Items
Subject is exactly
Rural
-
 2023-07-19
2023-07-19COVID-19 Archive Story_H. Crowder
I have uploaded a personal story of how COVID-19 impacted my life; and how, in my mind, there is a before and after, two different sections of my life. I also observe the changes that were influenced by the Pandemic. -
 2021-11-29
2021-11-29Pat and Caleb Linder Oral History, 2021/11/29
Pat Linder and Caleb Linder are father and son from Ellsworth, Wisconsin. They both are employees of McGough Construction. In this interview, Pat and Caleb discuss how Covid-19 has affected their lives at work, at home, and in their community. They talk about their experiences working in Minneapolis and St. Paul during the George Floyd protests as well as Covid-19 has affected the hospital in which one of them currently works and the changes they need to make because of the pandemic. They discuss their feeling and thoughts on the vaccine, how the media portrays the pandemic, and what they do to stay safe while living through the Covid-19 pandemic. -
 2020-04-17
2020-04-17Courtney Kelley Oral History, 2020/04/17
-
 04/11/2020
04/11/2020Talitha Brandel-Black Oral History, 2020/04/11
-
 12/03/2021
12/03/2021Brad Peterson Oral History, 2021/12/03
Brad Peterson is currently a pastor at Trinity Lutheran Church in Boyceville, Wisconsin. In this interview, Brad discusses COVID-19 and its impact on his career as a pastor, the community’s response to the pandemic, and his personal life. He talks about the challenges he has faced, specifically, living within a community that has shown resistance to COVID-19 regulations. COVID-19 has created many implications but Brad tries to focus on the positive outcomes of COVID-19. For example, Trinity Church now offers online worship and will continue to offer online services as it has proven to be a popular and comfortable way to worship. -
 11/29/2021
11/29/2021Don Knutson Oral HIstory, 11/29/2021
Don Knutson is the Rescue Squad Director for the Village of Colfax Wisconsin. In the interview, he goes into detail about his job and how it changed because of Covid. As he has taken care of patients that go by ambulance but as a director and how he has seen things change in the profession. He also is the health advisor for the Village of Colfax which was the main source for the community. While he also shares how his work life has also affected his personal life because of the added reasonability from Covid. Finally, he comments on how the political atmosphere has affected the pandemic. -
 11/30/2021
11/30/2021Melinda Ruzich Oral History, 2021/11/30
Melinda Ruzich is a 20-year veteran kindergarten teacher from Hibbing, Minnesota, a rural town 229 miles (about 4 hours) north of Eau Claire. Melinda is also undergoing treatments for breast cancer, and she has been immunocompromised for the entirety of the pandemic. In her interview, Melinda discusses how her cancer treatments impacted her ability to teach during the early stages of the pandemic in 2020 as well as how her job has changed over the past 20 months. Melinda shares how childhood development has evolved at the early childhood and kindergarten levels and how her role as a teacher has shifted. Melinda also discusses how parents and the public have interfered with her (and other teachers in her district) abilities to teach in schools safely. She discusses her school district’s mask mandate and the public’s response and pushback to vaccinations and masking in the small, rural community in Northern Minnesota. -
 12/08/2021
12/08/2021Jill Smith Oral History, 2021/12/08
Dr. Jill Smith is a retired professor from the University of Wisconsin Eau Claire, she currently lives in Menominee Wisconsin. In the interview, she talks about how Covid-19 has affected her family and her work within her community. As she started the pandemic as a caregiver for her husband who unfortunately passed in January. When she talks about her job as a contact tracer for Dun County and how that has shaped her life. While she also volunteers at Steeping Stones and interacts with her community. Commenting on the political side of how her community adapted to the pandemic. Concluding with her perspective on how the future may look with the new Omicron variant. -
 12/03/2021
12/03/2021Wendy Vorpahl Oral History, 2021/12/03
Wendy Vorpahl is from Gillett, Wisconsin which is a small town near Green Bay. She has four boys: Matthew, Mark, Aaron, and Adam who all fall on the Autism Spectrum with Mark and Aaron having classic/severe Autism. In this interview, Wendy talks about the impact the pandemic had on her small business and the small business around her, her family’s experience with all getting Covid at the end of 2020, as well as her thoughts and feelings about the vaccine and the handling of the pandemic. Matthew and Aaron also come into the conversation at a few points as Matthew answers some questions and Aaron can be seen and heard in the background. -
 12/13/2021
12/13/2021Teresa Kirchner Oral History, 2021/12/13
Teresa Kirchner currently lives in Southeastern Alaska with her husband and three children. She is a nurse practitioner working in an outpatient clinic setting, providing primary care needs to rural Alaskan communities. She discusses how the COVID-19 pandemic has affected her job, in both positive and negative ways. She shares many changes she has seen in her community during the pandemic, and how those changes affect the everyday lives of those who live there. She shares advice she would give to those in the future from what she has experienced during the pandemic and goes deeper into how Alaska in general has handled issues regarding the pandemic. -
 12/05/2021
12/05/2021Deborah Jorgenson Oral History, 2021/12/05
Deborah Jorgenson lives in Frederic, Wisconsin, and currently owns a salon in Hudson, Wisconsin. In this interview, Deborah discusses how the COVID-19 pandemic has affected her life, business, and family. She shares the struggles of owning a business in an affluent area during the lockdown and is concerned that if another lockdown comes in the winter she will have to shut down in Hudson for good. She also talks about how she’s grown closer to her family during this time and is able to see them more often. She also touches on how it’s frustrating that her business had to shut down while bigger businesses were able to remain open and had fewer restrictions. -
 12/10/2021
12/10/2021Shae Havner Oral History, 2021/12/10
In this interview, Shae Havner discusses her experiences as a mental health therapist during the pandemic and the changes in her career and her clients. She talks about how the pandemic affects mental health, both positively and negatively, and the rise in domestic abuse cases. She also gives insight into how COVID-19 affected her home life as a mother and how the pandemic has affected her sons as well as what her family and friends did to have fun during the shutdown. She lives in Fall Creek, Wisconsin, and works in Eau Claire, Wisconsin, and compares how the two cities responded to the pandemic. She also brings up vaccinations, the booster shot, and getting her children vaccinated. -
 11/27/2021
11/27/2021Rebecca Ferber Oral HIstory, 2021/11/27
Rebecca Lynn Ferber is a resident of Oronoco, MN, and currently works for the Mayo Clinic in Rochester as a CRNA (Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist). In this interview, Rebecca talks about how COVID has affected her job as a CRNA and Mayo Clinic as a whole as well as a mom and wife. She also talks about how it has affected her family and friends and how some of her relationships have been strained because of different views on COVID. She touches on how it not only affects people's physical health but mental health as well and gives some advice for future generations. -
2021-06-06
My Reverse Homecoming
