Items
Subject is exactly
Crime
-
 2023-05-16
2023-05-16Vigilantism in Pandemic Japan
It is about the excessive vigilantism that Japan experienced during the COVID-19 pandemic. Some people became the target of harsh criticism for failing to abide by governmental regulations, and I can remember that I felt a sense of experiencing the negative aspect of society seeing such harsh vigilantism against others. It is important to me because I can unconsciously become part of such vigilantism and should be aware of why I should not relentlessly accuse others of their actions. -
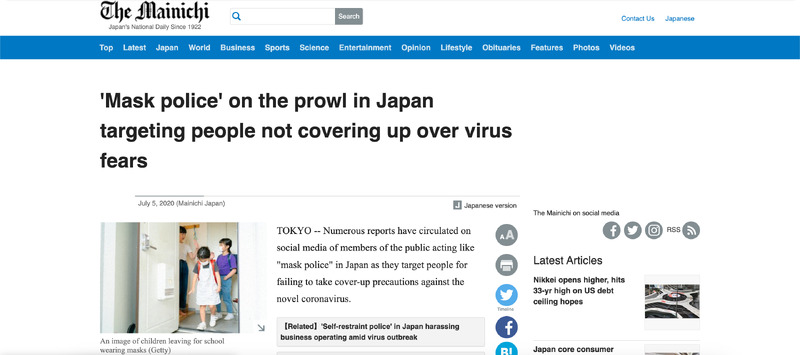 2023-05-15
2023-05-15Pandemics and Human Tendency
Human beings have experienced pandemic throughout the history. However, the there are always conflicts, violence, and division occur. In order not to repeat the history, it is important to learn from the past and apply to our everyday lives. -
 2023-05-15
2023-05-15What we need to learn from Covid
This is based off of what I have seen and heard throughout the pandemic. I have decided to post this because we need more awareness of the issues in education. -
 12/07/2021
12/07/2021Heather Perrault Oral History, 2021/12/07
Heather Perrault is an Eau Claire, WI resident and currently works for the Wisconsin Department of Corrections as a parole officer. In this interview, Heather talks about her experience with COVID and how it affected her life as a stay-at-home mom/ pseudo-teacher for her kids as well as her job that she rejoined about halfway through COVID. She also talks about how COVID has affected her family and friends in terms of their physical and mental health and how the people she oversees as a parole officer may be affected by COVID as well. Heather also gives future generations advice on how she thinks they should look at information about the pandemic in the future. -
 06/06/2022
06/06/2022Francisco Guzman Solano Oral History, 2022/06/06
En esta entrevista Francisco Guzman Solano es entrevistada por Carmen Kordick Coury concerniente al covid-19 en Costa Rica. Empiezan con los cambios que había pasado desde el ano anterior. Francisco habla de su familia y vida social. Hablan del uso de las máscaras, vacunas y la información falsa. De allí, hablan de la economía y la inflación, del gobierno y las elecciones. Hablan del crimen y las drogas. Para terminar, hablan de las fuentes principales de noticias y el futuro. -
 05/31/2021
05/31/2021Silvia Muñoz Mata Oral History, 2021/05/31
En esta entrevista Silvia Muñoz Mata es entrevistada por Carmen Kordick Coury concerniente al covid-19 en Costa Rica. Empiezan hablando de los cambios que habían ocurrido desde el ano anterior. Hablan del trabajo y el trabajo virtual. De la violencia domestica y otros problemas que existen en la sociedad. De allí hablan del crimen, violencia y las divisiones económicas que existen alrededor de ella. Hablan de las vacunas, gente conocida que no se quiere vacunarse y las teorías conspiratorias que existen sobre las vacunas. De allí hablan del gobierno, familia y salud física y mental. Para terminar hablan de narcotraficantes y del futuro. -
 06/10/2021
06/10/2021Francisco Guzman Solano Oral History, 2021/06/21
En esta entrevista Francisco Guzman Solano es entrevistado por Carmen Kordick Coury concerniente al covid-19 en Costa Rica. Empiezan hablar de los cambios que Francisco ha visto desde el ano anterior. Hablan de la economía y el gobierno, de su trabajo y la vacuna. También hablan del aumento del crimen, de las drogas, y de las noticias falsas. De la Caja y el ministro de Salud. Francisco también habla de su familia y su hogar, de las fuentes principales de información y la sociedad. Terminan hablando de las clases virtuales de su hija, de la educación y del Ministerio de Educación. -
 05/13/2020
05/13/2020Christopher May Oral History, 2020/05/13
En esta entrevista Christopher May es entrevistado por Carmen Kordick Coury concerniente al covid-19 en Costa Rica. Christopher es jefe de policía, tiene 42 años y vive en Heredia. Habla del momento que escucho del virus del covid por primera vez y como ha cambiado su vida desde ese momento. Habla de su trabajo como policía y los cambios que enfrentaron, del uso de la mascarilla y de la transición al trabajo remoto. Christopher también habla del crimen y la violencia doméstica. También habla de su hogar y dinamica familiar. De cómo era un día normal para ellos y como había cambiado por la pandemia. Habla se sus padres y suegros y como les ha afectado la pandemia. Habla de la salud mental de su familia y de sentirse aislado. Habla de la economía, el turismo y el gobierno. Para terminar, habla del capitalismo, las noticias, y el desempleo. -
 05/09/2021
05/09/2021Josh Miller Oral History, 2021/05/07
Josh Miller is from Eau Claire, Wisconsin and he is a police officer. We discuss how Covid 19 has impacted his work, family, and community and how he feels about the pandemic. -
 04/22/2021
04/22/2021Gary Luloff Oral History, 2021/04/29
-
 2021-06-11
2021-06-11My trip back To India
I study in Chicago. I am originally from India, so when the second wave of covid hit India I was still in school. Fearing my family's safety I decided to go back to India. Over the summer I spent most of my time inside trying to find oxygen sources for people in need. At one point my phone was filled with numbers of oxygen suppliers many of them turned out to be a scam artists. I still cannot believe how at a time when it seemed like everyone was dying from Covid people somehow still found ways to make money illegally. -
 03/29/2021
03/29/2021Jim Robinson Oral History, 2021/03/29
-
 04/30/2021
04/30/2021Daniel Monson Oral History, 2021/04/30
The contributor of this item did not include verbal or written consent. We attempted to contact contributor (or interviewee if possible) to get consent, but got no response or had incomplete contact information. We can not allow this interview to be listened to without consent but felt the metadata is important. The recording and transcript are retained by the archive and not public. Should you wish to listen to audio file reach out to the archive and we will attempt to get consent. -
 2021-09-21
2021-09-21HIST30060 Footage of smoke on the Westgate Bridge during anti-lockdown protests in Melbourne
This video was taken on 21 September 2021, capturing the view of the Westgate Bridge from Williamstown, Melbourne, as anti-lockdown protestors fill several lanes and disrupt traffic. The footage shows smoke coming from the bridge and all traffic brought to a standstill. There were also helicopters hovering and police car lights joining the scene later on. I was on a walk with a friend along the Esplanade at the time this footage was taken. It felt quite scary to be seeing aggressive, violent attitudes manifest so close to home. We knew what was going because of news updates coming through our phones. After the initial shock and fear at witnessing this happening on a few kilometres away, my friend and I walked the rest of the way in silence, too appalled by the behaviour to do more than shake our heads in dismay. -
2020-01-01
The real pandemic
during the covid 19 pandemic everybody was panicking and worrying about getting a vaccine. i just moved here from another state and i left my mom and brother back home. they lived in a bad neighborhood so during the pandemic they was not only afraid of the covid pandemic but the violent pandemic that plagued the streets where they lived. during the pandemic i lost both my mom and brother to gun violence. -
 2021-08-14
2021-08-14One person stabbed as COVID anti-vaxxers and counterdemonstrators clash in front of L.A. City Hall
The title of this article quickly caught my attention and then I immediately felt saddened by the reality that this pandemic has been politicized from the beginning. People have become so passionate that they have lost all reason. There are always two sides to every story but I find it so hard to understand who oppose vaccinations and reject science. Its not at all surprising that the anti-vax side of this particular story showed up in MAGA hats, its further proof of the political foundation of their argument to "fight for their rights". I understand that people want the right to decide, but then those same people refuse to get tested regularly. This issue has been a messy and passionate one from the beginning and its really hard not to blame Donald Trump for the misinformation that is still being used by the anti-vax community. -
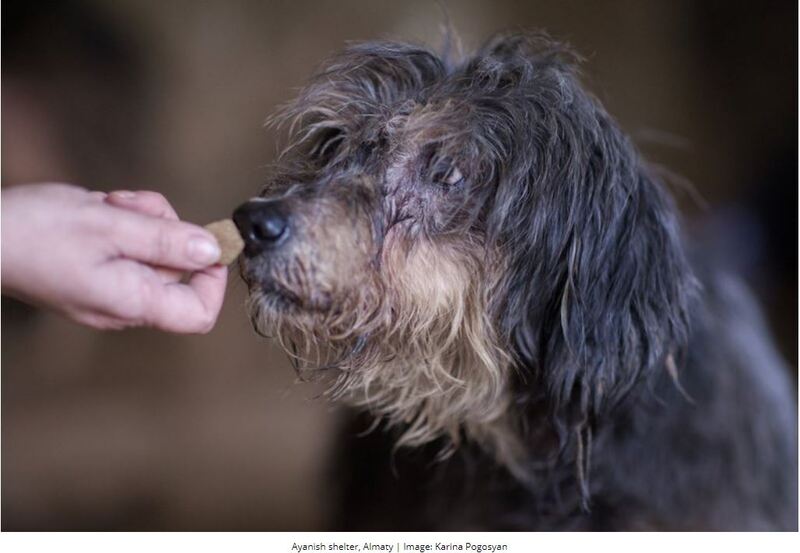 2021-03-10
2021-03-10Pandemic downturn leads to animal abuse crisis in Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan is facing a multitude of problems, including a weak currency, dependence on fluctuating oil prices, a closed political system and dire human rights. Amid all of this, the fate of its abused pets may seem trivial. However, passionate activists are rising up to take a stand for animal rights. As the Central Asian state’s socio-economic conditions have worsened over the past year due to the pandemic, more pet owners have been abandoning their animals or committing violence against them. And just as animal shelters are more needed than ever, they’re grappling with an influx of animals, a lack of funding and a legislative vacuum on animal rights. -
 2021-02-01
2021-02-01Why is Arizona worst for COVID-19 nationwide? Here are 7 contributing reasons
This article discusses why Arizona's Covid rate was the highest in the country as of February 1, 2021. Contributing factors included a lack of mask-wearing and cross-border traffic. -
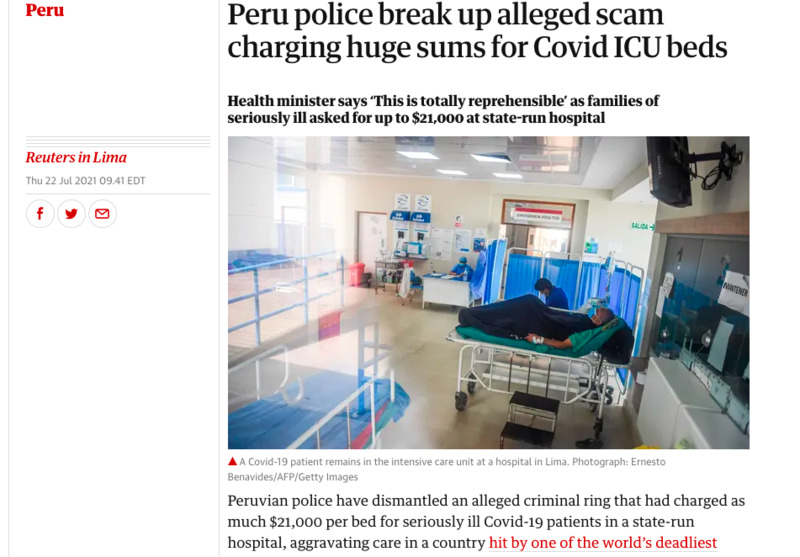 2021-07-22
2021-07-22Hospital staff charging $21,000 for an ICU Hospital Bed
Hospital beds and medical supplies face enormous pressure with the ongoing pandemic. This article indicates that hospital staff were charging over $21,000 for an ICU hospital bed, a scheme that was broken up by the Peruvian police. If one hospital has been caught, how rampant could this practice be? Also, how can the average Peruvian afford such astronomical prices? The fees and the fact that people paid them show the disparity in healthcare access between Peruvians of means and those without. -
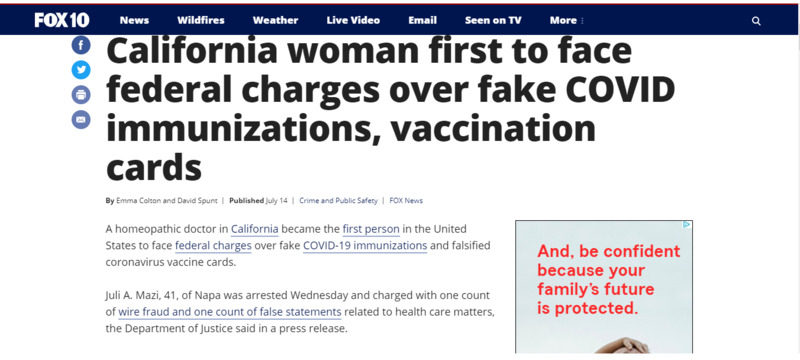 2021-07-14
2021-07-14California woman first to face federal charges over fake COVID immunizations, vaccination cards
A homeopathic doctor in California became the first person in the United States to face federal charges over fake COVID-19 immunizations and falsified coronavirus vaccine cards. Juli A. Mazi, 41, of Napa was arrested Wednesday and charged with one count of wire fraud and one count of false statements related to health care matters, the Department of Justice said in a press release. "This defendant allegedly defrauded and endangered the public by preying on fears and spreading misinformation about FDA-authorized vaccinations, while also peddling fake treatments that put people’s lives at risk. Even worse, the defendant allegedly created counterfeit COVID-19 vaccination cards and instructed her customers to falsely mark that they had received a vaccine, allowing them to circumvent efforts to contain the spread of the disease," said Deputy Attorney General Lisa O. Monaco. -
 2021-06-23
2021-06-23HERMIT HERALD, ISSUE 118
Portland promotion -
 2021-06-01
2021-06-01hermit HERALD, ISSUE 116
Ransomware made easy -
 2021-04-23
2021-04-23hermit HERALD, ISSUE 111
Chauvin appeal -
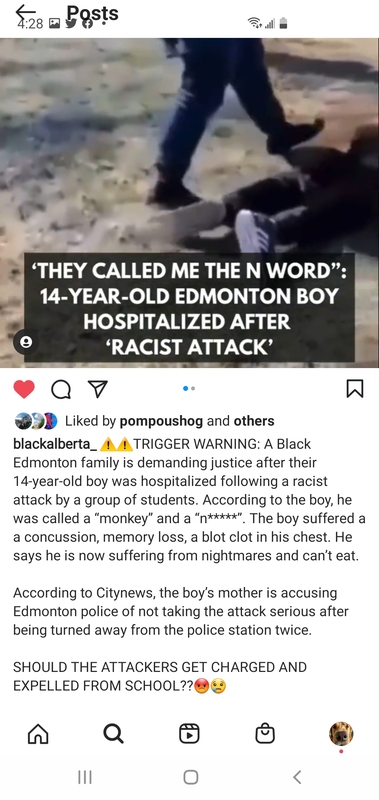 2021-04-24
2021-04-24Racist attack in Edmonton
