Items
Mediator is exactly
Vaccine Stories
-
 2020-07-07
2020-07-07Title: Navigating New Normals: Embracing Vaccination for Access in Brooklyn
This shows my point of view and experience to the pandemic -
2022-02-26
My Personal Experience with COVID-19
It was Christmas of 2020, and my eighty-four-year-old Dad was really sick. Up until then he had been healthy. He worked out at the gym every day and always went for coffee at Starbucks afterwards. I call him every day, and I could tell he was under the weather, but he didn’t want to admit he had COVID-19. He was sick for several weeks but came over on Christmas Eve to have dinner with our family. I remember being slightly irritated that he did come over because we could have brought him dinner at his house and minimized exposure to everyone else. Fortunately, our family and my sister’s family did not catch it that year. Oddly enough, we wouldn’t catch it until the following year. I remember being sort of surprised that we didn’t catch it because everyone around us had it. When the gyms and restaurants and grocery stores all closed, I would walk around our subdivision everyday to continue my exercise routine and I noticed I was tired and had shortness of breath. I remember going in for my annual physical with a face mask on and telling my doctor my symptoms. I remember him saying that those symptoms were too early to be COVID-19 and was probably a milder version of the flu. I was doubtful due to being heavily exposed by my dad, as well as so many others who had no idea they had it but were technically “super-spreaders.” My sister’s family and our family caught Covid within a week or two of each other despite not having any contact and being vaccinated the prior year. My husband and I both opted for the Johnson& Johnson vaccination because it was traditional with just the one shot. Our friend, who worked with my husband also got the same vaccination. My husband and I were sick after the shot, but we knew from friends that we would be. It lasted maybe a night and then we felt better the next day. Our friend wound up in the hospital after her vaccination with a small intestinal blockage which she blamed on the shot. She stayed in the hospital for about a week, but other than some follow-up monitoring, she is ok. Shortly after that, we read in the news that several women had died from embolisms after receiving the vaccination. Our daughter, who has special needs, sees many doctors and I remember telling him that I just gotten vaccinated and now there was this complication. He was very reassuring and said that the women who had passed away probably had a serious and pre-existing condition. He told me to stay active for the next week or two and drink lots of water which I did, but it was the longest two weeks until we were cleared from the risk. We did end up catching Covid in February-March 2022. It had been a normal week. I went to the store, gym, did carpool, walked the greenway, but I felt slightly off all week long. I remember coming home and making dinner, but I was exhausted and told my husband that I was unable to have dinner with everyone that evening. Sure enough, I was running a low fever. I took an at-home COVID test, and my results showed I was positive within a few seconds. I immediately quarantined in our bedroom for the next several days. My husband caught it about a week later, but his symptoms were different than mine. He had a bad sore throat and was cold and shivering for a couple of days, and had a cough that lingered. Our daughter, who has severe Cerebral Palsy, caught it next but thankfully she only had mild symptoms for two days and recovered almost immediately. Our son caught it last, and he had a very bad sore throat for a week. We made it through, and consider ourselves fortunate that we recovered without long-term issues. -
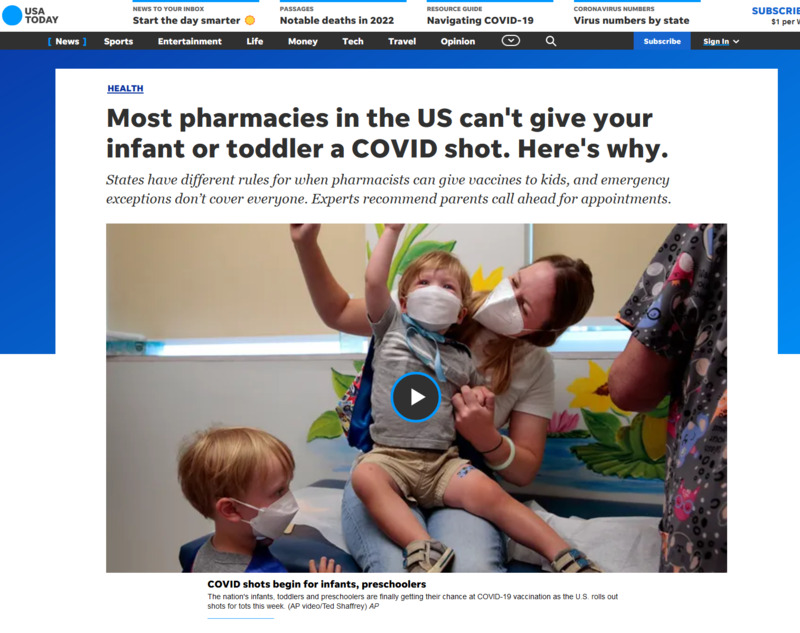 2022-06-23
2022-06-23Most pharmacies in the US can't give your infant or toddler a COVID shot. Here's why
This is a news story from USA Today by Adrianna Rodriguez. Most US pharmacies don't allow their technicians to administer the vaccine to children under five. The age in which the vaccines can be ministered to younger kids varies, with most putting a minimum of five or above. A lot of the reason administering vaccines has been restricted, according to the article, is because not enough pharmacists are trained to give shots to children that young. The overall target is smaller, and the needle even shorter, in addition to needing to calm and anxious child. This makes people hesitant to give young kids the COVID vaccine. It is recommended that if you cannot find a pharmacy that will give the shot to very young kids that you ask your pediatrician for a one-on-one appointment for the vaccine. -
 2022-06-08
2022-06-08Moderna says updated Covid-19 vaccine booster shows stronger antibody response against Omicron
This is a news story from CNN by Jamie Gumbrecht. Moderna believes that their COVID-19 booster is effective against Ominicron, and more effective compared to the normal two doses. The claim is that the booster provided a stronger antibody response than the initial two doses. -
 2022-06-09
2022-06-09Biden administration lays out its plan for Covid-19 vaccinations for children under 5