The first trip my wife and I took after the COVID travel restrictions were lifted was a doozy. Our first flight in over a year was a three-hop journey from our small Montana town to Alaska for an old friend’s wedding. With a six-month-old. On our laps. The whole time. My wife and I had our first round of vaccines but worried about our daughter, who was still far too young to have a dose. After much risk assessment and consultation with our pediatrician, we decided to go for it. Mask wear was strictly enforced on the airplane and in most of the public places we found ourselves, and there was a profound and somewhat discomforting sense that we and our fellow travelers were searching for a way to exist comfortably in this new not-yet-maybe-never-post-COVID world. The thing I remember most, though, was how incredibly freeing it felt to be somewhere new again. So much time spent at home, however necessary, had inflicted an unhealthy solitude on much of society, and my first time solidly stepping away from that felt energizing. I’ve always loved to travel and doing so after the darkest days of the pandemic felt like a happy return to form. A reverse homecoming, if you will. -
 2022
2022The West in the face of crises since the nineteenth century In the West, returning to the land and to locality is one of the traditional responses to crises
Confronted with what may appear to be a series of global crises - health, environmental, economic and even democratic - the ideas on the virtues of what is local and rural are becoming increasingly heard. This article aims at putting this return to locality in historical perspective. For almost three hundred years, Western societies have gone through profound changes, especially economic ones, at the cost of a break with nature, in a more or less dramatic, and more or less painful way. Throughout our recent history, surprisingly diverse voices (political leaders, artists, activists, etc.) have conjured up this return to the land, which has taken on various forms. This return appears to be a providential solution to these disruptive changes. The health crisis due to Covid 19 seems to have not only confirmed, but also exacerbated this trend. -
 2020-05-23T09
2020-05-23T09Sampling a dystopian world
We lived in a very town in western Illinois as the pandemic arrived in America. Covid-19 seemed abstract until circumstances caused us to travel to a major international airport. The eerie quiet, in place of what should have been a noisy, madcap atmosphere, elevated sounds I normally would not have heard. It was as if a scene from a science fiction film had jumped off the screen and into my life. The experience had a nightmarish quality that has stayed with me two years later. -
 2022-03-27
2022-03-27Ambulatory vaccination crews
The ministry of Peru is launching efforts to vaccinate people living in rural regions. This Instagram post shows a crew of three people carrying coolers of vaccines to rural areas in Peru. -
 04/29/2021
04/29/2021Kristina Jordan Oral History, 2021/04/08
This interview was recorded as part of The Covid 19 Oral History Project, a project of the IUPUI Arts and Humanities Institute associated with The Journal of a Plague Year: A Covid 19 Archive. Tina is an essential worker, working as a paramedic for an ambulance service in Southern Wisconsin. She is also a full-time faculty at the technical college where she trains EMS students. Her husband is also an essential worker as a volunteer firefighter. In this interview she discusses changes to clinical hours for her students, transitioning to using human simulators. Issues with PPE shortages. Transitioning to online learning and how teaching was different. How her local Governor response affected her and her community. Changes to her day-to-day life with family and friends. Fear for her parents getting covid, staying isolated and missing family during a years’ worth of missed holidays and getting vaccinated. The effects on her community and the political aspect that crept into the COVID pandemic. Frustration with COVID deniers, mask refusal and social media blasting false information. Seeing the realities of COVID as an EMS driver and transporting COVID patients. Her feelings for those who lost loved ones during covid and their grieving process. Political, both state and federal, response to COVID. News outlets and how she chose to receive news. Comparing COVID to other world events like 9/11 and Desert Storm. Living in a rural area. Her hopes for the future and the lessons she hopes we have learned. -
 04/23/2021
04/23/2021Gary Lato Oral History, 2021/04/23
This interview is done with Gary Lato who is 69 years old and has lived in Stanley, Wisconsin his whole life he is a retired mailman of 34 years. Here I discuss with him how COVID has affected those around him in his community as well as how it has affected him. Primarily I am getting his thoughts on the entire issue since he says he lives a mostly hermit lifestyle. During the interview, he spoke as an observer of all these things going on in the community and what he is noticing from his perspective. From Garys’s point of view as an older member of the community, he sees all this as something that is going to pass and just run its course. He also touches on how most in his area in the country are mainly just staying out of it and going about their lives as normal and not worrying about it in general. He also goes on to note how this is affecting people in a big way, due to there being restrictions on many aspects of life. He ends the interview with his own spiritual view, that if you have spiritual views may agree or disagree with them. -
 05/22/2020
05/22/2020Nancy Cambell Oral History, 2020/05/22
In this interview by Karen Kilby, a government contracts manager Nancy Campbell discusses how the COVID 19 virus has affected her life. She discusses the toilet paper shortage, the changes in her family dynamic, social isolation and the shortage of hand sanitizer and cleaners. Nancy also discusses her life as a senior citizen living in a rural area, the economy and her opinions on how government has delt with the virus. -
 04/18/2021
04/18/2021Morgan Ward Oral History, 2021/04/18
C19OH -
2020-04-02
The Silence of Nature
I live in a rural area of southeastern Louisiana. When I first moved here the only thing that you could hear at night was the natural sounds that one would think of when being in the country, but as developments started to move into my area the air was polluted with the sound of cars on the distant interstate. The nights become a harmony of grasshoppers and traffic all mixed into a melody that formed a hybrid of urban and rural life. On the night of April 2nd, 2020 I was enjoying a night of looking at the stars through my telescope. It was a mainly clear night when I closed my eyes and began listening realized that I could no longer hear the cars on the interstate. Louisiana was in the mist of the a very high spike in COVID and lockdowns were in effect meaning there were fewer cars on the roads especially at night. I sat and listened for hours as I was able to hear all the sounds that were once masked by the intrusion of development on my rural area. From about April 2nd until early July this quite remanded at night. It was not until Louisiana started to open up more that the sound of the cars returned to my nighttime symphony. When I look back on the early days of the pandemic this is the memory that stands out and how it will be remembered by me. Though a harsh time in the world and for humanity, the sounds of technology and modernization were drowned out by nature for a time and it made the nights a little more peaceful and less stressful with all that was going on in the world. -
 2020-03-18
2020-03-18The Show that Almost Was
After Susanville's Best of Broadway show was cancelled just a day before its opening night, Susanville's local online news editor Jeremy Couso reached out to the Best of Board members to see if he could publish an article about our show, the show that never happened. He and his wife attends the performance for a media night and he happened to have a video of the show. For a small production, the youtube video of the performance has had just under 900 views as of October 9th, 2021. I directed Wizard of Oz with a dear friend of mine, in a one year shot to direct. Watching the video of the show that didn't happen is honestly very sad and hard to do. We become family with the cast and to not reach the finale is painful. But the show must go on, and in 2022, Best of Broadway will take the stage again. -
 2021-10-06
2021-10-06Sharing Experience, Cochrane Times, October 6th 2021.