On April 16th 2020, a 14 year old 8th grade student named Pazo was brutally attacked by seven white students. This attack was entirely racially motivated, they screamed slurs at him, beat him mercilessly, taunted him. They dragged him, choked him, and recorded their actions which they posted on social media. They attacked Pazo because of the colour of his skin, Pazo has stated after the attack that this assault has "made me afraid to wear my own skin." This is more than unacceptable, this is disgusting. As the post stated, these 'kids' gave Pazo a concussion, memory loss and a blood clot in his chest; he could of easily have been killed. What's worse, is there was no action taken by the school, which called this brutal hate crime a "altercation" by the school board. Ontop of this, the post states that the Edmonton Police also refused to investigate this assault, turning away the boy's family twice. This assault would of likely been swept under the rug if it were not for the pushback of the community, and the outrage generated by the presence of the video online. With the growing pressure from the public, the Edmonton police service are being demanded to investigate this assault, which again is only made possible through the pressure of the people. Furthermore, the lack of action and attempts to nullify the significance of this assault by the principal and the school board has resulted in students and teachers pushing for the forced resignation of those accountable, such as the principal and superintendent. Other social media platforms have stated that this is not the first time the principal of the school has played down similar incidents; which has left students feeling vulnerable. This cannot continue, these students must be held accountable - Albertans need to understand that white supremacism is a very real problem, and it is not going anywhere by ignoring it. As we have seen throughout the pandemic, events such as this are a rarity - we only know of the severity of the attack and the response of our education institutions because this attack was recorded and circulated online. -
 2021-04-23
2021-04-23My Chaotic Covid
For me, the pandemic has been the exhaustingly consistent cherry on top of everything that’s gone sideways in my life over the past year. Now, this isn’t meant to be a pessimistic rant about the past 12 months, but just a sequence of events that kept things spiraling out of control while I tried my best to stay on top of the chaos and maintain an energetic passion for life and hope for the future. These traits used to come super naturally, as I had been following my ten year plan pretty successfully as of last March, until the rest of the year, which I thought to be set in stone, was pulled out from under my feet. I was having the time of my life in Rocky Point over spring break when Covid started hitting the fan. ASU announced a ‘temporary’ switch to online classes while I was on the road coming back home, and I drove straight into midst of a sudden global pandemic. Luckily, I had gotten out of Mexico in time before the borders were closed down. I was working at Harkins Theaters at the time, and my last shift was one with a whole bunch of disposable gloves and excessive new sanitization rules in concessions. I left that night not realizing that that would be my last shift there. I was at least planning on being there for another few months, before I would start a summer job I was recently contracted for. I was going to go on tour as a videographer with the Cavaliers drum and bugle corps, filming professional marching band videos and cutting together rad highlight reels all while traveling the country and getting paid for it. That was canceled soon after I was furloughed from Harkins. I went back home to visit my dad and brother in the midst of it all, but I don’t think my brother was ready for that kind of personal contact. He wound up giving me a black eye after I ended up getting too close to him and intentions were misconstrued. Shortly after, while already recovering from a destroyed face, I came down with a long, rough sickness that was aligned with the known symptoms and assumed by everyone to be Coronavirus. Unfortunately Covid tests were far from accessible at that point, and I was never able to confirm if that was the case. Trying to get away from the bleak outlook of everything, I took a few of my friends up to my grandparent’s empty house in Sedona. My roommate proceeded to secretly bring alcohol, drank too much and fall off a ladder, leaving a large-man-sized hole in the wall of my grandparents’ expensive house. While staying in Sedona the following week on one of my trips to head up and fix the wall, I got a call from my dad that my mom had passed away. She had been suffering for the past twelve years from a stroke and aneurism she had when I was eight, and on April 6th she finally let go. So that was a lot of emotion to throw on top of everything. After spreading my mom’s ashes with my dad and brother, I came back to find a baby monitor camera had been hidden on a shelf in my bedroom. I didn’t know who put this camera there, hidden in a sock, but it had been filming my girlfriend and I for the past three days and had gotten some pretty personal stuff on camera. It wasn’t hard to put together that that was the whole point of the monitor. My roommate felt violated as well, as he said he thought it was one of his friends who had put it there, and was on board with the whole police investigation we launched after the fact. I trusted my roommate, and while he had gone through a bit of an alcoholic phase the month before, I thought he was doing better. He had been one of my best friends for over five years at this point, and I didn’t want the worst case to be possible. But a few weeks later, my girlfriend’s phone mysteriously went missing in my apartment for a night. The next day she found a monitoring app downloaded onto it. My roommate had taken her phone, copied off all of all her private, ‘personal’ images of herself, and installed a program to track her and check in on her camera and microphone without her knowledge. Luckily we found this evidence soon enough, but it wasn’t an enjoyable experience kicking my best friend out of our apartment. The police found evidence that he put up the camera soon after and he was arrested. Two counts of voyeurism, one count of lying to the police, and everything he had taken off my girlfriend’s phone. I haven’t talked to him since last May, I can’t legally, it’s currently April of ’21 and his trial has yet to reach sentencing. After all that had happened, Summer was not what I had initially thought it would be. But it wasn’t all that bad. People started wearing masks, I got a temporary job making dough at Little Caesars, I was able to hang with my actual friends and the worst of it looked to be over. And while that much was true, the pandemic itself was far from over and slowly the months of lost experiences and thoughts of unfulfillment and wasted potential began to sit in. I got a different apartment in August, but it was an older and more run-down first floor unit with unexplainably loud upstairs neighbors. I’ve spent the entire lease of that unit trapped inside and longing for a normal college experience. These were supposed to be the craziest years of my life, and I felt like I had missed out on countless memories. I was working as a video editor from home on top of online school, and the days blended together into hopeless rituals of helpless procrastination. The motivation to thrive while held up in the new apartment was hard to find. But I still made it. I didn’t give up on pushing forwards. I’d put things off and the passing of time ultimately became an illusion, but I kept making sure I stayed productive. I edited together a vlog series through the beginnings of the pandemic, worked on other personal projects, and was able to get a pretty sweet internship doing remote editing work for a television studio in LA that I ordinarily wouldn’t have been eligible for as in person work. I made it through the 2020-2021 school year, my junior year, with good grades and came out on the other side more hopeful than ever. I got fully vaccinated a few weeks ago, I’m beginning to live again, and the bright outlook of a fresh start in a soon to be newly reintegrated world gives me an unparalleled excitement. I am looking insanely forward to all the new people I’ll meet, memories I’ll make, and experience I’ll gain through my senior year being back in person. Everything’s coming back together, and as long as everyone can make an effort to get vaccinated and keep each other safe, calm, and hopeful, I’m more than prepared to cram 13 months of missed experiences into the best, jam-packed, fulfilling, productive and exciting year of my life. …Yet. -
 2021
2021Policing Isn't Broken — It Was Designed This Way
Our policing institutions were designed to exert control over Black people. We need to limit the role, responsibilities, power, and funding of police so interactions that lead to the death of Black people don't happen in the first place. -
 2021-04-21
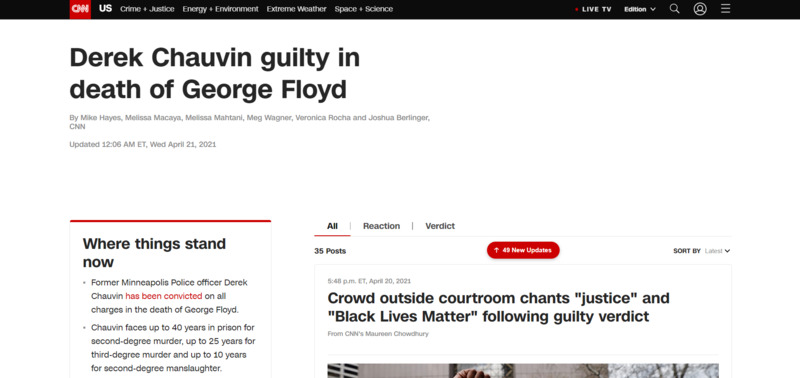
2021-04-21Derek Chauvin guilty in death of George Floyd
The jury found former Minneapolis police officer Derek Chauvin guilty of all three charges in the murder of George Floyd. Crowds outside the Minneapolis courtroom and at the location where Floyd was killed chanted "justice" and "Black lives matter" after hearing the verdict. -
 2021-04-15
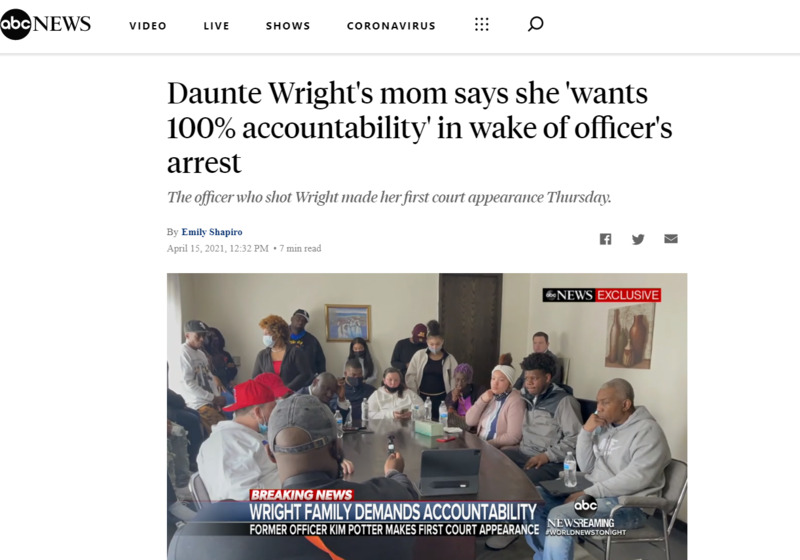
2021-04-15Daunte Wright's mom says she 'wants 100% accountability' in wake of officer's arrest
The mother of Daunte Wright, the 20-year-old Black man shot dead by a Minnesota police officer at a traffic stop, said she "wants 100% accountability" in the wake of the officer's arrest. "If that even happens, we're still going to bury our son," Wright's mother, Katie Wright, said at a Thursday news conference. "We're still never going to be able to see our baby boy." -
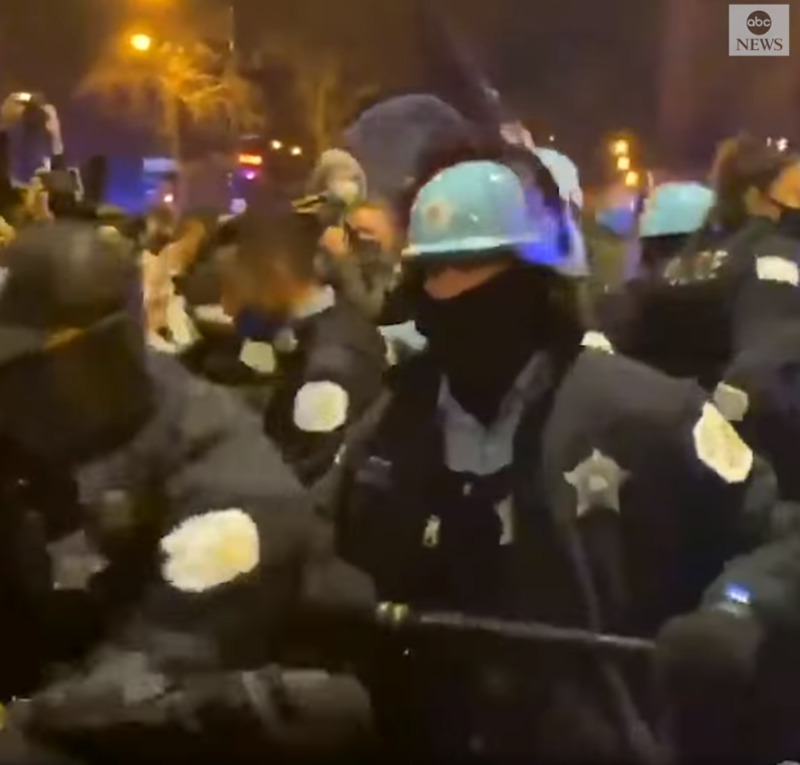 2021-04-17
2021-04-17Police clash With protesters during Adam Toledo demonstrations
Police in Chicago, Illinois, clash with protesters during demonstrations for 13-year-old Adam Toledo following the release of the police body camera footage. -
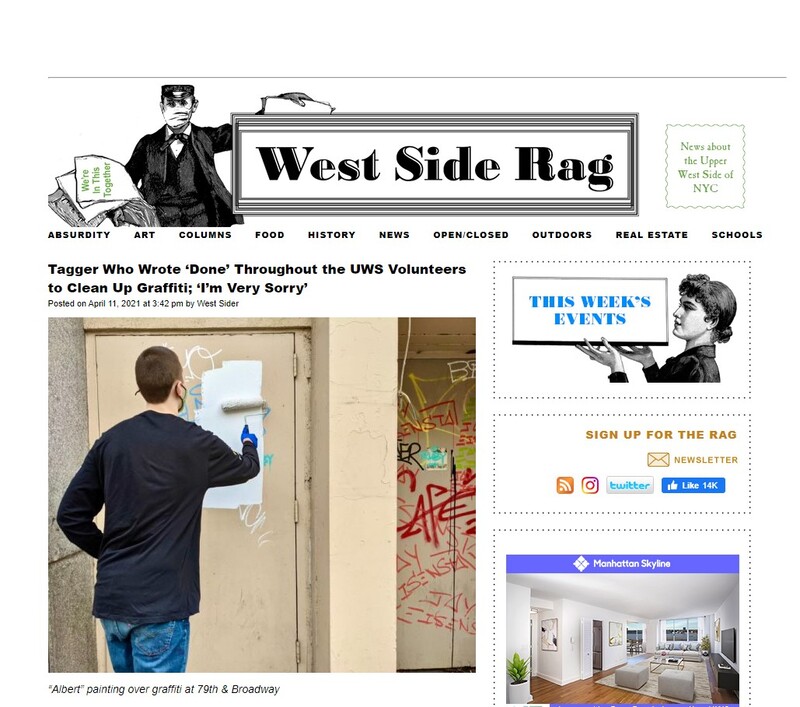 2021-04-11
2021-04-11Pandemic Street Art: teenage tagger made to apologize and cleanup
New York teen tags the streets in "response to multiple stressors. Quarantining boredom. Family problems. Feeling stuck since graduating high school and not yet finding a job or college that fit." -
 2021-04-12
2021-04-12Being Asian During Covid
This piece describes the minor hardships I have experienced during Covid as a young man who happens to be Asian. -
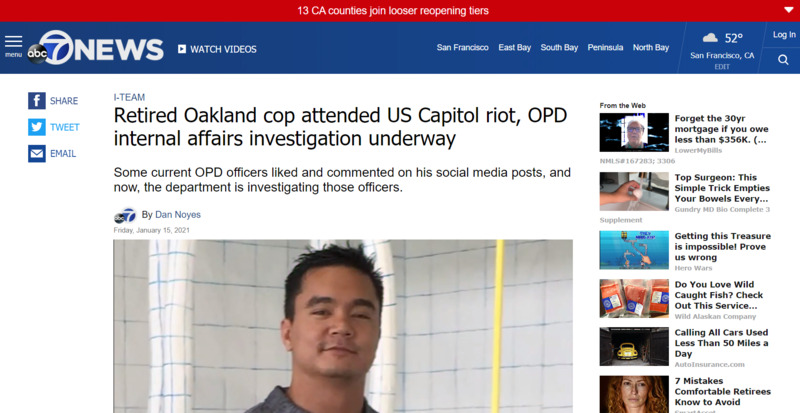 2021-01-15
2021-01-15Retired Oakland cop attended US Capitol riot, OPD internal affairs investigation underway
A former Oakland police officer has received a visit from the FBI. Jurell Snyder tells the ABC7 I-Team, agents interviewed him about attending last week's Trump rally that led to the assault on the Capitol, and about his social media posts promoting conspiracy theories. Some current Oakland police officers liked and commented on Snyder's posts, and now, the department is investigating those officers. -
 2021-03-29
2021-03-29Justice for Sofia Ramirez
Photographer Malcolm Dole has been documenting street art during the pandemic. -
 2021-03-29
2021-03-29Street art during the pandemic
Malcolm Dole is a Seattle photographer who is capturing photographs of street art during the pandemic. -
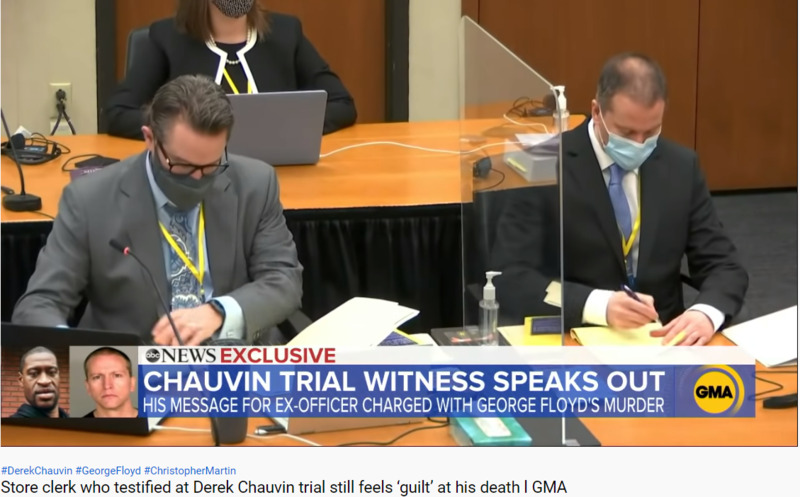 2021-04-02
2021-04-02Christopher Martin Testifies at Trial
Christopher Martin, 19, who reported George Floyd’s counterfeit $20 bill to his manager, said he feels like a “contributing factor” in his death. -
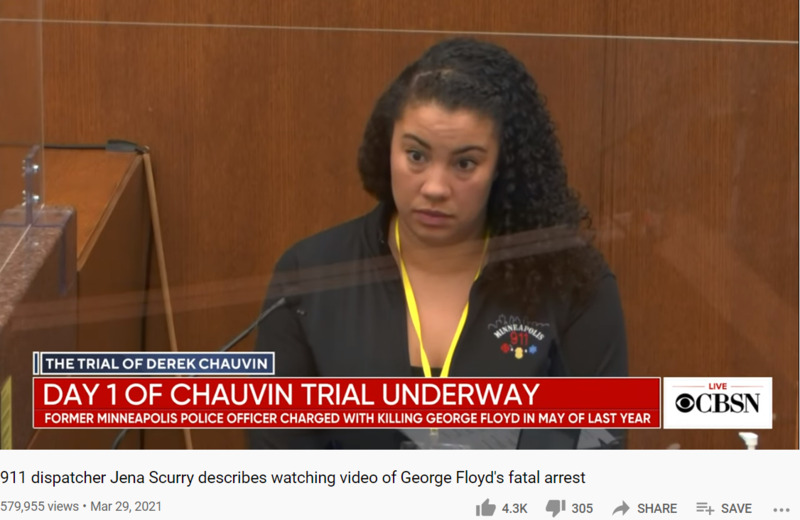 2021-03-29
2021-03-29911 Dispatcher Jena Scurry Testifies in Derek Chauvin Trial