This is a news story from CNN by Donald Judd and Betsy Klein. The Biden administration has announced a vaccine rollout for children five and under. The vaccinations are to start as early as the week of June 20. -
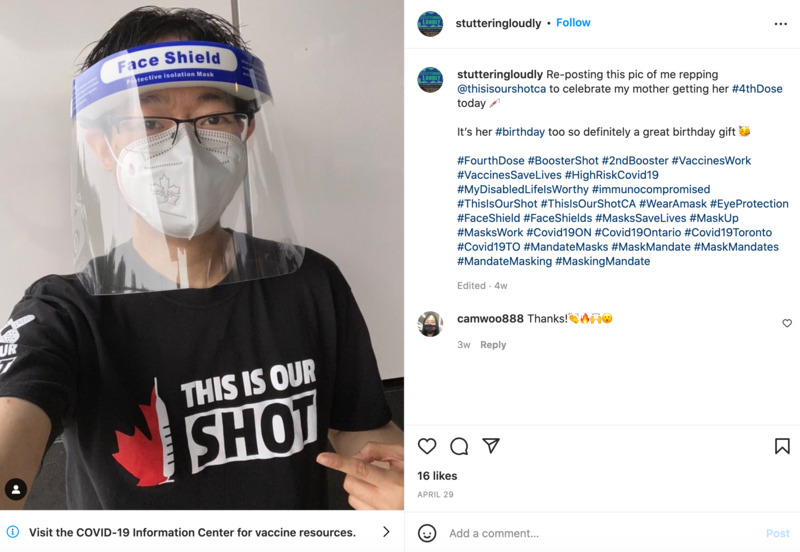 2022-04-29
2022-04-29This is our shot
This is an Instagram post by stutteringloudly. This person is celebrating his mom getting her fourth dose. -
 2022-05-10
2022-05-10High Rates of COVID Vaccination Among Adults With Autism
This is a news story from Health Day. Adults with autism have been shown to have higher rates of vaccination according to a new study. Those with autism are more at-risk for severe illness if they contract the disease, say researchers. To get the data, researchers sent online surveys to 431 autistic adults in Pennsylvania. They showed that about 78% of survey respondents said they had received or intended to get a COVID-19 vaccine, and more than 55% said that they had received at least one dose. In comparison, 42% of the overall adult population in Pennsylvania had received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine as of the median response date for the survey (April 2, 2021), according to the study. The findings were published in the journal Vaccine. -
 2022-05-05
2022-05-05FDA to create training program to inspect more mRNA vaccine manufacturing
This is a news story from Endpoints News by Josh Sullivan. With new faith being poured into mRNA vaccines, a new training program is being developed to help with the manufacturing process. This program will entail learning the application of mRNA vaccines, as well as laboratory training. BioNTech, Pfizer’s partner in its Covid-19 vaccine efforts, recently revealed that it is paying Matinas BioPharma to gain exclusive access to its lipid nanocrystal drug delivery platform for the oral delivery of mRNA. It also was one of the first companies to announce plans for the massive mRNA manufacturing sites that are being built. BioNTech plans to piggyback off the success of the technology by pivoting to work on malaria vaccines once the Covid-19 pandemic has subsided. -
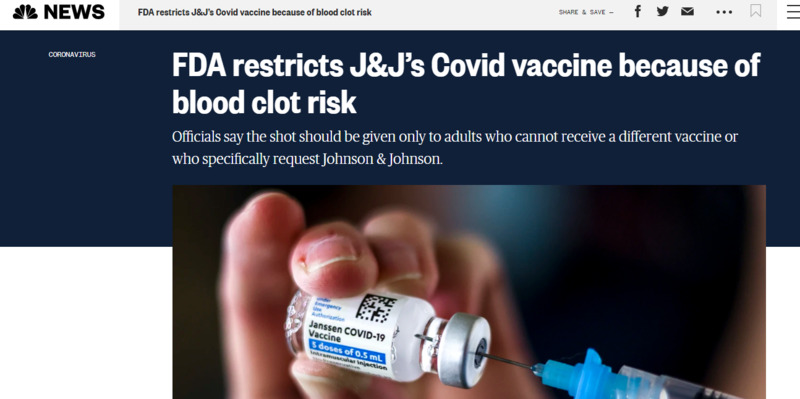 2022-05-05
2022-05-05FDA restricts J&J’s Covid vaccine due to blood clot risk
This is a news story from NBC News by The Associated Press. Due to new findings, the J&J vaccine has been restricted by the FDA due to blood clot risks. It is not to be given to anyone unless they can't receive a different vaccine. Americans are now recommended to only be using Pfizer or Moderna shots instead. -
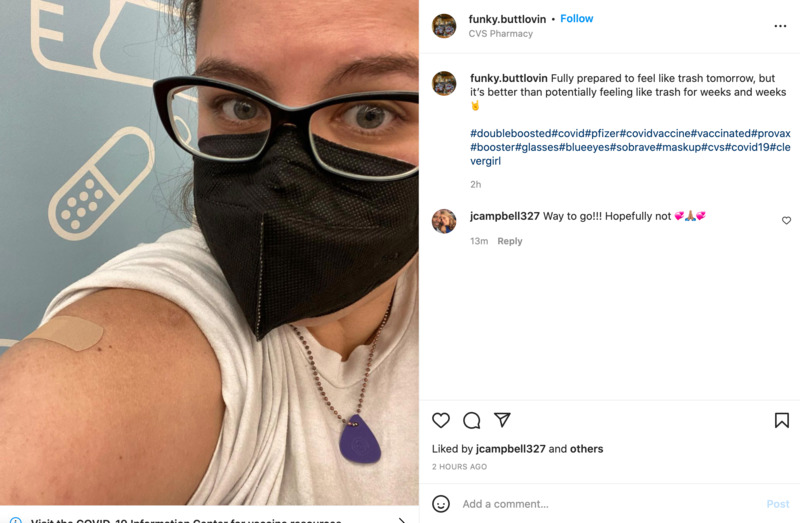 2022-04-29
2022-04-29Double Boosted
This is an Instagram post by funky.buttlovin. This person received their two extra doses of the COVID vaccine. People taking selfies has been a common trend on social media after having received a COVID vaccine. -
 2022-04-19
2022-04-19GB Oral History, 2022/04/19
The interviewee discusses vaccine hesitancy and life during the pandemic without having received the vaccine. -
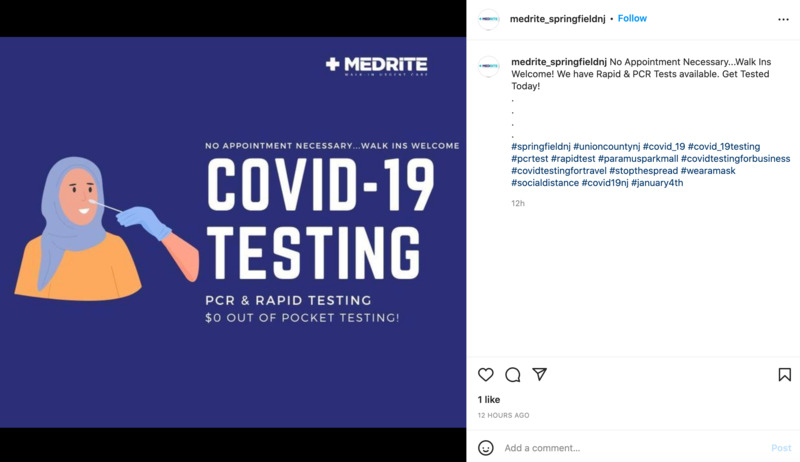 2022-04-11
2022-04-11COVID-19 Testing
This is an Instagram post by medrite_springfieldnj. This is a PSA welcoming people to get free COVID testing. It says that no appointments necessary and walk-ins are welcome. Since the start of the pandemic, rapid testing and PCR tests have become more available and free of charge in many places. The reason many of these are free is due to state and federal governments subsidizing the costs of the tests, in addition to people volunteering to help them get done. -
 2022-04-11
2022-04-11New Year, New Dreams
This is an Instagram post by ankletzdreams. This is a post of a woman who has received her Pfizer booster shot. From the hashtags and the post, she seems fairly content with it. -
 2022-03-13
2022-03-13Pfizer CEO says fourth COVID-19 shot 'necessary' due to waning immunity
This is an Instagram post by the New York Post. This is of a news story in circulation currently regarding vaccines. Below, there are commenters expressing doubts in the effectiveness in the vaccines. Of note, one commenter says that they have already been vaccinated and boosted, but do not want anymore shots. Another is asking for it to stop already. To me, this shows some of the overall fatigue some are having with the vaccines themselves. -
 2022-04-06
2022-04-06Fully Vaccinated
This is an Instagram post by lynobtena. It shows a picture of a kid that had just received his second dose of Pfizer. There is a place for kids to get their picture taken after getting vaccinated, with cardboard cutouts of a Paw Patrol character and Iron Man. -
 2022-04-07
2022-04-07The First Dose
This is an Instagram post by haelmron. This shows a picture of a little kid that had just received their first Pfizer dose. It looks like a special place was set up for kids to get their picture taken after getting vaccinated. -
 2022-04-07
2022-04-07Segunda Dose
This is an Instagram post by brunaemirella. This post is in Portuguese. This is a picture of a little girl that just received her second Pfizer dose. -
 2022-04-07
2022-04-07Be a Vaccine Hero
This is an Instagram post by thehesbrooklyn. This is a post encouraging children to get vaccinated. This post has a link to the New York City government website on more information on COVID. The picture shows a little girl dressed as a super hero as part of the PSA. -