2.) This is another photo within the Cochrane Times dedicated to documenting Canada’s first Orange Shirt Day; this was an article from the October 6th paper. The text underneath the photo reads: “Sharing Experience, Residential school survivor Jenny Clark shares her story with those gathered near the McDougall Stoney Memorial Church ahead of a ceremonial walk to Morley on the National Day for Truth and Reconciliation, September 30. -
 2021
2021POV of a Cattle Rancher
This is important to me because this is my partner speaking. At the beginning of the pandemic we were living in Montana on a working cattle ranch, so our experience was a lot different than what we were seeing on social media. We experienced extreme food shortages and ironically had an even harder time selling cattle to processors and feed lots. -
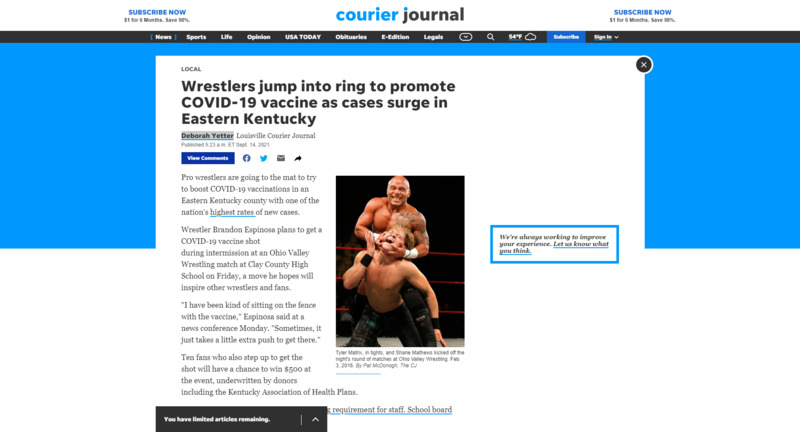 2021-10-08
2021-10-08Covid Vaccination Efforts
In the age of Covid, misinformation and disinformation runs rampant and we must meet this challenge with unconventional methods. The use of wrestling events to convince people to get vaccinated demonstrates a gendered response to the problem. What does a 'masculinized' approach say about rural and/or Appalachian culture? Is it now considered weak to comply? -
2021-09-29
Covid in Altus Oklahoma
I wanted to share my personal experience of living through the COVID-19 Pandemic in Altus Oklahoma. While my experience probably looked very similar to others, I believe it is very important to always information share so everyone can have the complete picture. I am active duty Air Force, and was residing in Altus Oklahoma during the pandemic in 2020. Living on a military base, it is not very often that you have quiet hours or down time. However, during the height of the pandemic, the majority of the base shut down and went to minimum manning for almost 30 days. It was strange to see operations halt, and all non essential workers staying home with their families for the duration of the town shut down. Organizations went from in person working to relying on home desktop computers to get the mission done. During this time people were also limited on where they were allowed to travel, and people they were allowed to see. At one point, some people were not even allowed to go on walks outside, because they were not sure how the virus would spread and if it would be safe being close to others. As doctors and scientists started discovering the make up of the virus and how to mitigate against its effects, we started gaining more liberties back. Members were no longer confined to their homes, we were able to do outdoor activities near the base, and were allowed to travel to nearby towns for any essential items. Looking back on the situation that occurred a little over a year ago, it is hard to imagine and remember what it was like to be confined to our homes and not being able to engage in social gatherings. One thing that is pandemic has highlighted to me is that despite all the adversity the world has faced, we are still determined to get the mission done efficiently and effectively everyday. I would also like to highlight the importance of social connectedness and gatherings. During the isolation period of the pandemic, the majority of people suffered from lack of communication and not being able to connect with those around them. If this pandemic has taught us anything it should be to not take your health for granted and to value the time you have with loved ones, because you never know when it will be your last time together. -
2021-09-29
Covid in Altus Oklahoma
When reflecting back on the height of the COVID-19 Pandemic in 2019, it is strange to think the whole country was isolated from other people for an upwards of three months or more. I was residing in Altus Oklahoma during the pandemic and there was a point where no one was allowed to leave their homes to even enjoy the fresh outside air. With this, a lot of local organizations were shut down for months including Churches, local eatery's, stores, and even some grocery stores. While I know my story is similar to many others, I believe that it is important to share all experiences with the community. Sharing will create a complete picture of how the pandemic shaped our society today. -
2020-05
Waiting to be Connected
I moved out of New York City for a month in the spring of 2020 during the period where my gallery furloughed most employees aside from the principal directors and a select number of sales people. I spent that time with my father in upstate New York in a close quarters quarantine. I was always struck by the quiet during the day and how visible and bright the stars were at night. Two things that seemed foreign to me at times as I grew up in cities and had lived in various Brooklyn neighborhoods for the past year. The passing sound of car stereos and people’s voices on fire escapes from a floor above were white noise. All vibrant - completely alive - no stars. His apartment was a studio and at the time he had not yet begun paying for internet service. Some nights we would drive four or so minutes down the road to the apartment complex where my Dad used to live a few years prior. We would camp outside the complex’s gym which housed one or two treadmills and the outside looked like a glorified garage - but it had wifi. As we were no longer residents and owners of a key pass to the facility, my Dad would pull up to the side entrance and put on his hazards. I would jump out and begin to search for a signal and attempt to connect to the complimentary internet. Whenever a stray person would emerge from their units to retrieve Amazon packages from their front stoop, I would make uncomfortable eye contact with them, as I held up my phone. Yes, yes, this is what you think it is. They hastened back up and quickly closed their door behind them. I found that the most expedient way of downloading content was to position myself by the exterior front left corner and stand with my back flush against the wall. Every night my Dad and I listened to podcasts and drank tea. Despite everything, moments like these helped us laugh and I look back at this memory fondly. -