Jena Scurry, a 911 dispatcher with the city of Minneapolis, testified in court Monday that she called police after watching footage of George Floyd's arrest because "something wasn't right." Scurry took the stand in the first day of testimony in the trial of Derek Chauvin, the ex-Minneapolis police officer charged in Floyd's death. Scurry saw Chauvin on camera kneeling on Floyd's neck during the fatal May 2020 encounter. Watch part of her testimony here and read more: https://cbsn.ws/3rvfM6F -
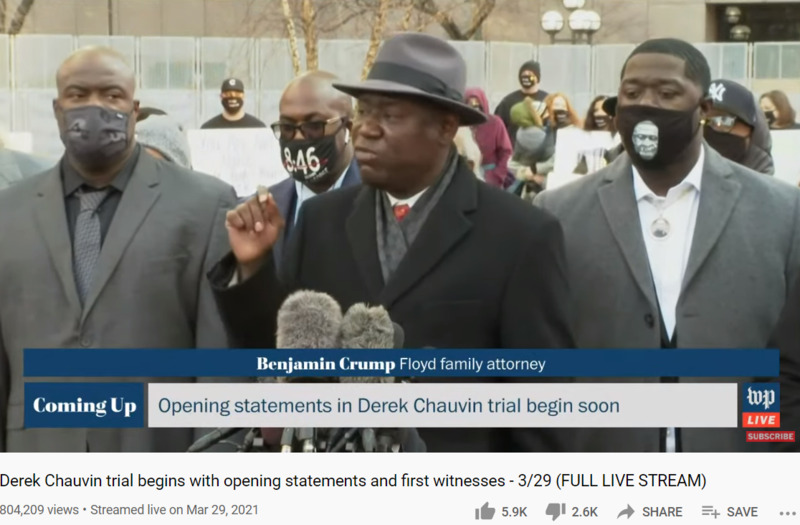 2021-03-29
2021-03-29Derek Chauvin trial begins
Derek Chauvin, the former Minneapolis police officer filmed with his knee on George Floyd’s neck in May, faces murder and manslaughter charges for the encounter that sparked months of historic protests around the world. This stream contains graphic content. Chauvin faces charges of second- and third-degree murder and second-degree manslaughter. Three other officers charged in the case — J. Alexander Kueng, Thomas K. Lane and Tou Thao — are set to be tried separately in August. George Floyd died on May 25 after being handcuffed and restrained facedown on a Minneapolis street during a police investigation of a counterfeit $20 bill that allegedly had been passed at a local market. The Post’s Rhonda Colvin will anchor live coverage featuring reporters Holly Bailey and Joyce Koh from Minneapolis. The program will also feature reporters Keith Alexander, Mark Berman, Tim Craig, Nicole Ellis, Hannah Jewell and Eugene Scott -
 2021-04-03
2021-04-03Mask trash #29
Two disposable masks one black and one blue and white outside the ACYR in Phoenix. -
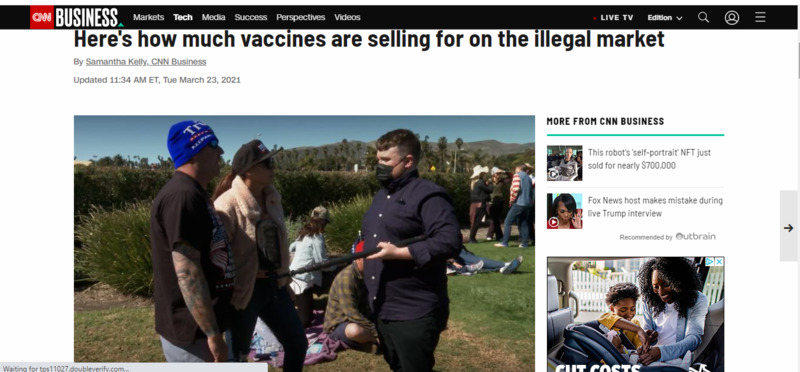 2021-03-23
2021-03-23News Article: Here's how much vaccines are selling for on the illegal market
This article relays data gleaned from cybersecurity firm Check Point Software to a CNN reporter, Samantha Kelly, related to the illicit market for COVID-19 vaccines and proof of vaccination cards available for purchase through the dark web. -
 2021-03-29
2021-03-29Senior Border Patrol officer says border migrant flow will only worsen
"Senior officer says border migrant flow will only worsen" By Lyda Longa, lyda.longa@myheraldreview.com, Mar 29, 2021 The situation with undocumented migrants flocking to the Southwest border of the United States from Mexico is only going to worsen, a senior Border Patrol agent warned Friday. The agent, who spoke to various media outlets during a conference call, said at least 380,000 undocumented people had been apprehended at the Southwest border in February and the numbers would be higher for March and beyond. The agent spoke on background with the agreement that media would not reveal his name. “I fully expect to see the numbers increase as we go into the summer months,” the senior agent said, concerning migrant crossings. In Cochise County that warning has begun to bear out near Douglas and in Willcox, where the already stretched-thin Border Patrol is arresting more single adults attempting to slip into the country or taking in and processing children who are flocking to the border unaccompanied. Douglas Mayor Donald Huish said Friday the latest information he received this week from Border Patrol agents at the station just outside Douglas is that they’re confronting and repatriating about 100 single adults daily who are trying to slip in illegally. “They are getting closer and closer to town,” Huish said. What concerns Huish even more is that Border Patrol agents from the Douglas station are being pulled out to help in busier areas such as Yuma and Tucson. “They’re siphoning them off to the western part of the state and leaving us with a skeleton crew,” Huish said. In Willcox, Mayor Mike Laws said he was told two weeks ago by the Border Patrol there were 54 unaccompanied children at the Border Patrol station. “That was two weeks go. Who knows now?” Laws said. “The station can only hold up to 81.” Laws said he was told by Border Patrol that a “third party” has been arriving at the facility and taking 10 to 20 children to Phoenix by via bus. The mayor said he does not know how often the transportation comes or who the third party is. “We have not seen anyone (undocumented migrants) running the streets so far,” Laws said. “All we have is the youths, but we don’t see them either.” Laws and Sierra Vista Mayor Rick Mueller said citizens in their respective communities would gladly help the undocumented migrants but there aren’t enough resources available to do so. Laws, Mueller and other mayors in Cochise County signed a letter recently asking the federal government for help with the matter. Last week, the town of Gila Bend, which has a population of about 2,000, declared an emergency after Border Patrol agents dropped off a group of migrant families with children in a park. Gila Bend Mayor Chris Riggs told reporters he and his wife ended up using loaned vans to drive the families to the Phoenix Welcome Center so they would have a safe place to stay. Riggs said Border Patrol agents told him to expect more of the same. Mueller said there have been no such issues in Sierra Vista, but he is worried that the municipality, if hit with something similar to what happened in Gila Bend, would have no resources to offer. Last week Arizona senators Kyrsten Synema and Mark Kelly announced they’ve been pushing for more federal resources to help Arizona cities with a sudden influx of undocumented migrants. The senators helped secure at least $110 million from the Federal Emergency Management Agency as reimbursement to cities that assist migrants left within their jurisdictions. Also last week, Arizona Gov. Doug Ducey and Florida Senator Rick Scott — who sits on the Homeland Security Committee — called on President Joe Biden and Department of Homeland Security Secretary Alejandro Mayorkas to visit the Southwest border. Ducey and Scott, accompanied by a handful of law enforcement and other elected officials, had toured a portion of the border near Douglas. At his first press conference on Thursday since taking office in January, Biden said he would come to the border soon, but thought a visit now would deflect attention from the issue at hand. The senior Border Patrol agent who spoke Friday, meanwhile, said 300 Border Patrol agents who work along the northern border of the U.S. have been “mandated” to the Southwest border to assist with the influx of migrants. He said about 2,000 family units out of the 6,000 who are trying to cross daily are being processed in Texas by the Border Patrol. The agent revealed that unaccompanied children are being kept in Border Patrol facilities longer than the 72 hours established by law because too many are showing up and agents are overwhelmed. “They’re keeping them a few days, sometimes up to a week,” the senior agent said. Once an unaccompanied child is encountered, Border Patrol contacts the Department of Health and Human Services. The latter makes arrangements for the migrant children to be taken by the Office of Refugee Resettlement. The agent also mentioned an increase in the criminal element among undocumented migrants. “The threats we see are significant,” the senior agent said. “We have seen criminal (undocumented migrants).” Additionally, he said that COVID testing for migrants is only being done in facilities in Del Rio, Texas, and soon in the Rio Grande Valley in Texas. Other than that, testing is being undertaken by non-governmental agencies that are helping the migrants and U.S. Immigrations and Customs Enforcement officials. He said it was probable that some migrants with COVID-19 may have been released into communities. -
 2021-02-14
2021-02-14"I'm Done Downplaying My Asian American Experience"
In response to the rise in anti-Asian racism and crimes, Allure magazine reached out to six prominent Asian Americans within the beauty industry to share their experiences as Asian Americans. They share not only accounts of bullying and racism, but also how the beauty industry can help change the narrative. -
 2021-03-23
2021-03-23Pandemic TikTok
With talk of everything going back to "normal" with vaccinations and whatnot, mass shootings are coming back. -
 2021-03-21
2021-03-21Oral History: Interview with Anonymous Peace Officer #2
James Rayroux 0:01 My name is James Rayroux, and I'm a graduate student in global history at Arizona State University, and I'm working as a curation intern with the "Journal of the Plague Year" COVID-19 archive. Today is March 21, 2021, and it's just after 8:12pm or 2012 hours here in Arizona. I'm speaking with a narrator who wishes to contribute to the COVID-19, archive anonymously. Sir, I first want to thank you for speaking with me and contributing to this COVID-19 archive. Do you consent to having this interview recorded, transcribed, and immediately posted to the "Journal of the Plague Year" COVID-19 archive, where it will be made accessible to the public? Anonymous Officer 0:43 Yes, I do. JR 0:44 Thank you again for agreeing to speak with me and making time for this interview. In lieu of your name, or location, can you provide a summary of your background and professional experience in law enforcement? AO 1:01 Sure, I've been sworn law enforcement for almost 23 years in a state in the Rocky Mountain region. I've worked both for municipal and state government, and I work for small to medium sized agency now about 35 sworn officers. I'm a military veteran, I was US Navy prior to my time prior to going to the police academy, and I worked a variety assignments from patrol to drug and alcohol enforcement, auto theft Task Force, Joint Terrorism Task Force, supervision, criminal investigations, and command. JR 1:44 During that time what are some of your most prominent or important achievements within the law enforcement profession? AO 1:54 You know, I think that this profession, namely, is typically not about the individual. I would probably point towards successes in the community and successful team building and successful growth of individuals into the business. I think one of my most proud achievements I think, something I'm tremendously, I feel tremendously accomplished for is somehow I failed to convince my son to be a firefighter, and he was just sworn in at another municipality in the same state as a sworn law enforcement officer. So while I have failed him and trying to convince him to do literally anything else, I'm also extremely proud and accomplished that I have raised my son into a similar professional lineage, and he's elected to take the oath to protect his community, as well. JR 2:57 What are your current roles or assignments within your organization? AO 3:04 I'm currently assigned as a patrol supervisor, a watch commander. I supervise a shift of a number of police officers and currently working day shift. So in those roles, I'm essentially the emergency manager for our smaller community, supervise police response to emergencies, meet with the public, interact with command staff, meet with public stakeholders, and then, essentially, a customer service rep who happens to be a sworn law enforcement agent. JR 3:37 When and how did you learn about the SARS-CoV-2 virus in early 2020, and what were some of the first conversations you remember having about it at work? AO 3:51 So COVID became on the tip of everybody's tongue probably in early January. And previously, in the end of 2019, it was somebody else's problem. It was, it was a China problem, it was a Wu Han problem, specifically. It was, it was out of sight out of mind. And, of course, you'll know this about law enforcement, there's only two kinds of problems in law enforcement, those being "my problem," and "not my problem." And during the first part of 2020, it wasn't our problem. There was a limited amount of cases in the US, they trickled in. Most of what we understood about the virus that causes COVID-19 