 2022-04-07
2022-04-07Vaccine drive for children in Peru
This is a video posted on Instagram by the Ministry of Health in Peru promoting the vaccination of children in Peru. On Sunday there will be an event at a public park where children can come and get the vaccine. -
 2022-04-06
2022-04-06Get Your Kids Vaccinated
This is an Instagram post by carlamaeperaltasalmoringfkfhdk. This picture shows a kid that just got their second dose of the Pfizer vaccine. The date says that the shot happened on April 6, 2022. -
 2022-04-06
2022-04-06Boosted
This is an Instagram post by sfhippy. This post is a selfie of someone who just got boosted with pfizer. Pfizer is one of the vaccines approved for boosters. The user used #safe, which I am going to guess that they believe the vaccine will make them safer than before. -
 2022-02-02
2022-02-02Engaged Couple Decide To Require All Wedding Guests To Be Vaccinated — Now Family Is Refusing To Comply
This is a news story from Your Tango by Dan O'Reilly. This is about a couple that required all family members attending their wedding to be vaccinated. The issue with this is that the family does not want to comply to those wishes. This story was originally found in r/wedding on Reddit. According to the bride, her fiancé's family was on board with imposing vaccines, but the bride's own family is 50% vaccinated, with the unvaccinated thinking this is a dumb idea. This has been part of a controversial issue on if vaccines should be imposed. Most of the Redditors had sympathies for the engaged couple and believe it is what was needed for a safe event. -
 2022-03-08
2022-03-08Florida Will Urge Parents Not To Vaccinate ‘Healthy’ Kids, Going Against CDC Advice
This is a news story from Scary Mommy, written by Lauren Levy. This story deals with Florida's position on vaccinating children and going against CDC guidelines. The author, Levy, is very against this and thinks it is irresponsible to be contrary to what the CDC suggests, claiming that it will make things more dangerous for kids if they don't take the vaccine. Some have been raising concerns that people are taking politicians words over those of doctors. Opponents have reminded parents that this is just a suggestion from Florida politicians, and not a mandate, meaning that they can discern for themselves if the vaccine is right for their kids. Ultimately, Levy believes parents should ignore what Florida politicians say and listen to doctors instead on what to do. -
 2022-03-30
2022-03-30Vaccination clinic in Callao
This Instagram posts shows that today, all day (8-5) people in Callao can head to the Centro de Salud Quendo to receive the COVID vaccine dose that they need. Children 5-11 can get their first or second dose and children 12-17 can get their 3rd dose 5 months after the second dose, and those over 18 can get their 3rd dose 3 months after the second one. The photo show s a bus that is carrying healthcare workers to the destination to help vaccinate the people there. -
 2022-03-30
2022-03-303rd dose is mandatory in Peru
This Instagram post from the ministry of Peru lets people know that they need to head to a vaccination center to receive their 3rd dose of the COVID-19 vaccine. A commenter asked what happens after April 1st? And someone responds that after April 1st it is obligatory for adults over 18 years old to have 3 COVID shots. -
 2022-03-27
2022-03-27Ambulatory vaccination crews
The ministry of Peru is launching efforts to vaccinate people living in rural regions. This Instagram post shows a crew of three people carrying coolers of vaccines to rural areas in Peru. -
 2021-01-28
2021-01-28Freezer Failure
January 28, 2021, around 11 PM one of my friends called me, we normally don’t talk on the phone so I assumed something was wrong. I could tell that she was driving and her voice was shaky. She told me that a freezer had failed at her mom’s work and that around 1,300 vaccines would be expired by 5 or 6 AM. She was told to try to get anyone she knew to get to the hospital in order to reduce the chance of wasting such a hard to get thing. This was prior to my state lifting restrictions on who was eligible for the vaccine yet. Not everyone could get it, just certain people due to age, pre-existing conditions, and career. The clinic did a good job at still trying to make sure that people who were eligible got to the front of the line, but they knew that they needed to make sure every vaccine was used. My girlfriend and I would not have made it there in time since we were over 3 hours away, but her family all lived within a 30-minute drive. We started calling her parents and brothers to wake them up and get moving. Her mother, oldest brother, and soon to be sister-in-law were all teachers and were going to have to start teaching in person again. None of them would have been eligible until a month or more after going back in person, and they were all decently nervous about being in person unvaccinated. Her family got lucky and was able to get vaccinated that night. I cannot thank my friend enough for calling me to keep the people who have become my family safe. -
 2020-08-28
2020-08-28A flier advertising free Covid-19 shots in Sacramento.