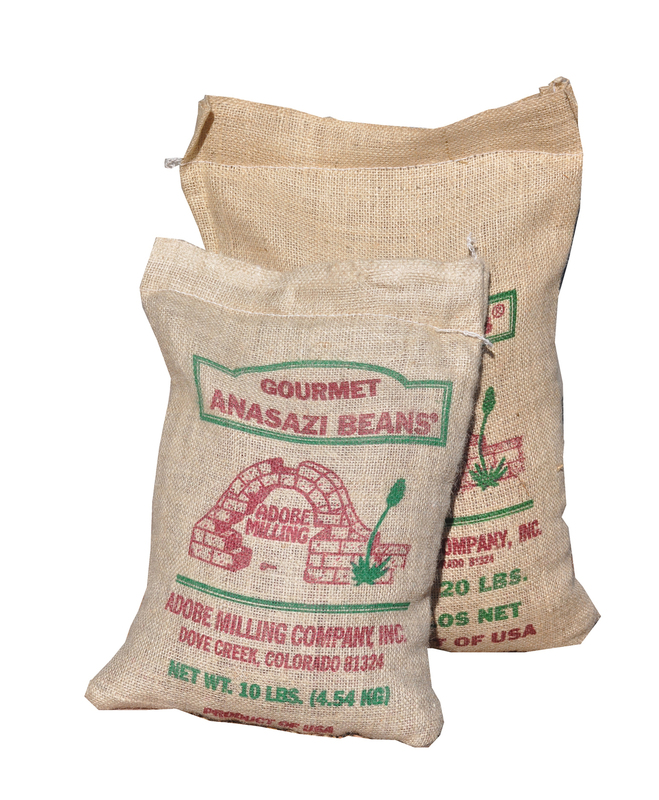 2020-05
2020-05In 2020 We Ate Certain Foods Because We Stopped Buying Fresh Produce and Meat
In late spring 2020, we begin to realize that it was too dangerous and too expensive to buy fresh produce and meat. The fresh produce was often out of stock for weeks at a time. Then other times the produce just seemed difficult to trust. The grocery store often had people without masks and the COVID numbers were rising. We really couldn't trust any fresh fruits or vegetables unless we cooked them. Eventually as the prices began to rise on fresh meats, we stopped buying those too. Eventually we found that the pandemic had completely altered our day to day eating habits. We didn't always trust restaurants for takeout since they had COVID outbreaks also. Living in a small rural town, we had limited options. This left us trying to buy a few canned foods at stores or ordering delivery of shelf-stable foods in bulk from online retailers. One of the things that I remember the most is how I began to struggle with my blood pressure. We were eating too many boxed and canned foods; not enough fruit and vegetables. My sodium intake was high and my potassium was low. We then decided we would start buying dehydrated vegetables and fruit. We tried not to buy canned versions that were preserved with salt. The main thing I remember is that one of the first meals that seemed so good and healthy was a meal of Anazazi beans. We had bought some in New Mexico the year before and really liked them. This time we bought a 10 lb bag and assumed that we may have to stock up as the pandemic continued on. We also bough dehydrated onions, dehydrated jalapenos, and other dehydrated mixed vegetables. We did an instant pot of the beans and what ingredients we had. We really enjoyed it. For the first time in weeks, it felt like a real meal. And this was a hot meal during a warm time of year, something we would normally never cook before 2020. Here is the instant pot recipe and with the ingredients we had, leaving out the ones we didn't have. We adapted as best we could. The original full recipe is linked for comparison. The recipe we found: Instant Pot Anasazi Beans Ingredients 2 cups. dried Anasazi Beans 6 cloves garlic, peeled and smashed 4 c. low sodium chicken stock 1 c. water 1 fresh bay leaf (or 2 dried) 1 t. cumin 1 t. dried oregano 1 t. dehydrated jalapenos 1/8 c. dried onion salt and pepper to taste Instructions: 1. Place dried beans, crushed garlic cloves, chicken stock, water, cumin, oregano, bay leaves, dehydrated jalapenos, and dried onion in instant pot. 2. Close lid and pressure cook at high pressure for 25 minutes, then pressure release for roughly 15 minutes. Open the lid carefully. 3. Switch pot to soup setting. Stir occasionally for about 10 minutes. Taste and season with salt and pepper. 4. Serve. http://eliotseats.com/2019/01/27/instant-pot-anasazi-beans/ -
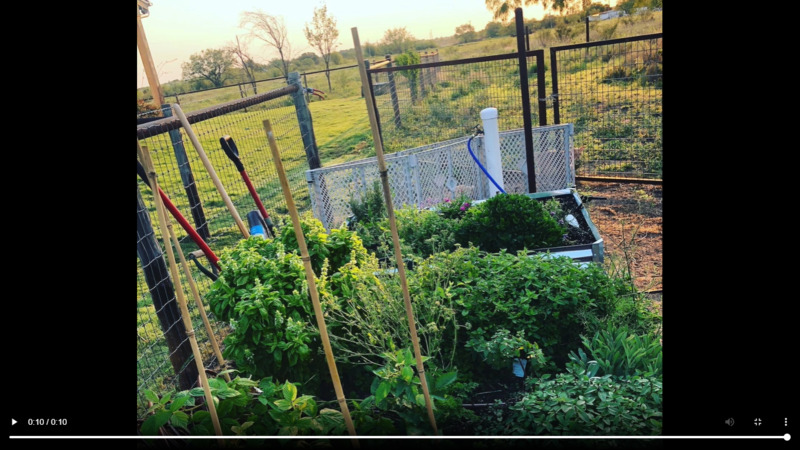 2021-08-06
2021-08-06Covid Gardening Story and Okra Recipe
I chose to focus on my garden and our chickens that we began right before the pandemic hit. I never realized how lucky I was to live in a rural environment until Spring 2020, when living in the country meant having a bit more freedom than in the city. Our garden and chickens provided us with foods that sometimes were out of stock in our small, local store. However, we also faced other things in our community that made the psychological aspects of the pandemic really hard, such as living with those who deny the reality of the disease and mitigation efforts that people like my husband promoted, as an ER physician. I suppose this story is a bit of a love letter to our little property out in the country, despite the differences in values that we have with our town. -
 2021-08-02
2021-08-02Macaroons
The COVID-19 Pandemic led me to try a new and challenging recipe of Macaroons. This is my experience. -
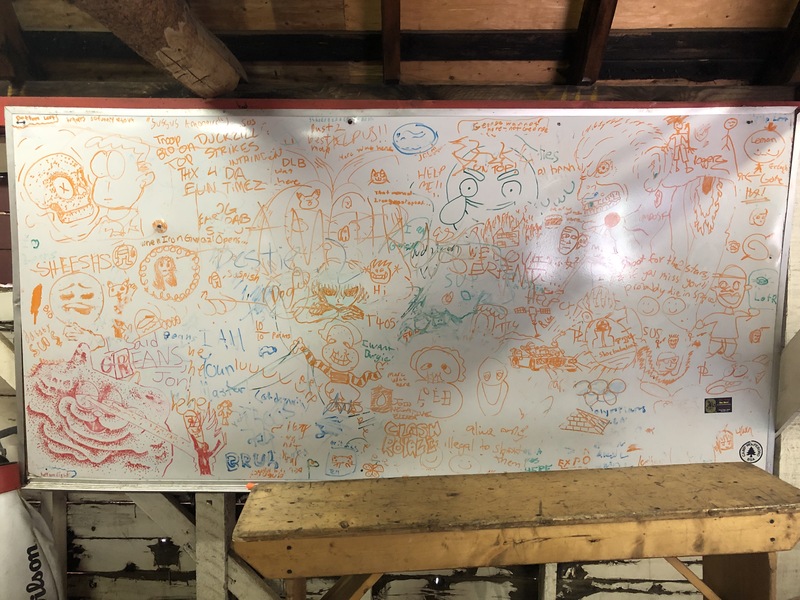 2021-07
2021-07Wolfeboro PO Whiteboard
The top of the program office at Camp Wolfeboro, where the camp director and program director offices are, has a large whiteboard every year where Scouts are invited to draw anything so long as it is Scouting-appropriate. The two photos of the whiteboard were taken at the middle and end of the fifth session of camp; IMG_5768.jpg was taken on Wednesday, July 21 at 11:41 AM, and IMG_5817.jpg was taken on Friday, July 23 at 4:17 PM. In the two and a half days between the photos, there were some additions made to the board. The whiteboard includes a variety of references to recent cultural trends, some of which include: -Upper left: text reading "whats [sic] so funny about Sussus Amongus", a reference to a YouTube video titled "What's so funny about sussus amogus?", itself an Among Us parody of the Biggus Dickus sketch from Monty Python's Life of Brian. -Center left, immediately next to the edge of the board: the word "SHEESH" in orange marker, which is used to show a sense of disbelief about something, with a positive tone (similar to how "dang" or "damn" might be used) -Upper center, slightly to the right: a dark green drawing of an open eye crying laughing emoji, an edited version of the laughing crying emoji that is used in memes to signify an emotional reaction to something -Bottom right: an orange-colored set of Olympic rings, with the words "Olympians [illegible]" in blue beneath it Some of the additions between Wednesday and Friday include: -Center left: an Among Us crewmate next to a text bubble saying "SUSSY!" (a reference to the slang term "sus", meaning suspicious, often used alongside references to Among Us) Many of the specific cultural references refer to the video game Among Us. According to the program director, the massive Garfield drawing at the bottom left was drawn during the 2019 camp season but became unerasable by the time camp opened in 2021 (camp did not take place in-person in 2020). -
