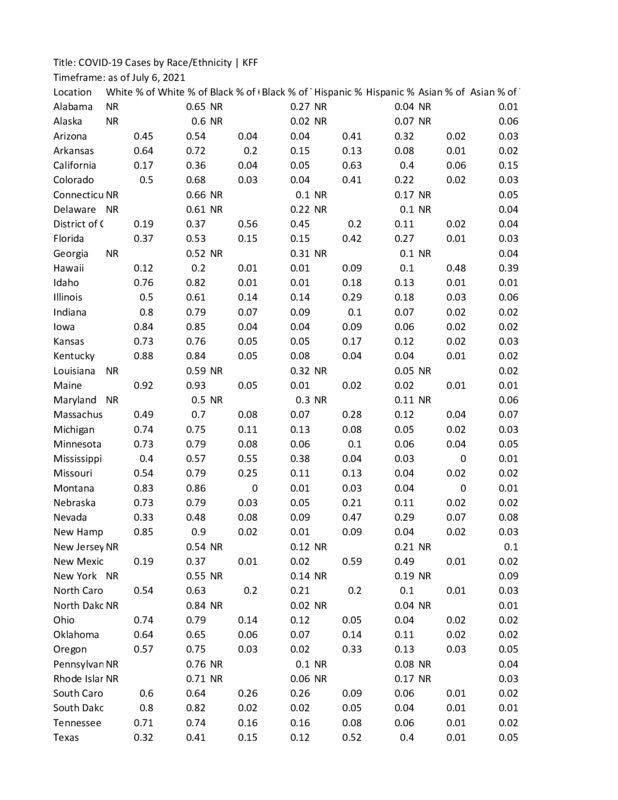 2021-07-06
2021-07-06COVID-19 Cases by Race/Ethnicity
This is an interactive chart and map that allows the user to look at covid rates by race and state. -
 2020-04-16
2020-04-16Infographic: 8 Big Ways Coronavirus Impacts Latinos
This infographic and the accompanying articles discuss the disproportionate impact that coronavirus has on Latino communities. -
 2020-04-30
2020-04-30Offline and left out: Not all Arizona students can connect for remote learning
This article focuses specifically on Arizona's efforts to provide students with internet/technology access in order to achieve online learning. It goes into detail about how several Phoenix schools dealt with the pandemic and online learning in the spring semester of 2020 as well as discusses how some students dealt with internet access issues in creative ways, either due to lack of internet or hotspot issues. Some examples are utilizing hotspots or through just going to public areas despite quarantine conditions to complete schoolwork. -
 2020-04-30
2020-04-3053% of Americans Say the Internet Has Been Essential During the COVID-19 Outbreak
This Pew Research article discusses how different socioeconomic status and political preference influences how Americans believe schools should provide technology for their students. More importantly, the article goes into detail about how parents with lower incomes are more likely to struggle to provide some sort of adequate situation for their children, especially when the majority of Americans view technology and the internet as an essential tool during the pandemic. Besides student access to technology, economic class is also having an impact on how some individuals can afford their own internet connections and phone plans, thereby limiting their access. -
 2021-02-01
2021-02-01Just 5 percent of vaccinations have gone to Black Americans, despite equity efforts
An article discussing how racial disparities can be viewed in regards to Black communities and the coronavirus. -
2020-11-09
HIST30060
1. The Trump family contracting Covid When my friend first texted me about Donald and Melania Trump contracting Covid-19, I let out a hysterical laugh. To me, it wasn’t Trump, the person, contracting the virus that was funny but rather Trump, the one who belittled the effects of the virus and avoided taking meaningful measures to minimise its impact, that was funny. It was a stark reminder that boundaries between the powerful and the powerless, between the wealthy and the disadvantaged, between the authorities and the ones subject to authority, between varying socioeconomic standings can be blurred, especially in the case of a global pandemic. While pandemics have an undeniable impact on the disadvantaged or those with lower socioeconomic means, its impact on a figure such as Trump somewhat demonstrated that no one is beyond a virus. 2. Stigmatising Migrant Communities in Victoria When the second outbreak unfolded in Victoria, it was really interesting to, firstly, see the socioeconomic inequalities come into light and, secondly, the Victorian migrant communities framed as the problem. They were projected to be the cause of the second outbreak in Victoria which prompted the media to monopolise on this racist and bigoted rhetoric of migrants causing trouble. The media and some members of the public (through social media) insinuated that migrant communities’ culture was, by default, antithetical to the Australian way of life and thrust Victoria into another lockdown. It later became clear that the Victorian government’s hotel quarantine disaster prompted a second outbreak. The security personnel and other staff employed by the Victorian government spread the virus to a handful of postcodes in Victoria. The areas where the outbreaks first began to emerge were areas with lower socioeconomic standing and migrant communities. Considering that these staff members were from these postcodes, the outbreak seemed to be prompted and furthered by the migrant culture which supposedly allowed for the flouting of restrictions, mass gatherings and, therefore, quick local transmission of the virus. The wealthier suburbs or postcodes weren’t hit as hard. Thus, demonstrating the existing socioeconomic inequalities in Victoria and the way in which some communities were hit harder than others. It was striking to see how easily a community can be framed and dismissed as the other and the troublemaker. Additionally, this may speak to the debates or concerns which are left outside the national discussion which, in turn, can contribute to a specific historical record based on the dominant narrative. In Victoria’s case, perhaps this can be the more general covid lockdown narrative which for the average Victorian is divorced from any ethnic implications whilst for other Victorians, the connotations associated with their ethnic identities, particularly in the context of the covid pandemic, is warped and bigoted. 