This event offered Pfizer and Johnson and Johnson vaccines, free Uber rides and Spanish and Hmong interpreters. The event was sponsored by the NCNW Sacramento Valley Section and La Familia Counseling Center. -
2021-10
The Division of Covid-19
Since the pandemic started life has definitely changed in plenty of ways, not just for me but for everyone. From the way we learn in school and work jobs to the way we interact in public and meet people. One thing covid brought that I saw prevalent in a few different aspects of my life was a new reason for division amongst people. This new reason for division is almost a political thing, where there are people that are nervous and scared that covid is harmful and then the people who do not care and believe covid is blown out of proportion. I see this division in things like media, politics, family, and friends. It makes a lot of things confusing for me because I never know which side to listen to. The crazy thing to see for me is how a pandemic can come around and cause so much separation. At a point it started to seem like it was the only thing I heard people talking about and it would drive me crazy. If I put on the news, it was always someone saying everyone needs masks, then I flip the channel and the next station is saying mask are bad and should not be on all day. Then it came to my family, my dad would tell me I needed all the vaccines and booster but my mom on the other hand told me to do whatever I wanted and did not care. Seeing all of this back a fourth throughout this time would frustrate me because it made making my mind up so difficult. This eventually even got to my friends, and I saw friends that would argue about whether people should get the booster or not, and I thought it was so ridiculous. The reason I bring up this point of division is because I believe it is interesting how everyone has reacted to covid. I also feel like it has made people feel the need to push their opinions and ideas onto other people, it is something I have seen first-hand in my life. Similar to the way Hitler or Stalin pushed their ideas on everyone, but on a very different level. Maybe one day people will just let each other choose for themselves. -
 2020-10-25
2020-10-25My Life with Covid 19
In 2020, The week of my 22th birthday I tested positive for covid-19. I had no signs that I had even feel sick or had covid. I tested three times before that due to my family friend having covid but I was not really in direct contact but wanted to test anyway. Negative all three time that day. I don't know why they tested me three times but whatever. When I was at home resting and trying to "do my time" I felt totally normal. It was like any other day to me. However, when I got my shots I when I had all the side effects and was out for a good two days at school. I felt like I was gonna die. I had to wait the two days out and nothing felt good to me,I could not get comfortable, and I was sore all over. It even felt like that when I got my booster. Overall, covid sucks! -
 04/25/2021
04/25/2021Lou Fraise Oral History, 2021/04/25
Dr. Lewis Fraise details his service as a geriatric doctor during the Korean War and Vietnam War. He mentions his service in both Washington D.C. and Korea and continues to break down how the Coronavirus actually infects one's body and the response of the government as the pandemic ensued. Dr. Fraise criticizes the actions of Donald Trump and states that the spread of more medically-accurate information would have led to a better outcome in terms of the early stages of the pandemic. -
 05/03/2021
05/03/2021Kyle Sauley Oral History, 2021/05/03
-
 05/12/2021
05/12/2021Katherine Running Oral History, 2021/04/22
Katherine Running was raised in Eau Claire, Wisconsin. She currently resides in Fargo, North Dakota. She is currently occupied as a graduate student and a lab researcher at the USDA in Fargo. In this interview, Ms. Running talks about how the covid-19 pandemic has affected her professional and personal life. She also discusses how people have stopped trusting science and facts. -
 04/27/2021
04/27/2021Jody Pabich Oral History, 2021/04/27
Jody Pabich lives in Chippewa Falls, Wisconsin, and works as a senior safety manager at the corporate office of a nationwide big box retailer. Jody directly handled all of the COVID-19 protocols for her company across the country, and talks about how counties, states, and the country have been handling the pandemic differently. She explains how her family and friends have dealt with COVID-19, addressing health concerns about her daughter, mental health concerns about her friends, and the politics and distrust of media. She describes how her community has come together to support each other and local businesses. She also discusses her experience with and concerns about the vaccines. She talks about how her experiences have made her value life and experience more than she did before COVID-19. -
 2021-12-06
2021-12-06Amberley L. and Elsa Hanson Oral History, 2021/12/06
Elsa Hanson and Amberley L. interview each other about how they think COVID-19 compares to past pandemics. They also discuss how the public has dealt with the pandemic if there will be long term effects of the pandemic, and what precautions they have been taking. -
 2021-10-01
2021-10-01My Breakthrough COVID-19 Case
October 1, 2021, I woke up with a mild headache and a stuffy nose. I didn't think much of it—I had started drinking coffee again and needed a cup, and I’m mildly allergic to my own cats. My headache went away after I had my coffee, and my congestion ceased after I took my Claritin. After working remotely and basically not socializing for all of 2020 and up through August 2021, I was happy to be out and doing things again. In August, I started working and attending class in-person again, as well as spending time with friends. I still masked up and washed my hands according to guidelines, but it did seem like standards for that were slipping. I take public transit most days, and I’d seen a number of people who either weren’t wearing masks or not wearing them properly. But I still thought I was fairly safe since I followed COVID-19 recommendations, was fully vaccinated, and my campus has an extremely high vaccination rate (100% of students are vaccinated or have exemptions, and 98% of faculty/staff). So