 2020-12-31
2020-12-31The Summer Your Librarians Became Youtubers...
I am a children's librarian in rural Louisiana. We are approximately two hours away from all major forms of entertainment, so the library acts as not only a community hub but a place for children to learn and participate in extracurricular activities year-round... until Covid. Though our community hardly noticed the virus itself, the effects of being locked down soon took hold, and we were left with a community of children, families, and elderly people more isolated than they usually were. The depression set in. And my director had the fabulous notion to take what we did to the airwaves... Or rather the internet. Our seriously underutilized Facebook Page became the hub of activity, and overnight we went from librarians to Youtubers leading digital craft and art classes, Zoom creative writing workshops, and nightly bedtime stories. What initially began as a means to cheer up the children soon developed into full-fledged outreach. Local politicians, law-enforcement, and other community leaders read stories for us on our page as a means to connect with the people in our community. We did special digital story hours with schools once they opened back up in the fall, and also read stories to patients in the nursing home. Continuing with this train of thought, we partnered with our local American Legion Hall, which is located on a main thoroughfare and has large windows clearly visible from the road, to set up our annual "Christmas Around the World" exhibit (which features Christmas traditions from many different countries as well as Kwanzaa and Hanukah traditions) since there was no way to feature the display in our small meeting room safely. Every program was modified, digitized, and brought to the people of our community in the best possible way they could be... which turned the 'year of the plague' into a year of learning, cooperation, and ingenuity for us. -
 2020-06-18
2020-06-18Why COVID-19 will end up harming the environment
This article warns that COVID will only offer a brief respite from environmental problems like air pollution. Post-COVID, we may see even worse pollution and accelerated climate change. -
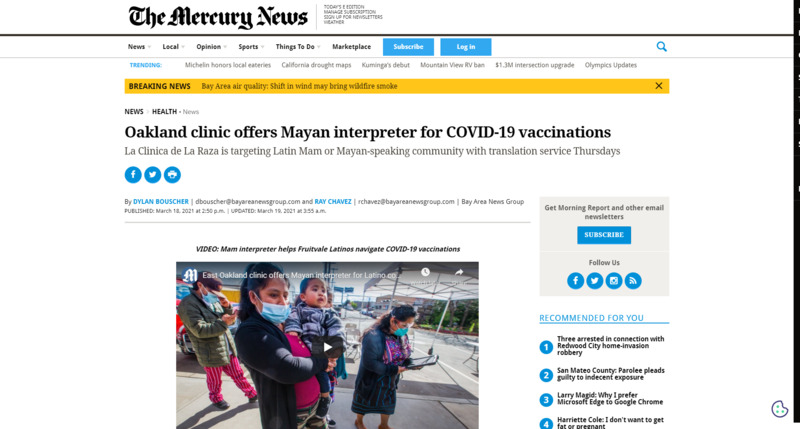 2021-03-18
2021-03-18Oakland clinic offers Mayan interpreter for COVID-19 vaccinations
Oakland clinic offers Mayan interpreter for COVID-19 vaccinations La Clinica de La Raza is targeting Latin Mam or Mayan-speaking community with translation service Thursdays OAKLAND — A new COVID-19 vaccination clinic in the Fruitvale neighborhood is offering interpreter services for the Latin Mam or Mayan-speaking community. This month, La Clinica de La Raza began offering the community-targeted vaccination service at 32 locations across the Bay Area, including ASCEND Elementary School on East 12th Street, where Latinos who speak Mam, K’iche ‘and Q’eqchi’ can get translation help from appointment to inoculation on Thursdays. There are over 22 different Mam dialects spoken primarily by people of Guatemalan and Mexican descent. According to a recent UC San Francisco study, Mayan people with Guatemalan roots are the fastest-growing ethnic group in Oakland. “I’m here to support my community, getting them the service that they deserve,” Brenda Sucely Perez, the on-site interpreter at ASCEND, said last week while about 450 eligible people were vaccinated. Staff at the Fruitvale site have administered roughly 2,000 Moderna vaccines per week since opening on March 4, according to La Clinica officials. Salvador Garcia, an Oakland firefighter, volunteered at the vaccination clinic. “Coming to get the vaccination is a good thing because it would help prevent the spread,” Garcia said, adding that it’s especially important given how close relatives in the Latino community live. “When you’re around people in such tight quarters around here, the way the families live with each other, it’s just good to have the preventative measure of the vaccination.” It’s also one of the reasons the nation’s first and strictest stay-at-home orders proved ill-suited for the hard-hit Latino community, a four-month Bay Area News Group investigation found. That analysis showed case rates for the region’s Latino residents are nearly four times higher than White residents, while the Latino population has fared worse against the virus across California. During the fall case surge, economic pressure to keep working outside the home became another major factor in the Latino community’s higher COVID-19 positivity rate in the Fruitvale neighborhood than the rest of the state, according to a UCSF study conducted in September. The results of that study found that antibody-positive prevalence was 9.8% overall among people who live and work in Fruitvale, a predominantly Latino neighborhood. The number spiked to 26.8% among the Latin Mam, or Mayan, speaking community, USCF [sic] researchers noted. The COVID-antibody test shows that someone once had coronavirus. -
 2021-05-28
2021-05-28Alaska face mask sign in rural arctic camp
Cute face mask sign on front of arctic store on the Yukon river in Alaska. -
 2021-05-28
2021-05-28Yukon Social distancing graphic
Found in entrance of remote camp on the Yukon river in Alaska. -
 2021-04-28
2021-04-28Allison Oskar Oral History, 2021/04/28