was based on the media, was based on, you know, what you might catch a snippet of on NPR on Fox News, which has no news about foxes, I might add, and essentially, just the snippets we would get on the media and I don't remember having official tangential conversations about the COVID-19 virus in a strategic way, until probably February. A lot of those initial conversations, you know, as, as trained observers and trained investigators, I know many, many law enforcement officers who don't immediately give a lot of trust or credence to things their government tells them. So, for the first little while, it was kind of an attitude of scrutiny, one of a lack of credibility. We weren't really sure whether this was hype and whether there was really any risk, and there was a lot of conversations about the corollary between, you know, the standard flu and other illnesses that killed just as many if not more people, and there was a lot of disagreement about their trajectory, and the volume, and the scope, and really how this thing was going to manifest. JR 6:04 How did your agency first deal with the COVID-9 pandemic in an official way? AO 6:12 The first steps that were taken initially, mostly just surrounded, strategic outward facing changes to how we did business on the street, basic social distancing, wash your hands, don't touch your face, basically just mimicked CDC advice. You know, be careful more to come. Very low level, very basic, no real operational changes, no testing, no recommendations for symptoms that was, you know, under the umbrella of "flatten the curve," keep yourself healthy sort of jargon, that was shared from both the government and from the administration of our, our small community downwards towards the police department and other, other trades in the region. JR 7:13 What did your first pandemic briefing or roll call look and feel like after those changes were made? Where you and your squad entirely in masks for that first time, or was that yet to come? AO 7:29 When the government of our state first mandated masks, there was specific legislation that excluded law enforcement. It was quickly decided that masks were recommended, but were not required initially. So there was this sort of juxtaposition and feeling out period in our community where not a lot of people wore masks. It was recommended. You were supposed to wear them when you were outside, you were supposed to wear them, you know, when you were in contact with others. The science hadn't really been affirmed. There weren't a lot of links to credible research yet. And, of course, a pandemic of this nature has never been experienced or dealt with for generations previous to this. And so, you know, I'm 100% cofident telling you that literally everyone was just winging it, and that was immediately apparent in that first briefing where we discussed what we were going to do. Still scrutiny, still somewhat lack of credibility, lots of, lots of eye rolling with a few critical and strategic thinkers, you know, raising, you know, what would later be the first semblance of some alarm, saying, "Hey, you know, maybe, maybe this is going to be a big deal. Maybe we haven't experienced anything like this before, we ought to be as careful as possible." JR 9:03 How did your agency's policies and procedures change over time after that initial effort? AO 9:13 So the, you know, the, the tide came in, in a big way very quickly. And as you'll remember, as the COVID-19 virus, sort of sieged Italy and New York and the Eastern Seaboard, everybody started paying attention in a big way. And we're, you know, a couple 1000 miles from there, but local and state governments started reacting very, very quickly. Masks were mandated for all persons in contact with the public. A scramble was afoot to obtain PPE [personal protective equipment], which supply chains being, you know, any resemblance of the way they were in 2019, there was no problem. You just got on Uline or Amazon or, you know, you know, whoever your main commercial supplier was, and you ordered them by the skid and PPE was readily available and there was no reason to hoard it. But all of a sudden, there weren't any. There wasn't any, the supply chains were just curb-stomped into this sort of perpetual waiting period where nobody was sure what they were going to need, and everybody thought that N-95 respirators were the new hotness, and everyone had to have some from car dealers to people working the drive thru to baristas to, you know, the guy doing my front end alignment. So all of a sudden, we were trying to balance what was practically happening on the street, what our day-to-day call volume looked like, and what we were really supposed to do with the PPE we had knowing that our resupply was probably distant. And when we wove all that together and put all that minutia in a pot and stirred it up, what we came up with was pretty much this overwhelming sense of nobody knowing anything that was reliable. And it was anybody's best guess how long this was going to last and what we're going to need. That was echoed among our local hazmat [Hazardous Materials responders], our local health departments, our local health organizations. Nobody had any PPE to give us, nobody knew how long it was going to last, and nobody could have any real recommendations except for this sort of parroted, you know, don't touch your face, wash your hands, wear a mask in contact with everybody. Once masks were required, we had some pretty significant changes to the way that we did business in the community. You know, as a forward facing law enforcement agency, we contact, you know, one officer might contact 10s of people every day, sometimes might make 15 or 20 contacts before, you know, the afternoon's said, and by doing so, what we know now to weave a fabric of a contact trace that is essentially impossible. I mean, we remove Degrees of Separation all day long just by talking to people. And none of that technology and contact tracing and science had really entered the social jargon. But we were out there just trying to be as careful as possible, and it wasn't until probably...probably late March is when you know rivers turned to blood and the sky fell as far as the government was concerned. And it was then that definitive, codified changes were made to procedure where there was a moratorium put on traffic enforcement and all proactive street contacts, except for egregious emergency violations. We didn't make traffic stops for weeks. There was a moratorium immediately placed on warrant arrests and on booking people at the jail because, having a potential infectious patient in your vehicle, nobody knew what the consequences of that were or how to decon [decontaminate] it. So we didn't arrest anybody. If it was a crime of violence, or a crime against a person with a victim, we would screen it at the jail first. Everybody warned N-95 mask, and we would transport them as quickly and safely as possible. If it was a warrant for anything nonviolent, warrant for bench warrants, and courts and anything, we just let them go. Even if somebody told us that they had COVID symptoms, or were COVID positive, there was still no viable testing in the system, and no way to confirm or deny that those statements were true so we didn't book them. So many suspects in cases either went uncontacted, cases were dismissed, or the warrants were skipped just because the precautions weren't in place yet, and the agency and all the businesses and other agencies we worked in the region were trying to just to stay healthy. Proactivity probably took a, I think, I would call a permanent shift. I have not seen a resurgence of practice enforcement and the likes of which I might like. Cops just stopped doing business the way that they used to, and some of the badges we'd wear and some of the honor that we took in protecting the community came from making contacts: suspicious vehicle, suspicious people, you know, local transients, patrolling, you know, bike racks and stealing cars and stealing bikes and harassing people and it, it turned into kind of this proactive wasteland where law enforcement was worried about exposing themselves. They were worried about exposing each other. They were worried about exposing their families. And they were worried that if they happen to make a contact, they might expose the next people, the next 10 or 15 people that they talked to that day. So the only way to eliminate that was just to stop doing it. So by eliminating, you know, the patient zero style traffic stops, we hoped to have an impact on that, and flatten our own curves by just not talking to anybody unless it was an emergency. JR 15:38 Do you remember the first call or the first contact that you went on where you and the public were both wearing masks? AO 15:51 I don't remember it specifically. But I remember a handful of contacts that were made in right around March when, you know, when I said that when the king tide came in with news and with panic and fear. And I remember a handful where nobody really was sure what to do. Everybody was, had this sort of weaponized social distance, and people would walk the other direction when you tried to talk to him, and we hadn't mastered the, you know, the little elbow bump or the little nod, and so nobody could figure out how to talk to one another, and there was quite a few instances of the COVID card being played where people just simply didn't want to talk to the police. So they, they feigned fear and panic for exposure and wouldn't come out of their homes and open their car doors or their windows. And then shortly thereafter, it became socially stigmatic to participate in the fear and panic. And if law enforcement didn't wear masks, we sort of became this pariah immediately. So it was, it was optional for a very short period of time, but then very, very quickly, virtually every single contact we made had to have a mask on, of course, which, you know, brings with it all the problems associated with not being able to see somebody's face. It's hard to hear, it's hard to talk on the radio. It's hard to smell intoxicants, you know, it just added sort of this, it was basically like dimming the focus one click on your whole world by having to cover your face. But, you know, at that point, some of the science was starting to become more consistent and more published, and every, most everybody at that point was pretty convinced that at least when in contact with the public and the unknown, that some sort of mask was viable and necessary. JR 17:50 In Western society, handshaking has long been a very important social event. And that's obviously gone by the wayside with the general public since the pandemic began. In lieu of having that physical contact to make direct human connections, how have you tried to establish rapport with the public when you do have to contact them? AO 18:21 It's been weird. You know, handshakes have been sort of the status quo of a show of respect and humility for so many years. I mean, you know, you hold your hand out, it's almost instinctual. It's almost primordial. You know, in this culture in Western culture, someone holds your hand out, and you don't take it, like, them's are fighting actions, right? So it's, it was weird. We had to figure out ways to break the ice, we had to figure out ways to do that acknowledgement, and I'll answer it two ways. The first way was we had to figure out how to communicate with people even though they couldn't really see our faces, and there could be no sort of context to breaking sign of respect, like the handshake. So you know, you come up with this weird elbow bump, or you give the little, you know, the little nod that one bro gives to another across the urinal, and you find out ways to just break the ice