when I woke up experiencing what I thought were symptoms of seasonal allergies, I didn’t think anything of it. I went on a date that afternoon, and then out for drinks with friends later that night. I was very tired when I went home that night, but I chalked it up to how I’d over-committed myself in the initial euphoria of being able to participate in things again. Besides, I was sleeping better than I’d slept in years. The next day, my congestion was worse and I was coughing. I had an intermittent headache, but I assumed it was just a cold. One of my classmates that I sit next to had had one recently, and she’d tested negative for COVID, so I just assumed I’d picked it up from her. I remained congested and feeling gross that weekend, enough to call out from my shift on Sunday out of an abundance of caution, but I figured I’d be ready to be back by the time I had class and work again on Wednesday. But Monday afternoon I was working on some of my reading and realized I couldn’t smell the new (and very strong) candle in my living room. To test whether it was just the candle or whether it was me, I sniffed my perfume and finally even put peppermint essential oil right under my nose, and...nothing. Figuring that it was likely I had COVID at this point, I scheduled a test for the next day. I felt bad about having to get there—was it better to take an Uber or a train/bus? Which was safer for everyone involved? I ended up taking a Lyft, but I left the windows down and made sure I had cough drops so I wouldn’t cough. Once I arrived at the testing center (where I was the only patient), they got me through quickly and told me they’d be doing PCR testing and I could expect my results within a couple days. I called out of work for the week and let my professors know I likely had it. I woke up on Thursday morning to see my results had arrived, and I had tested positive. I called my school for contact tracing, and they notified the classmates I sit next to and my coworkers. I texted my friends I’d been out with Friday night and the person I went out with, and it was strange to feel almost ashamed. I had behaved responsibly, but I still felt as though I’d done something wrong in contracting COVID. And I was exhausted, tired of coughing, and just wanted my mom. I continued to improve, and I felt mostly better by the time my isolation period ended on the 11th. My sense of smell had started to come back, so I wasn’t as worried about a permanent loss there. I was a little concerned by the disregard for no-contact delivery I’d requested when getting food/groceries, but it had mostly been okay. My shifts at work had been given away, even though I was better and out of isolation by then. On the bright side, my cats were thrilled to have had me home that much, so at least it was a good experience for someone. Everyone I notified directly or via contact tracing tested negative, fortunately. When I started going back to things, I just wanted to scream on the train when I saw people not wearing masks or wearing them improperly. I still do, especially as the number of cases rises. -
 2021-05-25
2021-05-25Breakthrough COVID-19 cases possible but rarity shows vaccine effectiveness
This graphic shows the rates of infection and hospitalization for breakthrough infections for COVID-19 among vaccinated people (as of May 2021) -
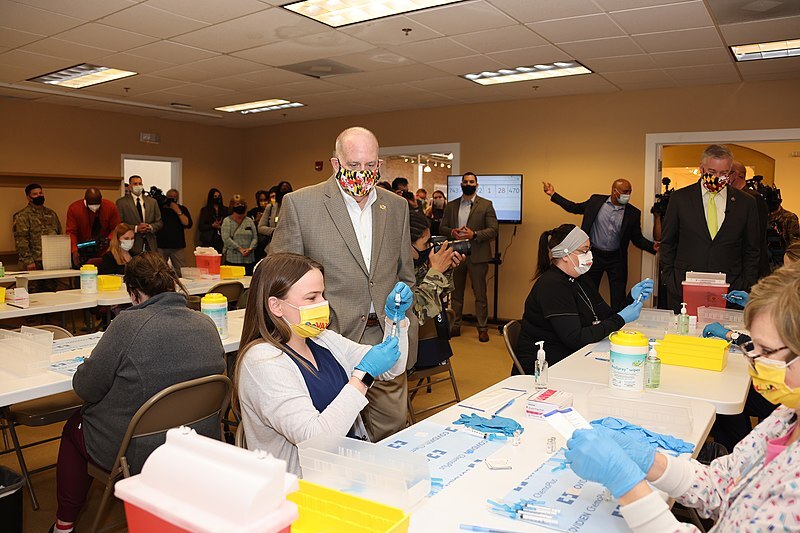 2021-03-26
2021-03-26Hagerstown Mass Vaccination Site
This photo shows a number of people at a mass vaccination event. -
 2021-03-26
2021-03-26Participating in a Mass Vaccination Event
I was excited to get my vaccine as soon as the FDA approved the Pfizer vaccine. However, as a fairly healthy person who worked remotely, I was by no means going to be the first wave of vaccination. Truthfully, I thought I wouldn’t have a chance to get vaccinated until June or so, and I resigned myself to staying inside. In early March, I got an email from my school—the United Center was hosting a mass vaccination event, and they had more doses than the original target groups could use. I hurried to sign up. It filled quickly; I had a few friends tell me they were unable to get in. I was lucky, and I went to get my first dose near the end of March. Supposedly, Uber was offering free rides to/from the United Center (up to a certain amount, at least) for those seeking to get vaccinated. However, I kept getting error messages, so I made my way there by other methods. I panicked since I was almost late to my appointment for the first dose, but my worries faded when I arrived. The clinic volunteers kept the roped off lines going quickly and smoothly, though everyone was kept at least six feet apart. Once you’d been fully signed in—you showed your ID, your appointment voucher, got your temperature taken, and were issued an information packet—you waited to be sent to one of the FEMA people doing the vaccinating. I was called and got my first dose over with quickly and without any fuss, and then I was sent off to the tent where you waited to make sure you didn’t have any adverse side effects within the first 20 minutes. I was fine, so I went home with my vaccination card and instructions to return in 3 weeks. I returned 3 weeks later (in mid-April), and it went even more smoothly! They had worked out even more kinks, and everyone seemed relieved. While I’d been tired and a little sick a couple days after the first dose, the second one presented no problems. Later, I learned that a few of my friends were not only also part of the United Center mass vaccination event, but were there on the same days! I didn’t see them, but I’m not surprised given the efficiency of the process. Over the summer, the United Center’s vaccination program closed after it slowed significantly. So while I will be getting my booster shot soon, it won’t be as part of a mass vaccination endeavor. I’m a little reticent, simply because I don’t know what to expect from going to a pharmacy for it! -
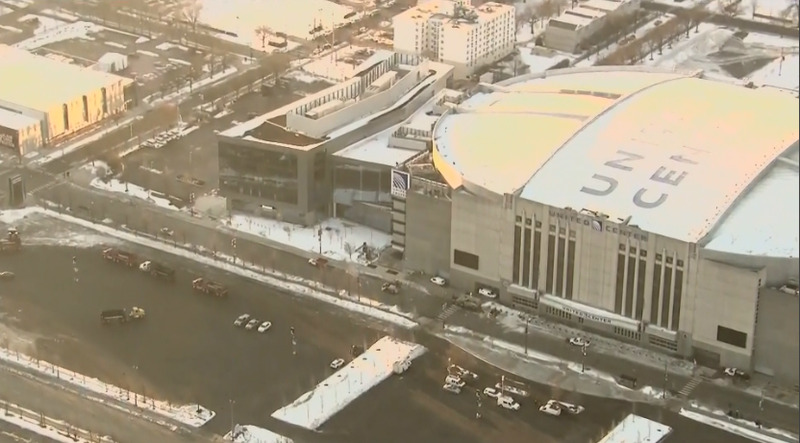 2021-02-26
2021-02-26Illinois to open federal mass vaccination site at United Center