This oral history focused on how smaller communities tackled the COVID-19 pandemic. The interview discusses how hospitals tackled the pandemic, and it goes into depth about what it was like to work for a hospital during this time. Also discussed were the ways in which the pandemic affected mental health and how it proved to be beneficial in some ways. There was a large focus on the ways in which COVID-19 affected the 'work life' balance of the interviewee. -
 2021-05-02
2021-05-02Charlotte Botenhagen Oral History, 2021/05/02
This was an interview from Jennifer Botenhagen who is a preschool teacher living in a tiny mountain town. This interview details her experience adapting to teaching during the COVID-19 pandemic. -
 2021-04-07
2021-04-07Indigenous Peoples and Vaccines
“The coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic poses a grave health threat to Indigenous peoples around the world. Indigenous communities already experience poor access to healthcare, significantly higher rates of communicable and non-communicable diseases, lack of access to essential services, sanitation, and other key preventive measures, such as clean water, soap, disinfectant, etc.” -
 2021-04-13
2021-04-13Tribes of north-central Montana pause use of Johnson and Johnson vaccine under recommendation by CDC and FDA
"Native American tribes in north-central Montana are responding to today's CDC and FDA recommendations that the Johnson & Johnson COVID vaccine temporarily stop being used. The reason for the "pause" is because it has been linked to blood clots in at least six people out of the more than 6.8 million who have received that version of the vaccine." Tribes including Little Shell Tribe, Rocky Boy Reservation, and The Blackfeet Tribe are coordinating with providers and pausing use of the Johnson and Johnson vaccine. -
 2021-04-21
2021-04-21James Rayroux's JOTPY Portfolio
--Reflections on the Pandemic Archive-- Looking back over my experience with the “Journal of the Plague Year” COVID-19 archive, my prevailing emotion is gratitude. This opportunity granted me experience that few historians earn, and the remote, asynchronous work schedule allowed me to collaborate with my colleagues in ways that maximized our respective contributions. The breadth and depth of our individual experiences and perspectives tremendously improved our collective process and products. I spent enough time in the Arizona State Archives last year to recognize such collections as historical treasure chests, but I have now participated in processing an archive’s content and navigating the ethical dilemmas those submissions sometimes create. Archivists and curators are the history profession’s truly unsung heroes, and their work facilitates society’s perception of itself. My background in police work and public safety drew me to the archive’s existing Law Enforcement collection. In taking on that subset, I succeeded in reshaping the collection’s parameters to now include stories about police and law enforcement. I wanted to diversify the collection to encompass perspective of both the police and the public with whom they interact and serve. While some overlap exists between the Law Enforcement and Social Justice collections, each remains distinct. Through my contacts and writing, I promoted a Call for Submissions to an international audience of law enforcement professionals to reduce their relative silence within the archive. Within the archive’s content, I recognized that one’s location might shape their pandemic experience, and I created and designed an Arizona-based exhibit to explore that. Further research and discussion with my mentors and colleagues ensured the exhibit illustrated these differences without excluding visitors whose diverse experiences could further enrich the archived and exhibited content. I am proud of my “Arizona’s COVID-19 Pandemics” exhibit, particularly because of its compressed, one-month incubation period. Beyond displaying images, data, and stories representative of the diverse pandemic experiences within the state, the ACP exhibit offers visitors numerous levels of interaction and engagement to became active participants and create their own exhibit experience. Visitors can complete opinion surveys, add a story to the archive, explore additional content related to the displayed pieces, view ever-changing results from pre-defined archival content searches, conduct their own archival search, view collective visitor survey results, and apply to join the staff. The exhibit’s searches will include the archive’s future submissions, which reshapes both the exhibit and the experience visitors may have with it. A more detailed explanation of my ACP exhibit may be reviewed here: https://covid-19archive.org/s/archive/item/43037 Because of Dr. Kathleen Kole de Peralta and Dr. Mark Tebeau, I stand prepared to join research, curation, and exhibition teams and immediately contribute to their work products. Despite my gratitude for this experience and the opportunities it presented, I look forward to the day COVID-19 is no longer part of humanity’s daily vernacular. James Rayroux 22 April 2021 -
 2021-04-20
2021-04-20JOTPY Exhibit: "Arizona's COVID-19 Pandemics" by James Rayroux