with people. And the second challenge that we experienced was that we could no longer show those signs of respect to one another in view of the public. So if one cop was touching another, or, you know, giving a little handshake or playing grab ass, or high five, or even just a fist bump, all of a sudden, we were cast out, right? All of a sudden, those little, that that lack of social distancing became this socially virtuous thing to exploit and to ridicule, and so we had to be exceptionally careful in public even though within shifts, we considered our shifts to be close contact circles. I mean, any sworn law enforcement officer working during the COVID shutdown very likely saw their shift mates more than they saw their blood families. And so there was just no way to socially distance internally at work, because of the, just close knit manner in which the job is done and the proximity we had to one another throughout the day. Yet in public, you know, we're in our own cars we're socially distanced, we got to have masks on, you better boil yourself between each contact, and you got to wear booties and a Tyvek suit and touch everybody with a little wand. And in the mix, I feel like our isolationism increased, and I feel like our bonds of society from a law enforcement perspective became even more tenuous. So, you know, one of the things I adopted was I started using my first name with everybody. I stopped using rank, I stopped using identifiers. I just told him who I was. I asked them for their first name, I use my first name, I tried to break it down. And I would always, you know, have these little catch conversations I do and I introduced everybody, and just try to acknowledge that this is a new time and, you know, you hear in the media and you see it a lot. And in every, every, you know, corporation, commercial for six months, it was, "in these trying times." So, that sort of became the catchphrase like, "Hey, in these challenging times, things are different. Here's the business I'm here to do. My name is so-and-so. We're trying to keep the peace, how can we be helpful?" And we interacted with all kinds of people. Some people thought it was a hoax. Plenty of, plenty of sovereign citizen scam-demick, plan-demick jargon being thrown our way. And then on the other side of that spectrum, were extremely scared, extremely isolated...people wouldn't come out of their houses, people were afraid to take a Grubhub delivery. People were, you know, boiling their utensils. And somewhere in the middle, law enforcement just kind of figured out a way to break the ice, and I think it's, I think it's going to be permanently different. And I can tell you that because the day before yesterday, I was on a burglary call where I talked to the informant. Without even thinking, I reached my hand out to shake his hand because he told me his name. He said, "Hey, thanks for coming. I'm so and so." And without even thinking about it, my mammal brain shot my hand out in a greeting. And it took him about five seconds of staring at me before I figured out that we just don't do that anymore. And it's super weird, but we, we're working around it. JR 22:51 What do you miss most about your job or your daily work duties from 2019? AO 23:02 You know, I don't know if this is going to be directly related to the pandemic. I think that in 2019, we were dealing with a community that understood what the rules were. Everything was, you know, we call it "pre-COVID," we call it "olden days," I don't know if we're ever going to return to those times, but cops are out there doing business in the community, and we were fighting crime and protecting people. And we were making this self sacrifice and serving our community and being forward facing and just eatin' meat and just leaning in just to get business done. And we did it no way that served our customer and served our client base. And I don't know any law enforcement officer who's been on the job for more than 10 minutes who doesn't do this because they love the community they work, or they love the service that they provide, or the people they protect. And I think we've permanently changed the way that law enforcement officers are viewed by their communities. I think we've done, and I say "we," I mean we as a culture, good, bad, or indifferent, have done irrevocable damage to the reputation of law enforcers in our community and the public trust that they must hold in order to be successful. And then all of a sudden, the communities "why nots" became really, really strong. And cops had to start making excuses really quickly about why we weren't the bad cops. And why we weren't doing this to violate your civil rights. And why we're just, we're just out there trying to do the job and just trying to, you know, serve policy and serve the constitution and it might not be about you and your mask. And I feel like this stigma, the social stigma became leveraged against law enforcement in a really big way without any real underlying facts. No one, you know, it just became this sort of socially virtuous stigmatic status to hate the cops, whether it was for their efforts to preserve the public peace in the pandemic, or whether it was your interpretation of their worth based on events taking place in the national landscape. It became cliche to hate the cops. And I think I miss, I missed the real relationships we had in 2019 that were based on sort of a shared respect, and a common understanding and actual virtues of character and integrity. And now, you know, it's, it's an uphill climb. We're sort of this Sisyphussian rock-pushing force, just always trying to push this public opinion and public trust rock up the hill only to, you know, take two steps back, and I miss that quite a bit. JR 26:15 What do you wish that the public understood about law enforcement during the COVID-19 pandemic? AO 26:27 I think if I could choose one thing, I wish that the public understood that nothing changed in the way that law enforcement supports and loves and wants to collaborate with the community. During the pandemic, law enforcement was shined in three or four different colored lenses varying from, you know, rosy to catastrophic, and most police officers on the street during the pandemic, were humans just trying to figure out how to navigate their space and provide for their families, and to continue to protect the public and somehow navigate shark infested waters of this, the sudden unknown COVID-19 enemy. And it was a huge struggle, you know, policy was changing on the daily. Science and procedure was being released several times a day at, you know, at its busiest, and most law enforcement were just caught in the wake of this rapidly changing information, hugely volatile work environment, and trying to keep themselves and their families healthy while still being effective. I wish the public knew how much most law enforcement officers hate racism and prejudice and corruption. I wish they knew that nobody hates dirty cops more than we do. And that virtually all the law enforcement officers they contact on the daily are still doing the job because they've considered the risks to their lives and their risks to their health and the risk to their family's health, and are still willing to suit up every morning or every night, and put body armor on, and put 30 pounds of gear on, and go out there and risk their health and safety to protect our community, and mostly people they don't even know and have never met. And I think that's what's really at stake when the rhetoric gets really loud and the disinformation gets really deep. And the panic and the fear really starts to grab older people is they start to lash out against the government as a whole and what they don't understand in, you know, in some way is that that uniform represents just another member of their same community who is trying to stand between the two entities and make good decisions, and protect the constitution and uphold the peace and protect the, you know, the victims and protect, you know, the weak from the oppression and you know, all the things we stand for. But all those cops out there are just the same community members. Some of them don't have any toilet paper at home. Some of them couldn't buy peanut butter. Some of them didn't have fresh food for weeks because they couldn't go to the grocery store because of their shifts. So it wasn't that there was this divide. It wasn't that there's this this pantheon of law enforcement officers who were out there trying to screw everyone, it was members of the very same community who just happened to put that uniform on by choice to save it and protect the community despite the fact that there was this, you know, this crazy pandemic and all the fear and panic going on at the same time. JR 29:56 Knowing that I intended to speak with you about law enforcement and your experience in that profession during this pandemic, what, perhaps, was one of the questions that you hoped to answer or that I didn't ask? AO 30:18 One of the things I was thinking about talking about was that, for the first several weeks, I would say maybe even two months, there was no viable testing for any first responders in our region. So if one of my guys or gals was symptomatic, they simply had to be quarantined, and there was no way to test. We begged and borrowed and pled, and, you know, by hook or by crook, tried to figure out how to make a relationship with a clinical entity so that we could protect our people and keep them in place and keep them effective and keep them assigned on the street. What happened was any flu-like symptoms were just viewed as COVID quarantine, and so there was a couple of days there where I almost didn't have an emergency dispatch center because I didn't have anybody to work. There was a couple of days where we were hemorrhaging overtime money paying the cops that were healthy to cover the cops that were not because we couldn't get them tested. It took quite a while until we had a viable, and until the turnaround was fast enough that it was sustainable to test people. Because if the turnaround was 10 days, and the quarantine was 14 days, and almost was you know, half a dozen, six of another, you were gonna stay home anyway. So until the testing was fast enough and efficient enough, we burned a lot of time, and a lot of cops sat at home for 14 days under quarantine who maybe didn't mean to, and there was no way to test them. Once testing was viable, and available, I feel like we did a better job of that. But at the beginning, there were several of us who were pretty sure we had contracted the virus and suffered its effects as early as January or February, a ton of us were sick in January and February and early March before, way before viable testing was available in our communities. And that was, that was a challenging and an alarming period of time where even my first responders we just didn't know. And if you weren't admitted to the ER, if you weren't seen clinically, and if you didn't have co-morbidities or other risk categories, you just didn't get tested because the resources didn't exist. And why would we waste a test on a first responder who can just quarantine for two weeks and be otherwise healthy when we need to use it on, you know, the septuagenarian co-morbid patient who's, you know, got 15 different ailments, and I understand that math. But it was pretty frustrating to just have to hemorrhage overtime money and just suffer and figure out how to cover shifts and work 16, 18 hours in a row because there just wasn't anybody else. JR 33:23 I am incredibly grateful for your time and for sharing your expertise and your thoughts with us. Thank you so much. AO 33:31 You're very welcome, sir. Thank you for the opportunity. Transcribed by https://otter.ai -