Parking lots of the United Center will soon host a new mass vaccination site for Illinoisans. Gov. JB Pritzker says the site will have the capacity to give 6,000 doses of vaccine per day. The home of the Chicago Bulls and Blackhawks will open as a vaccination site on March 10. But, construction is already underway. This will be one of the several community vaccination centers led by the Biden administration. Doses will come directly from the federal government instead of taking vaccine away from the allotment for the state and the city of Chicago. Leaders explained seniors will have exclusive access to appointments before the site officially opens. However, FEMA hasn’t set dates for those appointments at this time. Reporters asked how Pritzker could guarantee this facility would create easier access for those in need compared to wealthy Chicagoans. “In the city of Chicago, in Cook County, and across the state, we’ve all made and are continuing to make efforts to attract people of color to people who are most vulnerable to making those appointments, giving them access wherever we can. Having a site in a location like the United Center makes it more easily accessible,” Pritzker emphasized. Chicago Mayor Lori Lightfoot said rideshare service Uber will provide 20,000 free rides to help people get to the site. Information about scheduling appointments for vaccinations should become available in the coming days. “With this new site, we’ll now be able to take our vaccination success to a whole new level and bring to bear the historic and inclusive recovery that is soon to come,” Lightfoot explained. Getting Black and brown residents vaccinated Still, the state has a significant issue getting Black and Latinx Illinoisans vaccinated. U.S. Sen. Dick Durbin explained a recent study showed minority neighborhoods in Chicago had a vaccination rate of 5%. The majority-white areas of Chicago currently report 13% of the population vaccinated. Durbin says the United Center site should help. “The faster we can get people vaccinated, the more quickly we can escape the grip that this pandemic has had on our nation for so long, the less likely we’re gonna see mutations and variations which we have to fight in different ways,” Durbin added. The Springfield native said the federal government could provide more help with vaccine distribution bypassing the American Rescue Plan. President Joe Biden has asked Congress to approve the $1.9 trillion package with specific portions going to mass vaccination sites and $1,400 stimulus checks. Pritzker noted things are getting better in the long battle with COVID-19. “Someday not too far from now, we’ll be at the United Center not for a life-saving shot, but for a game-winning shot,” Pritzker said. -
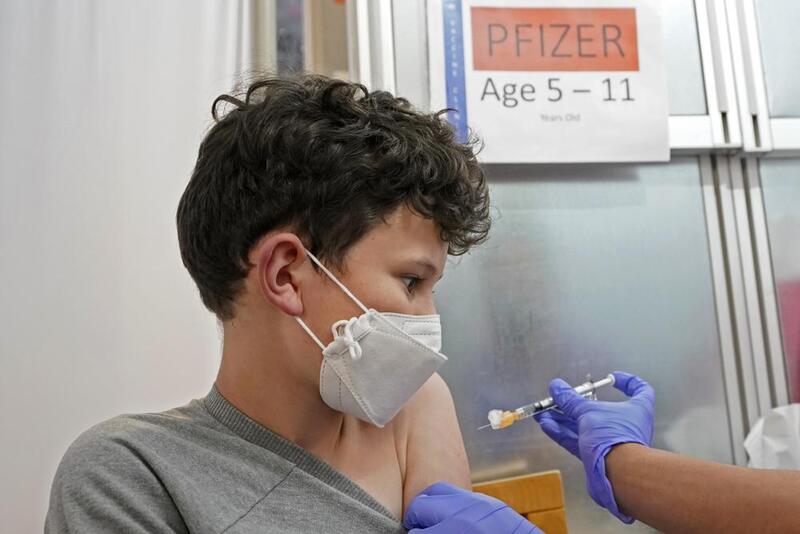 2021-11-10
2021-11-10Children Ages 5-11 Now Eligible for Vaccine
The campaign to vaccinate elementary school age children in the U.S. is off to a strong start, health officials said Wednesday, but experts say there are signs that it will be difficult to sustain the initial momentum. About 900,000 kids aged 5 to 11 will have received their first dose of the COVID-19 vaccine in their first week of eligibility, the White House said, providing the first glimpse at the pace of the school-aged vaccination campaign. “We’re off to a very strong start,” said White House COVID-19 coordinator Jeff Zients, during a briefing with reporters. Final clearance for the shots was granted by federal regulators on Nov. 2, with the first doses to kids beginning in some locations the following day. The estimated increase in vaccinations in elementary school age children appears similar to a jump seen in May, when adolescents ages 12 to 15 became eligible for shots. Now nearly 20,000 pharmacies, clinics and physicians’ offices are offering the doses to younger kids, and the Biden administration estimates that by the end of Wednesday more than 900,000 of the kid doses will have been given. On top of that, about 700,000 first-shot appointments are scheduled for the coming days. About 28 million 5 to 11 year-olds are now eligible for the low-dose Pfizer vaccine. Kids who get their first of two shots by the end of next week will be fully vaccinated by Christmas. The administration is encouraging schools to host vaccine clinics on site to make it even easier for kids to get shots. The White House is also asking schools to share information from “trusted messengers” like doctors and public health officials to combat misinformation around the vaccines. A initial surge in demand for vaccinations was expected from parents who have been waiting for the chance to protect their younger kids, especially before the holidays. About 3% of newly eligible children in the U.S. got first shots in the first week, but the rate of vaccinations in varied widely around the country, as it has for adult vaccines. California Health and Human Services Secretary Dr. Mark Ghaly said Wednesday that more than 110,000 Californians ages 5 to 11 have received their first coronavirus shot — 9% of kids that age in the state. “We are starting to see this pick up and I’m really encouraged about what this means for our state,” Ghaly said. On the other ends of the spectrum, Idaho reported just 2,257 first shots, or 1.3% of the newly eligible kids there. In West Virginia’s Cabell County, high demand led local health officials to start setting up vaccination clinics in all the county’s public middle schools. A spokeswoman for the county health department said there were some lines for vaccines in the first few days after the doses were approved for kids ages 5 to 11, but that things have slowed since then. Some experts say that nationally, demand could also begin to recede soon. They note polling data suggests only a fraction of parents have planned to get their kids shots immediately, and they suspect the trend will play out like it did earlier this year when kids ages 12 to 15 were first able to get shots. In the first week after vaccines for that age group were authorized in May, the number of adolescents getting a first shot jumped by roughly 900,000, according to an American Academy of Pediatrics review of federal data. The next week, it rose even further, to 1.6 million. “There was an initial burst,” said Shannon Stokley of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. But then the number dropped steadily for months, interrupted only briefly in early August as the delta variant surged and parents prepared to send children back to school. Adolescent vaccinations have since flagged considerably, to just 32,000 getting