While working as a curatorial intern on ASU's 'A Journal of the Plague Year' COVID-19 archive, I created this exhibit on the pandemic experience within the state. In addition to obvious, overarching realities such as socioeconomic status and immediate access to healthcare systems, I initially believed one of the greatest deciding factors that determined one's experience in Arizona was an individual's residence in either predominantly urban or rural environments. The proposed exhibit had been originally titled "A Tale of Two Arizonas" to pay respect to Charles Dickens and the differing realities experienced here. To test my proposed hypothesis, I went about finding data, stories, and submissions that substantiated or disputed my premise. Within a short time, I had identified four distinct environmental drivers of personal pandemic experiences; to me, that indicated the existence of many more I hadn't yet found or had overlooked along the way. My evidence suggested a minimum of four pandemic locales: Urban, Rural, Border, and Tribal within the State of Arizona and its fifteen counties. The recorded health data and personal experiences demonstrated the naivete of my initial hypothesis, and I retitled the exhibit: "Arizona's COVID-19 Pandemics." The Exhibit Background section illustrates the vast dichotomies within Arizona in terms of population density and access to healthcare facilities. Given the virus's respiratory nature, these factors seemed especially relevant to driving diverse local experiences. I chose to include a flyer from the Coconino County Health and Human Services' "Face It! Masks Save Lives" campaign. The flyer included a specific line to "Stay Home When Sick" that seemed to illustrate a different public health paradigm than the broader "stay home" orders from Maricopa and Pima county. This section also features an image of Sedona's red rocks and a portion of The Wave to remind visitors of the wide-open rural areas accessible to all, as well as those with cultural significance to the Native American tribes and limited access to the general public. The next section asks a short, five-question survey in which visitors may participate. The Silver Linings piece features a short audio clip of a father and husband discussing some unexpected benefits of the pandemic. Visitors may explore additional Silver Linings stories and submit their own experience. The Tséhootsooí Medical Center piece seeks to illustrate the different pandemic experience on the state's tribal lands. I hoped to inspire some relevant emotional turmoil for the visitors through the piece's visual presentation. I wanted to create a series of waves with quotes from the medical center's healthcare workers. I hoped visitors' attention would be drawn to the large, bolded key words, and that they would first experience the segments out of sequence because of that. After potentially feeling a sense of chaos, they might settle themselves into a deliberate reading of the texts and find their own order within the experiences provided here. This piece allows further exploration of Native submissions and topics, a review of an additional related news article, and a submission prompt that invites visitors to offer guidance to hospital managers. The next piece illustrates the differences between mask mandates in communities across Arizona. In addition to hearing an audio clip of interviews with mayors and a public health official, visitors can explore additional submissions related to mask mandates and submit their thoughts on statewide mandates. The Arizona Department of Health Services provides zip-code specific infection data on its website, and the wide array of known case infections therein further illustrates potential dichotomies across the state. In working to include and represent this data in a consumable way, I encountered inconsistencies with tribal data. The nation's Indian tribes are overseen by Indian Health Services, a federal public health agency, and it does not collect or report data in the same manner as the State of Arizona or its counties. At first glance, the data would seem to suggest that tribal areas had less severe pandemic experiences than the rural and urban areas, which was not objectively true. I wanted to offer the unedited data to visitors, allow them to drawn their own conclusions, and invite them to offer their thoughts on what potential misunderstandings might emanate from these reporting differences. Visitors may also choose to review the foundational data from this piece, as well. I used the following two sections to offer submission prompts about the visitor's overall pandemic experience as a function of their location, as well as what they might have done if placed in charge of their city, county, or state during this pandemic. A diverse Search section allows visitors to explore additional topics of interest to them. 23 hyperlinks offer pre-defined search parameters. An Advanced Search link allows self-defined research, and a Join The Staff link connects visitors with opportunities to work within the JOTPY archive. A final section asks visitors to provide feedback on the exhibit, its content, and the pandemic in general. Both surveys within the exhibit will display overall results to visitors who participate in them. Through this process, I found incredible amounts and diversity of data outside the archive that spoke to these generally localized experiences, but not that much yet within the archive explained what Arizonans had experienced outside the state's urban environments. I created a call for submissions and delivered it to fifty rural entities that might help support the effort to collect and preserve more rural Arizona stories. Between all the local libraries, historical societies, museums, small-town mayors, and county health officials to whom I asked for help, I am optimistic the archive will better represent all Arizonans in the coming months and years. Despite the exhibit having been created, I ensured its internal search features would include future submissions and allow the exhibit to remain relevant long after its release. -
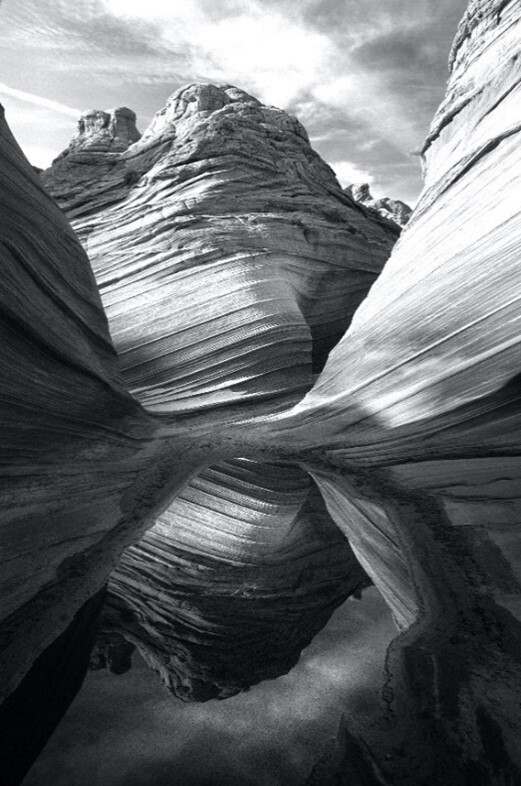 2021-04-20
2021-04-20Images and Audio from "Arizona's COVID-19 Pandemics" Exhibit