 2021-03-20
2021-03-20Oral History: Interview with Anonymous Peace Officer #1
James Rayroux 0:00 My name is James Rayroux. I'm a graduate student in global history at Arizona State University, and I'm working as a curation intern with the "Journal of the Plague Year" COVID-19 archive. Today is March 21, 2021, and it's just after 5pm or 1700 hours here in Arizona. I'm speaking with a narrator who wishes to contribute to the COVID-19 archive anonymously. Sir, I first want to thank you for speaking with me and contributing to this COVID-19 archive. Do you consent to having this interview recorded, transcribed, and immediately posted to the "Journal of the Plague Year" COVID-19 archive, where it will be made accessible to the public? Anonymous Officer 0:39 I do. JR 0:40 Thank you, I greatly appreciate you making time to share your experience with us. In lieu of your name and city, can you provide me with a summary of your background and professional experience in law enforcement? AO 0:57 Yeah, I've been a sworn police officer for a little over 10 years in northern Colorado. I've worked for a couple different departments during that time. I started off at a small municipality, and at one point worked for a state law enforcement agency and then working for a municipality that has approximately 150,000-160,000 citizens within the jurisdictional limits of our department. JR 1:25 Can you give me a summary of your life before law enforcement and what led you to police work? AO 1:33 Yeah, so I grew up with a family of cops, a grandfather and two uncles who were police officers, so I'd always kind of had that in the back of my mind. When I was a teenager, I started working out with an alcohol and tobacco compliance team. So I would go in and attempt to buy tobacco and alcohol products underage to ensure that corporations were properly ID'ing the people who came in to buy those products. I studied criminal justice a little bit in college, although that's not what my degree's in. I went to a police academy and then worked at the departments that I previously mentioned. And then within the realm of police work, my emphasis has mainly been of a traffic safety, impaired driving nature, so that's where my expertise kind of lies within the realm of police work. JR 2:38 What are some of your professional goals over the next few years, and where would you like to, what would you like to accomplish before the end of your career? AO 2:50 My sights in the next couple of years, I'm currently working on a master's degree in organizational leadership. With that degree, I would like to promote within my department to at least the rank of sergeant. And like I said earlier, I work for a larger department. Previously, I came from smaller departments, and I kind of missed that small town feel, so eventually, I'd like to parlay that supervisor experience in my larger department into being a supervisor at a smaller municipality or a smaller county agency where I think I could bring both sides of working for a small agency as well as looking at working for a large agency to help a smaller agency, because they don't usually get a lot of super qualified candidates for the higher positions. It's kind of what is already at the department, which sometimes is great, and sometimes it's not so great, and I think that having somebody that just hasn't came up through that agency to bring some new kind of fresh ideas is really good for us. That's ultimately the goal. JR 3:58 And when and how did you first learn about the SARS-CoV-2 virus in early 2020? AO 4:08 Initially, I heard about it on the news, broadcast news, and then I visited enough websites, mainly Reddit, which is often called "the front page of the internet" that kind of started talking about it and how it was kind of on the West Coast. Obviously, Northern Colorado is more westerly in the US, than, you know, the middle of the country, and Denver, our biggest city in Colorado, obviously has an international airport, and there's lots of things that come through, so I kind of kept an eye on it. Also with the nature of my work, I come into contact with people of all different kinds of races, religions, sexes, creeds, orientations, all of that both, willingly and unwillingly, so I kind of kept my eye out and knowing that there could be a good chance that if it came to Colorado that I would be involved with it just because, traffic stops, disturbances, sometimes we have to take people into custody against their will if they have a warrant, or they're fighting us, so that's a really close contact, like hands-on situation. So I knew if it did get worse, I didn't expect to be this bad, but if it did get worse, that it'd probably end up affecting us in one way or another. JR 5:22 Do you remember what some of the early conversations were like that you had about the SARS-CoV-2 virus or COVID-19, what those conversations at work were like or were about? AO 5:36 Yeah, a lot of them were just kind of like, you know, this is just a really bad flu. As long as you, you know, sanitize your hands after you deal with people, which is a pretty common thing that cops do. I know, the majority of cops that I work with carry around a little bottle of sanitizer, either on their person or in their what we call a "war bag," a little bag that sits in the front seat that holds all our tickets and everything else we need for the shift. So it was initially just, you know, be smart. If somebody's sick, keep your distance if you can, wash your hands, sanitize. And then once summer comes in, because early it was spring, where it's still pretty cold here, that once summer comes, the heat will naturally kill it off, and it's not going to be anything worse than the normal flu was initially the talk around town. JR 6:24 How did your agency first deal with the COVID-19 pandemic? AO 6:30 So initially, we got multiple emails, kind of just updating it from what they've heard from the Surgeon General in Colorado that was disseminated to people higher up in the city side of our agency, with just tips, kind of like what I just talked about, wash your hands, you know, don't touch your face or mouth, sanitize your hands, sanitize your cars. And it was just kind of a more official version of what we all kind of thought, which was that it was just a worse flu as long as you, you know, stay at home with your sick, don't voluntarily interact with sick people, etc, etc, that it would be good and we'd be done by summer. JR 7:13 At what point did your agency start encouraging or mandating mask use by employees? AO 7:23 So I want to say early March is when the governor of Colorado put us on a statewide lockdown. So I want to say maybe mid February to late February, is when we got a order to make sure that we're wearing masks, if we're around each other, if we're going to be in somebody's house. They were saying they prefer it on traffic stops, but they know because of the nature of us standing in traffic and it's kind of already hard to hear that, that was kind of our discretion. But I want to say mid to late February was the big one. It's also when we stopped doing in-person briefings. We have a specific briefing room where our sergeants, commanders will talk to us about what happened earlier in the shift, what they expect of us tonight, just conversations about our shift in general that's usually done in a room. It was about that time that we move that outside. So we all just kind of stood outside our police department and ended it to be a little bit safer than being in the booking room. But even when we did that we still wore masks were outside doing our briefing. JR 8:28 What do you remember or what did that first pandemic briefing or roll call look like when everyone showed up in, in masks? AO 8:37 It was definitely interesting. You know, it's just something that you usually don't see unless you're in a hospital setting, which we obviously go to sometimes if we have bad car accidents or bad assaults. But again, even that's usually if the person is thought to have been sick or something else, where you're obviously not standing in the emergency or the surgery department. So it was a little bit different seeing everybody with these, at the time, surgical masks. We ended up getting given cloth masks and everybody eventually started you know, finding a mask they liked better, but initially, it was just paper surgical mask like you see at the hospital, so it was definitely a strange sight to see twenty cops standing around with their mask on. JR 9:23 How have your agency's policies and procedures changed since that initial response in February 2020? AO 9:31 Um, so as COVID kept going up and more and more cases and especially in Colorado, and especially Northern Colorado where there was a higher outbreak than the rest of the state, we got, I don't know the name of the product but it's essentially a super medical grade cleaning product that is so strong that you have to wear gloves and a mask anyway when you're using it because it can burn your hands and you don't want to inhale it. So we are given directives to wipe down everything we touch on our car. So steering wheel, driver-side door handles, radio mics, computers, shifter, etc, with that cleaning product both before and after our shift. And then our department also bought a bunch of small hand sanitizer bottles for everybody to carry with them. And then we had two big jugs in our, what we call patrol room where we type our reports, that we could refill those smaller bottles with. And then we were given a mandate to wear masks anytime we were in contact with somebody. And if we could, any calls that we were, we can, we would normally take in person, such as like a cold theft or something just for customer service reasons, if we're not super busy, we'll usually go to that person's house and just get their statements so they can have a face-to-face contact. We were given a directive, though, to do all that over the phone as much as we can. So there would be nights that just wasn't a busy in-progress night, and I would take fifteen calls, all from my car parked in a parking lot somewhere. So after a decade of doing this, that was a big difference in what I was used to. JR 11:12 For the benefit of the audience, can you explain what a cold theft report is? AO 11:17 Yeah, so a cold theft report is if somebody came home from dinner, and let's say their son, their twelve-year-old son left their bicycle just outside in the front yard leaned up against the house, they get home and that bike was gone. And they don't have any kind of surveillance systems, you know, they weren't home when it happened, so they know that something was stolen, but they have no idea of exactly when, no real description of who might have taken it, and we call that a cold theft. It just means that it's not something that's in-progress. Like if somebody were to call and say, "Hey, you know, there's actively a fight going on right now at the mall." Um, that would be an in-progress call, or a hot call is what some people call it. Anything cold, so a cold theft, a cold burglary, a cold auto theft just means that it's something that's not actively happening, and they don't really have much information to go on. JR 12:05 Thank you. Do you remember what your first inperson call was after you began wearing masks, and maybe your first call after the public started wearing them as well? AO 12:19 I don't recall the specifics of either. I know that there was a couple calls I went to when you know, we were mandated to wear the masks. And you know, police officers still have freedom of speech just like everybody else does. But, you know, working for any organization, whether public, like the government or private, you still follow the rules and policies, procedures