their first shots last week. Only about half of adolescents ages 12 to 17 are fully vaccinated, compared to 70% of adults. It’s unlikely that vaccination rates in young kids will be as high as what’s seen in adults — or even in adolescents, some experts said, unless they are required for school. Part of the reason is that adults are far more likely than children to suffer serious illness or die from COVID-19, they noted. “Parents may have the perception it may not be as serious in young children or they don’t transmit it,” said Stokley, the acting deputy director of the CDC’s Immunization Services Division. But more than 2 million COVID cases have been reported in U.S. children ages 5 to 11 since the pandemic started, including 66 deaths over the past year, according to CDC data. “We’re going to have a lot of work to do to communicate to parents about why it’s important to get children vaccinated,” she said. Zients said the effort to vaccinate younger kids is still ramping up, with new clinics coming on line. Government officials expect the number of children who are vaccinated to keep rising in the days and weeks ahead, he said. “We are just getting started,” he said. Earlier this year the White House set — and missed — a July 4 goal to have at least certain percentage of U.S. adults vaccinated. Officials have not announced a similar target for kids. Dr. Lee Savio Beers, president of the American Academy of Pediatrics, called the new numbers reassuring and said the rollout appears to be going smoothly for the most part. She noted however that with a lower dose and different vials than for older kids, the rollout requires more steps and that some states have been slower in getting vaccine to providers. Initial data from some areas show Black children lagging behind whites in getting their first doses, which Beers said raises concerns. “It’s really important to make sure the vaccine is easily accessible in a wide variety of places,” Beers said. -
 2021-09-16
2021-09-16The Importance of Context in Covid-19 Vaccine Safety
Vaccine safety is critical for the successful implementation of any vaccination program, especially during a pandemic. In February 1976, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention confirmed a cluster of cases of severe influenza-like illness among Army recruits at Fort Dix, New Jersey.1 A swine influenza A strain that resembled the 1918 pandemic influenza strain was identified,2 and a vaccination program was subsequently initiated for the entire U.S. population. After more than 40 million persons were vaccinated, a small excess risk of Guillain–Barré syndrome was noted, with an attributable risk of approximately 1 case per 100,000 doses administered. Given these concerns and because the pandemic did not materialize, the vaccination program was halted in December 1976 so that the issue could be explored further. This experience shed light on the need for real-time vaccine safety surveillance and the importance of context in decision making during a pandemic. In a study now reported in the Journal by Barda et al., the investigators simultaneously evaluated the risk of adverse events among persons (≥16 years of age) who had received the BNT162b2 vaccine (Pfizer–BioNTech) and the risk of the same events after severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection.3 The authors used data from the largest integrated payer–provider health care organization in Israel, in conjunction with data on SARS-CoV-2 polymerase-chain-reaction tests and data on coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) vaccine administration from the Israeli Ministry of Health. This use of multiple data sets highlights the importance of investment in digital capabilities and meaningful integration across systems in order to provide real-time answers to key public health questions. The design of rigorous postauthorization vaccine safety studies during the Covid-19 pandemic has been a challenge because the pandemic itself has caused changes in health care utilization, the rollout of Covid-19 vaccines has occurred in phases because of initial supply limitations, and there have been disparities in access to vaccines. Barda et al. broadly addressed many of these challenges by emulating a trial that matched eligible vaccinees to unvaccinated controls according to sociodemographic characteristics, the number of preexisting chronic health conditions, previous health care utilization, and pregnancy status. In the vaccination analysis, the study included 42 days of follow-up (i.e., 21 days after the first dose and 21 days after the second dose). This analysis accounted for seasonal and secular trends by matching on the day of vaccination, rather than relying on historical risk estimates that may not have been comparable in the pandemic setting. In the SARS-CoV-2 analysis, a similar approach was used to match persons with a newly diagnosed infection to uninfected persons. Although the risk estimates in the vaccination and the SARS-CoV-2 analyses were not directly comparable because of differences in the populations (i.e., events were evaluated per 100,000 vaccinated persons and per 100,000 infected persons, respectively), these risks were placed in context. The most salient example is myocarditis, which has received much attention recently given the preponderance of reported cases after vaccination among adolescents and young adults and the incidence of myocarditis observed after SARS-CoV-2 infection.4-6 In the population-based cohort in the study conducted by Barda and colleagues, the risk ratios for myocarditis were 3.24 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.55 to 12.44) after vaccination and 18.28 (95% CI, 3.95 to 25.12) after SARS-CoV-2 infection, with risk differences of 2.7 events per 100,000 persons (95% CI, 1.0 to 4.6) and 11.0 events per 100,000 persons (95% CI, 5.6 to 15.8), respectively. What is even more compelling about these data is the substantial protective effect of vaccines with respect to adverse events such as acute kidney injury, intracranial hemorrhage, and anemia, probably because infection was prevented. Furthermore, the persons with SARS-CoV-2 infection appeared to be at substantially higher risk for arrhythmia, myocardial infarction, deep-vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, pericarditis, intracerebral