During March and April 2021, I created an online exhibit from content within Arizona State University's "A Journal of the Plague Year" COVID-19 archive. Entitled "Arizona's COVID-19 Pandemics," the digital exhibit contained images previously submitted to the archive, along with several copyright-free images I found on pexels.com. I have attached all these images. Listed by their order of appearance within the exhibit, their sources are as follows: 1- "Face It" Campaign flyer: Coconino County Health & Human Services ( https://covid-19archive.org/s/archive/item/42998 ) 2- Red Rocks, Sedona: Courtesy of Gregory Whitcoe via Pexels.com 3- Online Learning: Courtesy of August de Richelieu via Pexels.com 4- Tséhootsooí Medical Center staff: Courtesy of FDIHB Marketing Department and Navajo Times newspaper ( https://covid-19archive.org/s/archive/item/41189 ) 5- Arizona's Mask Mandate Map: created by Sarandon Raboin ( https://covid-19archive.org/s/archive/item/26267 ) 6- Arizona COVID-19 Infection Zip Code Map: Courtesy of Arizona Department of Health Services ( https://covid-19archive.org/s/archive/item/42035 ) 7- Woman Shopping: Courtesy of Anna Shvets via Pexels.com 8- Woman on Rural Arizona Road: Courtesy of Taryn Elliot via Pexels.com 9- Masked Woman in Crowd: Courtesy of Redrecords via Pexels.com 10- The Wave: Courtesy of Flickr via Pexels.com (this image is found only in the PDF submission of the exhibit, not in the public-facing exhibit itself due to document formatting technicalities - the PDF version can be found at https://covid-19archive.org/s/archive/item/42998 ) -
 2021-04-14
2021-04-14News Article: Navajo Nation reports no COVID-19 deaths for 3rd day in row
Despite very grim months through the last year's COVID-19 pandemic in the Navajo Nation, the Associated Press reported continuing indications of success for the Navajo people and their rural communities: WINDOW ROCK, Ariz. (AP) — The Navajo Nation on Tuesday reported two new confirmed COVID-19 cases, but no additional deaths for the third consecutive day. The latest numbers brought the pandemic totals on the tribe’s reservation to 30,269 cases and 1,262 known deaths. Tribal officials had ordered a lockdown last weekend over fears that a new variant could drive another deadly surge. The Stay-At-Home order required all Navajo Nation residents to refrain from unnecessary travel to help limit the spread of the virus, including a new and more contagious strain. Navajo Nation President Jonathan Nez recently announced the first confirmed case of the COVID-19 B.1.429 variant on the reservation that covers parts of Arizona, New Mexico and Utah. -
 2021-03-05
2021-03-05News Article: Gila County's COVID-19 efforts lead more urban counties
"By Christopher Brito, March 5, 2021, CBSnews.com While a majority of states and cities are still vaccinating higher priority groups of people, one county in Arizona is now allowing any resident over the age of 18 to receive the COVID-19 vaccine. Gila County, which is located east of Phoenix, entered Phase 2 of their vaccine prioritization late last month, opening up eligibility to the general population. Part of the the decision to open vaccine eligibility is because Gila County has one of the lowest percentages of COVID-19 vaccine doses used in Arizona. Michael O'Driscoll, director of Public Health and Emergency Management for the county, told CBS affiliate KPHO-TV that they received permission from the state last week to offer the vaccine in a drive-thru clinic last weekend. "Prior to that, we were struggling to find enough people to make appointments to that, so the state gave me permission to offer it to any resident 18 and older," he said. About 56,000 people reside in the county. According to the Arizona's Department of Health Services, more than 13,000 people – or almost one fourth of residents – have received at least one dose of the COVID-19 vaccine. "We did a survey before to get a sense of how many people in Gila County would consider getting the vaccine, and our survey came back about 50-60% of the residents would choose to get the vaccine if available," O'Driscoll said. Based on the data, over 5,600 people under the age of 65 have received the vaccine, including 73 people under the age of 20. One of the younger recipients, 18-year-old Jacob Jost, told KPHO-TV that he was "excited" to get the shot. "I have a little nephew, a little baby, so having the vaccine puts a peace of mind for that," Jost said. First published on March 5, 2021 / 12:13 PM © 2021 CBS Interactive Inc. All Rights Reserved. Christopher Brito is a social media producer and trending writer for CBS News, focusing on sports and stories that involve issues of race and culture. -
 2021-03-22
2021-03-22Apache County (AZ) Library COVID-19 Guidelines after March 22, 2021
This copyright-free image of a public-facing government webpage displays the COVID-19 protocols in place at Apache County (AZ) library locations after Governor Doug Ducey ordered local governments to phase out public health mandates on March 22, 2021. Unlike urban areas within the state, rural Apache County in northeastern Arizona no longer required mask use inside private or government (public) buildings and facilities. -
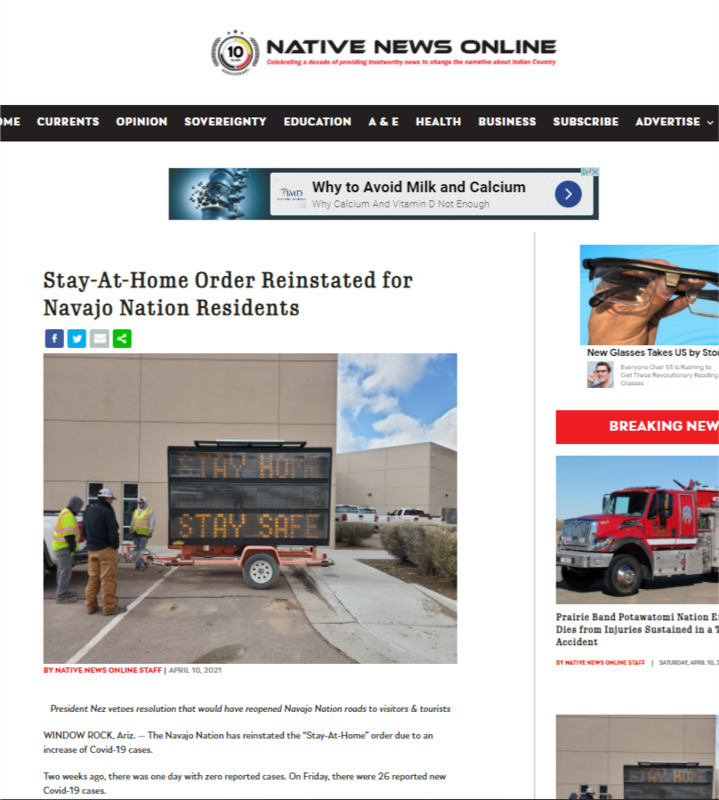 2021-04-10
2021-04-10Stay-At-Home Order Reinstated for Navajo Nation Residents
The Navajo Nation has reinstated the “Stay-At-Home” order due to an increase of Covid-19 cases. Two weeks ago, there was one day with zero reported cases. On Friday, there were 26 reported new Covid-19 cases. -
 2021-04-07
2021-04-07Indian Health Services COVID-19 Infections by Service Area through 04/07/2021
Indian Health Services is an agency of the United States federal government that oversees and administers healthcare to that nation's Native American populations and tribal reservations. This webpage from the Indian Health Services has three sections that address general Coronavirus (COVID-19) information and links, COVID-19 Vaccine Distribution and Administration by IHS Area, and COVID-19 Cases by IHS Area. it also includes a hyperlink to an interactive map for up-to-date COVID-19 Cases by IHS Area: https://maps.ihs.gov/portal/apps/StoryMapBasic/index.html