of your police department or your, your company. In this case, my police department or my company said that, you know, there's a new policy that we'll wear these masks. So it was weird, because there are some houses we go to where we would talk to people in-person and, you know, they'd be like, "Well, this is dumb. I don't know why you're wearing this mask. This is essentially the flu, why would you wear it?" You know, I'd have to be like, "Well, you know, my opinion on it is irrelevant. At this point, I'm here for a reason, but my boss told me to wear this, and my department told me to wear this, and that's why I'm doing it." And then we get the opposite where we go somewhere, and we would have the mask on and so would they and they're like, "You know what, I'm really glad that you guys are taking this seriously, and, you know, there's a lot of people that aren't." At that point, they're happy so I'm not going to say anything to change it. But you know, we would give people a mask that would ask us. "I'm glad you guys are doing this. Do you think this is as bad as it is?" And I would say, "You know, well, my again, my opinion on it's irrelevant. My boss told me to wear this mask, my department told me to wear this mask, so that's why I'm wearing it. Anyway, how can I help you with the reason that you called today?" JR 13:53 Has the pandemic changed your sense of security around fellow cops or fire crews or EMS personal? AO 14:02 I don't know if it's so much has changed my sense of security. I know it's changed things that we've, we've done things a lot different. It's not uncommon for police officers and my agency or anywhere across the United States to also be dispatched to fire medical calls. And we provide what's called scene security. So firefighters, a lot of them also double as paramedics and EMTs. And obviously EMTs and paramedics are those things. They have a job to do, and that's you know, rescuing people or providing life saving medical intervention on people. And sometimes especially if it's drug or alcohol fueled, there can be other people on scene that are concerned or upset and they want to get involved with it. And so law enforcement will get dispatched to assist with that and make sure that the scene is safe or secure, so that the firefighters and EMTs can do what they need to do. And usually we'd always go to those. It changed a lot where if somebody was COVID-19 positive or had symptoms of it, and it didn't seem like we needed to be there, we would go to a lot less of those just to keep our officers safe and not put them in unnecessary danger. JR 15:11 Has the COVID-19 pandemic affected your process or procedures for detaining, arresting, or booking suspects or arrestees? AO 15:23 Not so much for detaining or arresting, those thresholds are met at certain times, and for various reasons. You know, so I've detain people before that, I don't think are alleged to have committed crime at that point. But because of their general behavior, or things they've said or things they've done it, they're detained from an officer safety perspective, so they can't hurt us, and they don't hurt anybody else. Obviously, I've detained people because I feel like they may flee from us, and, you know, I have a reasonable suspicion that they've committed a crime, and so they're going to get detained until we can figure everything out. So our department is really great about stressing as far as keeping yourself and your partner safe, nothing changes. So whatever you need to do to make that happen is fine. I work for a municipality, so our "booking standards" is what we call them, so what we can and cannot book people for is set by the sheriff of our county, who runs the the jail. Because of the COVID things, and obviously, you get inmates that are together in tight spaces, and there's a lot of them, he relaxed them, and essentially lowered the threshold of crime that it would take. So in Colorado, we have three different classes of misdemeanor with M-1 or misdemeanor-one being the highest and M-3, or misdemeanor-three being the lowest. Same with felonies, there's one through six, one is the highest sixth lowest, he essentially made it where we can't book on any misdemeanor charges for a while, which are the majority of what we deal with, I'd say. And two, we just cite them into court and give them a summons to court to appear in front of a judge to address the charges that they're alleged to have committed. That was different. So I think that was the sheriff's way of trying to control the inmate population so it just doesn't have as many people packed together. JR 17:18 In the past few months, do you suspect or have you thought that, during your interactions, a member of the public or a suspect or even another officer has attempted to use the pandemic or a possible COVID-19 infection to, to alter your interactions with them? AO 17:42 I don't think I've seen that from officers. We have definitely seen it from people that we've contacted on the street, and especially people that still meet those arrestable jail booking standards. We were told by the jail to ask a series of questions before we brought them in. You know, "Have you been in contact with anybody with COVID recently? Have you tested positive for COVID? Have you been out of the country?" There's a bunch more other ones, and it's pretty easy to kind of tell what we're getting at by the directions, the questions go. And we've had people that have been like, yep, I have COVID, my mom has COVID I've been in contact with them. And they think that that's going to make it where they don't go to jail. In all actuality, all it really did was delay that slightly because we had to go to the hospital. At which point the, the medical staff would give them a quick COVID test if they were running a fever show any outward symptoms. If they didn't show any outward symptoms, they would clear them for jail, which just means a doctor says this person is healthy enough to be incarcerated right now. And then I believe that jail would quarantine them in a separate wing. If they said they had COVID or if they did have a positive COVID test. Jail, for people that don't know, is a little bit different than prison. It's either filled with people that are doing shorter sentences, so like weeks, months sentences, not ever years, or people that have just been arrested on crimes. And a lot of times especially in Colorado, they will quickly get them out of what's called a PR or "personal recognizance" bond, essentially a piece of paper they sign that just says "I promised to come to my court hearings," and if they sign that piece of paper, the jail will release them without paying any money. So the jail would usually try to turn them out pretty quick, so give them that PR bond and get them out of the jail just as a further way to lower the risk to the jail staff and the other inmates that were in there. JR 19:39 Have you had to personally enforce any aspect of COVID-19 pandemic compliance with any member of the public? AO 19:48 No. Luckily, again, our department's been pretty great about things. We got a directive from our chief of police that said you know, "We're not enforcing governor orders," essentially. The businesses have every right to refuse service people that aren't gonna wear masks, and that's fine. If those people you know, then try to assault somebody or, or do something like that, then that's a police issue at that point. But if it's just one of those things where the people won't leave, and they've told them multiple times, he said, we can show up and you know, tell them, "Hey, this is probably business, the owner doesn't want to here. Please leave." But we are given pretty strict orders not to forcefully remove anybody for violating a civil policy from the store, essentially, the police deal with criminal matters. So if you know Guy A punches Guy B in the face that's assault, can't do that, it's criminally protected. If Guy A said he's going to pay Guy B $20, and he does not pay him $20, that is a civil matter. There's nothing criminal they agreed into, or entered into an agreement, so the masks generally fall into the civil matter. So we haven't had too many people, too many issues with it. Stores have refused service, and we've gotten a couple of calls from customers who said that it's a violation of the Americans with Disabilities Act and all the things that people have seen on any "Karen" videos. But generally, when the people say, "Hey, we, we don't want to get you in trouble, please leave or we're going to call the cops," the people left. So we don't have too many issues with it up here. Luckily. JR 21:23 Part of some of the changes that have taken place during this pandemic are the way that people interact with each other, and in Western society, shaking hands has long been a critical foundation of trust in humanity. And I suspect that's probably also true between many cops and the people that they serve. How have you worked to build rapport without having direct human contact? AO 21:51 Yeah, that's actually one of the things that you can tell a cop besides their ages, you know, there's there's officers that get into this career, late life, I got into it pretty early. I was in my very early 20s. And that's a common thing, as you know, me, somebody looked me in the eye and shake their hands. It's pretty easy to tell cops that have been doing this for any amount of time. Because if somebody does that, they usually have the canned response of like, "Oh, no, no offense, I don't shake hands. It's just, you know, a hygiene thing." Most cops are borderline germaphobes, after some of the stuff that we see and deal with, so people understand that even more now because of COVID, which is nice. The, the one that I think every cop has gotten pre and during and post COVID is the drunk guy who was just trying to be cool with everybody, and he wants to shake your hand or give you like a, you know, knuckles, pound it out. You know, we just tell him, "Oh, yeah, no, man, because of COVID we're just not trying to touch anybody." And it's cyclical, like, "Oh, no, man, I get it." Sometimes it turns into like being angry because he thinks we're being rude to him, or he just forgets and then goes back. So usually, for the 99.9%, we just explained that, "you know, because of the COVID and our policies, we're not allowed to touch anybody unless we absolutely have to," and most people are like, "Nope, I totally understand." So they've, our citizens have been really great at understanding that. JR 23:11 What do you miss most about your job and your daily tasks from 2019? AO 23:17 Um...I'm really over sanitizing my car twice a day. It's a process that isn't too long. It's, you know, five, ten minutes, but um, it just adds another checklist thing that we have to do before we start our shift. Cops by personality traits are usually Type A people, so they are very, "This is the way we do things." But that involves getting my gear in the same way it is on my belt and my vest every day, setting my car up the way that I want to set it up, getting logged into our computer, our MDT system. It's just another thing that we have to do. And I work for a pretty busy municipality, so there's times that we'll we'll be called "hit the street" or we come on-duty, and there's already a bunch of calls holding. That means there's no officers at them, and they're just sitting there waiting for somebody to take them and a whole shift is delayed by fifteen or twenty minutes because we're cleaning out our cars and sanitizing them, which is for our and for everybody else's safety, but just another thing that we have to do on top of everything else. JR 24:22 What alterations to your work life, to your daily tasking, do you expect you'll keep from