3. Burqa vs. facemask hypocrisy – facemasks can become the normalcy but burqa’s never will With the introduction of the coronavirus restrictions around the world, it was interesting to see the discourse around face-covering change, particularly, in the West. For about two decades, following 9/11 in America, there has been negative messaging around the burqa some Muslim women choose to wear. It was deemed socially unacceptable and antithetical to societal norms or appropriateness. Muslim women have been subjected to vilification and have been told that the burqa limits communication and is a symbol of an anti-western patriarchal tradition. There seems to be a hypocrisy around this issue in that while a health concern can normalise a face covering, religious reasoning seems insufficient. While the historical baggage associated with the burqa far surpasses this debate of covering versus revealing the face and, of course, while the health benefits of a face mask is of great importance, there is room to view it with a somewhat binary approach. Put more plainly, it seems while the health implications of any form of face covering or clothing items can allow officials to impose policies around mandatory face covering, religion or, more importantly, freedom of choice, does not offer enough of an incentive for officials to consider burqas as societally and socially acceptable. I believe the policies begat from health concerns are of prime importance. However, these policies can coexist alongside policies of acceptance. Thus, the reframing of societal norms to accommodate for another’s interpretation of their religious obligations. 4. Family member in hospital during Covid With the Covid pandemic, 2020 is probably one of the worst years to approach a hospital in any way. My family and I were unfortunate to have experienced a situation (not Covid-19 related) which required us to rush a family member to the hospital. I found that it was one of the hardest things I have had to cope with throughout my life. This is a photo of my family member’s patient wristband. As nurses in the emergency were asking one another about whether the incoming patients were swabbed for covid, the added difficulties of this situation were clear. The limited contact I was able to have with my family member due to the hyper alert covid environment at the hospital deeply frustrated me. These were perhaps the organic happenings of life, however, not having the option of being beside my family member and only seeing my family member for 2 hours in a day was tormenting. It was also a reminder of how varied the experiences of the lockdown and restrictions could be. Alongside the general difficulties of the pandemic and the lockdown, there could be added layers of complexity which may range from living arrangements, work, race, socioeconomic status to, in our case, an unexpected health condition. 5. TikTok dance Similar to the millions of others out there during the lockdown, I had my fair share of busting some dance moves on TikTok with my house mate. This made me appreciate the little fleeting moments of happiness even in a very grim-looking world with the virus ravaging communities across the globe. Making this video, learning the dance moves and continuously getting the moves wrong was the most upbeat, thrilling and enjoyable fun I had during quarantine. Also, given that I thought I would never use TikTok, I somewhat understood the solace most of its users found in the app, especially, more than ever, during a global pandemic. -
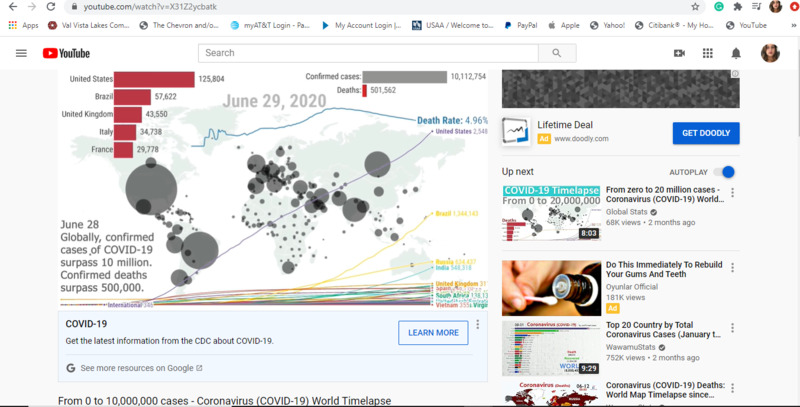 2020-07-06
2020-07-06Visual
Though the submitted thing isn't necessarily personal, it is certainly important because it allows people to openly see the disparity in cases across the globe in comparison to the United States -
 2020-05-09
2020-05-09"The First 100"
"In Chicago, 70 of the city’s 100 first recorded victims of COVID-19 were black. Their lives were rich, and their deaths cannot be dismissed as inevitable. Immediate factors could — and should — have been addressed."