this pandemic, and what do you wish to change immediately? AO 24:35 Uh, I think personally, I like handling a lot of things by phone that don't require an officer in-person. It allows us to be a little more centrally located and if something else big comes up, we can tell the person "Hey, I'll give you a call right back," and we can take off and do that. I also think that there's a lot of people that actually prefer just having an officer call them back because they're at home. They don't, you know, want the officer coming to their home, or sometimes they're not at home, they report something that happened at home when they get to work. So I like that portion of it. I was already kind of a germaphobe before this happened. I think that's probably going to, at a minimum stay the same and if not amplify a little bit more. But just doing a better job personally of, after I've been in somebody's house, even if I don't shake hands with them, just making sure I throw on hand sanitizer, wash my hands, just as a force of habit. No matter how clean and dirty the house is, we just don't know the people generally, so just kind of keeping that cleanliness I think is going to be a big help going forward. JR 25:39 Through this pandemic, and your experience working as a police officer during this time, what do you most wish the public knew about the COVID-19 pandemic, as it relates to your profession and to cops and police work in general? AO 25:58 I think, for us, it's real easy to see every police officer as one entity, just the person with the uniform and the badge. They forget that we also have families that are out, you know, in the same public places, that we have children that go to the same schools as the people that we deal with daily, that all of the stressors that everybody else has from this, this pandemic of not being able to, it's loosening now, but especially last summer and this fall, the same stressors of not being able to go out to eat with friends and blow off steam, or just go to the bar and have a beer with a buddy. We have all those same stressors because, you know, we're cops 40 plus hours a week, but the rest of the time, we're citizens that live in the same community as everybody else. So it's, it's understandable when, when the people that we deal with, you know, think that we're just the the strong arm of the government enforcing these rules that you know, they don't think are constitutional, or whatever it is, but we have to follow the same rules and get the same stress from that on top of having the stress of having to enforce those rules, which whether or not we do or don't agree with them, we have a job do and we signed up to do that. So just wishing that people would understand that we have, we go through all the same stuff they have on both sides of it, on our work side and also on our personal side, and just being a citizen of the same community that they live in. JR 27:21 Now, knowing that I was going to ask you about your experience as a police officer during this pandemic, what question did you most want to answer during this or that you wish I would have asked you during this interview? AO 27:40 I think my biggest one we actually touched on, which was how did the officers feel about the mask mandates and the, you know, various states closing down in-person dining and all that. And my answer, which I touched on, if it was asked directly, was at the end of the day doesn't matter. You know, there's officers are just a small segment of the whole population. You know, we have men, women, gay men, gay women, trans men, trans women, black, white, Asian, Hispanic, those are all actual officers that I work with in every single one of those categories, so they're just a small sample size of the entire agency. So you're gonna have people that are far left Democrat, that are far right Republican, and at the end of the day, our personal beliefs should not and in my case, don't matter. As far as if I believe this is a real virus, if I, you know, think that everybody should wear masks, they don't, you know, we're sworn to uphold the Constitution of our state and our country, and rules and regulations set forth by our municipalities or counties. So just knowing that kind of, you know, you should never know after talking to a cop for any length of time, what their stance is on is on any polarizing subject. So you should never really know what religion they are, if they're religious, what Republic or what political party they lead with. That's one of the, the what I think makes a good cop is they can help anybody, no matter where they're at in life, rich, poor, whatever color religion they are. So realizing that, you know, we have our own thoughts on it, but we still have a job to do. It's just something I wish that people would realize that wherever we stand on it doesn't matter because we're given our policies, our procedures, and we're going to follow those and hopefully that, in the end, will help this get over a little bit sooner and help everybody get back to a normal life. JR 29:44 I greatly appreciate your time and willingness to share your expertise. Thank you so much. AO 29:49 Thank you Transcribed by https://otter.ai -
 2021-03-19
2021-03-19Stop AAPI Hate
Nearly 3,800 anti-Asian racist incidents occurred in America last year, mostly against women, based on data by Stop AAPI Hate. Yesterday, Asian Americans and allies called for solidarity and condemned discrimination and racist violence in Minnesota. They also honored the lives of Delaina Ashley Yaun, Xiaojie Tan, Daoyou Feng, Julie Park, and Hyeon Jeong Park -- employees of an Atlanta-area spa who were killed on Tuesday by a gunman. -
 2021-03-10
2021-03-10Justice for Angelo Quinto
Tonight AAPIWL joined Angelo Quinto's family + community, the incredible organizers of @justiceforangeloquinto, Civil Rights Attorney @johnburrislawfirm , the mother of Oscar Grant- Rev. Wanda Johnson, @justice4steventaylor grandmother, @robbonta, Cat Brooks @antipoliceterrorproject, Antioch's elected officials, and hundreds of community members from all over the Bay Area to celebrate Angelo's 31st birthday. Tonight we all learned that Angelo was well loved by his family in Antioch and in the Philippines. His family talked about how amazing and special he was, and they were proud that he wanted to pursue his passions in art. We learned more about the powerful community that will continue to support the Quinto family in their fight for Angelo. Thank you again to the organizers for this beautiful celebration and vigil, for uplifting Angelo and his family, the call for solidarity, the need for mental health resources, demanding the end of police violence and the need for accountability for Angelo and the countless men who were also murdered by the Antioch Police Department while having a mental health crisis. We will continue to fight with you all. #JusticeForAngeloQuinto #JusticeForAngeloJusticeForAll #AAPIWomenLead #InSolidarity #StopAAPIHate -
 2021-03-13
2021-03-13Love Our Communities
There are different events happening today - thanks to the organizers across the US for your work. We’ve been learning alongside LA in particular - THANK YOU to all of the organizations + individuals who’ve been working SO hard to make today happen. We love our communities + we are building collecting power. Hope you join this movement. #InSolidarity @ccedla NAME CHANGE: In an effort to amplify our message of solidarity, we are no longer using “Stop Asian Hate” in the title for this event. CCED recognizes that the emphasis on hate crimes limits the scope of the conversation, implying these attacks are merely isolated racist attacks + that policing is the solution. Hate crime legislation funds surveillance but does not actually change the material realities that working class Asian Americans live in. Anti-Asian violence is tied to the collective struggle of BIPOC under white supremacy. We’ve provided some reading materials in our link in bio for folks to learn further! . . Join our communities THIS SATURDAY 3/13 @3:30PM @jamuseum in Little Tokyo (in person or via livestream!) for “LOVE OUR COMMUNITIES: BUILD COLLECTIVE POWER”--a grounding, healing space in the wake of anti-Asian Violence. Meet, collaborate, and build with grassroots organizations doing direct work in Los Angeles Asian American communities. Artwork by Cynthia Yuan Cheng @cynthiaycheng Organized by: Chinatown Community for Equitable Development @ccedla Ktown4BlackLives @ktown4blacklives Tuesday Night Project @tnproject Nikkei Progressives @NikkeiProgressives Sunday Jump @thesundayjump API Equality LA @apiequalityla Kabataang maka-Bayan / Pro-People Youth @kmb_la Progressive Asian Network for Action (PANA) Palms Up Academy @palmsupacademy J-Town Action and Solidarity @jtown.action.and.solidarity Hosted by: The Japanese American National Museum @jamuseum **Masks required. Double masking encouraged. Social Distancing required per CDC Guidelines** ADA accessibility + streaming details to be announced. Check out the FB Event Page @ccedla link in bio. [image description - more info on @ccedla page at comments] -
 2021-03-16
2021-03-16Surge in Hate Crimes Against Asian Americans
As the U.S. continues its battle against COVID-19, it is also battling a rise in hate crimes against Asian Americans. A recent report found that hate crimes against Asian Americans in major U.S. cities surged by nearly 150 percent in 2020 —even as the number of overall hate crimes fell. Stephanie Sy looks at how the violence has marred one community, and how they are coming together in its wake. -
 2021-03-14
2021-03-14Brenda Cohen Oral History, 2021/03/14
In this oral history, I interview my mom, Brenda Lee Cohen on her pandemic experience with a particular focus on her work with the Calgary police service as a crime and intelligence analyst supervisor. In this interview, Brenda talks about her initial experience with the COVID-19 pandemic, she recalls the first day of the pandemic as she and her husband were stuck in America. This particular interview touched upon what her work environment was like during the pandemic and topics such as systemic racism, the police ‘culture’ and the revocation of a popular program for city employees known as the ‘golden handshake’ in the midst of the pandemic. Brenda also spoke briefly about her experience with misogyny within the workplace and how these ideas are so prevent within a space which mixes the civilian and police worlds. Finally, Brenda also spoke about what she is most thankful for in this pandemic, and ultimately reflects on her own inability to express her thoughts and emotions – and how one day when she is out of the police environment, things will be different. Interviewee Name: Brenda Cohen Interviewer Name: Padraic Cohen Date of Interview: 03/14/2021 Location: Cochrane, Alberta Canada. Transcribed by https://otter.ai Partially transcribed by Padraic Cohen -
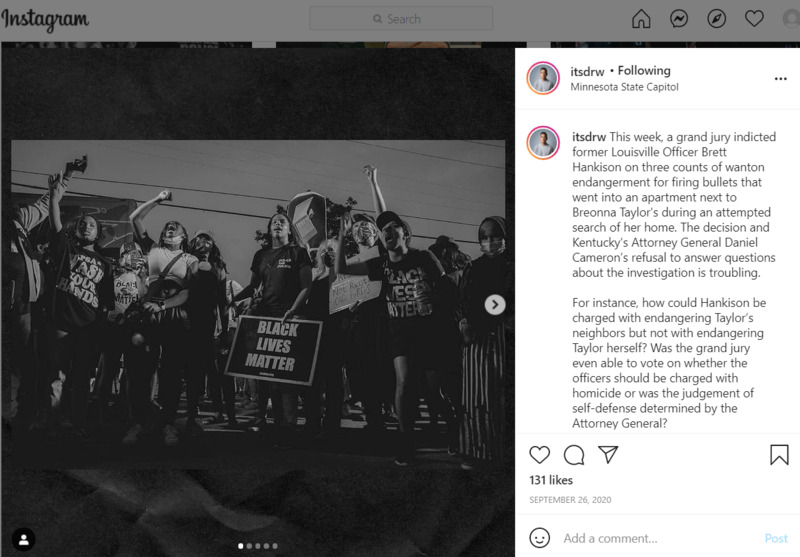 2020-09-26
2020-09-26This week, a grand jury indicted former Louisville Officer Brett Hankison on three counts of wanton endangerment for firing bullets that went into an apartment next to Breonna Taylor
This week, a grand jury indicted former Louisville Officer Brett Hankison on three counts of wanton endangerment for firing bullets that went into an apartment next to Breonna Taylor's during an attempted search of her home. The decision and Kentucky's Attorney General Daniel Cameron’s refusal to answer questions about the investigation is troubling. For instance, how could Hankison be charged with endangering Taylor’s neighbors but not with endangering Taylor herself? Was the grand jury even able to vote on whether the officers should be charged with homicide or was the judgement of self-defense determined by the Attorney General?