hemorrhage, and thrombocytopenia than those who received the BNT162b2 vaccine. National discussions about benefit–risk balance often focus on the benefits of preventing symptomatic disease, hospitalization, or death due to Covid-19 and the risks of serious adverse events after vaccination.7,8 As specific adverse events such as myocarditis are highlighted, however, the lack of corresponding specificity about benefits can hamper efforts to communicate effectively with patients. Messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccines may be associated with myocarditis, but they can also prevent cases of myocarditis, acute kidney injury, arrhythmia, and thromboembolic disease. The key to comparing these risks depends on the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection to an individual person, and that risk can vary according to place and over time. Given the current state of the global pandemic, however, the risk of exposure to SARS-CoV-2 appears to be inevitable. One major limitation of this study is the lack of risk estimates according to age group and sex. For example, thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome occurs predominantly in young adult women who have received adenoviral vector vaccines against SARS-CoV-2, whereas myocarditis predominantly occurs in male teens and young men who have received mRNA vaccines.5,9,10 Age- and sex-stratified comparisons that reflect local epidemiologic factors might support public understanding of different approaches to vaccine use in different countries, such as Israel, the United Kingdom, and the United States. Other limitations of the study include the paucity of data regarding younger teens and children, the conservative assumption that vaccines have no effect on transmission, and the absence of medical record review to validate computable phenotypes (i.e., algorithms used to identify a cohort on the basis of patient records). As new knowledge of the safety and benefits of vaccines continues to evolve, studies like this one may help to support decision making about the use of Covid-19 vaccines. The benefit–risk balance should be reassessed, refined, and communicated as the disease burden changes, new variants and safety signals emerge, and vaccine effectiveness begins to wane. Context matters, which means that we as a country need to be ready for continual learning and change. -
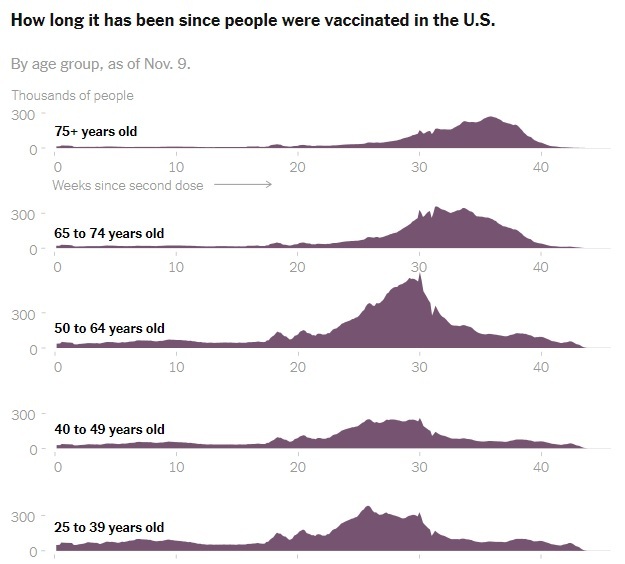 2021-11-11
2021-11-11What We Know So Far About Waning Vaccine Effectiveness
As tens of millions who are eligible in the United States consider signing up for a Covid-19 booster shot, a growing body of early global research shows that the vaccines authorized in the United States remain highly protective against the disease’s worst outcomes over time, with some exceptions among older people and those with weakened immune systems. But while the vaccines’ effectiveness against severe disease and hospitalization has mostly held steady, even through the summer surge of the highly transmissible Delta variant, a number of published studies show that their protection against infection, with or without symptoms, has fallen. Public health experts say this decline does not mean that the vaccines are not working. In fact, many studies show that the vaccines remain more than 50 percent effective at preventing infection, the level that all Covid vaccines had to meet or exceed to be authorized by the Food and Drug Administration back in 2020. But the significance of these declines in effectiveness — and whether they suggest all adults should be eligible for a booster shot — is still up for debate. -
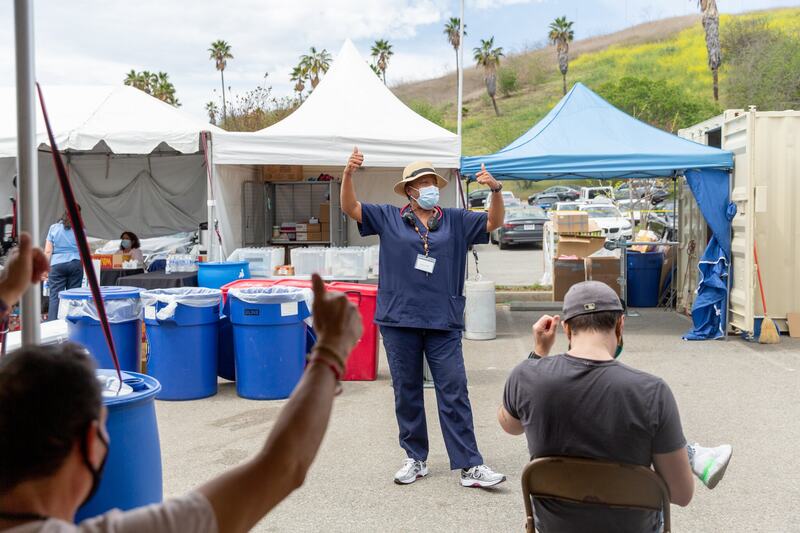 2021-04-06
2021-04-06Biden will offer a virus update as the pace of vaccination accelerates
President Biden will promote his administration’s success in accelerating the pace of coronavirus vaccinations during two appearances on Tuesday, as officials in nearly every state say they will make shots available to all adults by his target of April 19. Three months into his presidency, Mr. Biden confronts an escalating migrant surge at the border with Mexico and has embarked on a grind-it-out effort to ram through a $2.3 trillion infrastructure bill. But the virus remains his primary focus. And he wants the country to know that — so he is offering multiple updates each week, along with helpful visual cues, like standing next to a giant Easter bunny wearing a mask. On Tuesday afternoon, Mr. Biden will travel to Alexandria, Va., to tour a vaccination site at the Virginia Theological Seminary. Later, at the White House, he will deliver remarks emphasizing recent successes, including the milestone of delivering four million vaccinations in one day over the weekend. More than three million doses are now being given on average each day, compared with well under one million when Mr. Biden took office in January, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Every state has now given at least one dose to a quarter or more of its population. About 62.4 million people — 19 percent of Americans — have been fully vaccinated. On Monday, Gov. Larry Hogan of Maryland announced that all Maryland residents 16 or older would be eligible from Tuesday for a shot at the state’s mass vaccination sites, and starting April 19 at any vaccine provider in the state. Also on Monday, Gov. Philip D. Murphy of New Jersey and Mayor Muriel Bowser of Washington, D.C., said residents 16 or older would be eligible on April 19. Gov. Kate Brown of Oregon announced Tuesday that all Oregonians over the age of 16 were eligible to receive a vaccine. The state had been limiting the doses to those with underlying conditions and frontline workers. That leaves one state, Hawaii, keeping to Mr. Biden’s original deadline of May 1. In Hawaii, 34 percent of residents have received at least one dose. Alabama has vaccinated the lowest proportion of its residents, at 25 percent. Along with dangerous coronavirus variants that were identified in Britain, South Africa and Brazil, new mutations have continued to pop up in the United States, from California to New York to Oregon. The shots will eventually win, scientists say, but because each infection gives the coronavirus a chance to evolve further, vaccinations must proceed as quickly as possible. For now, however, cases are rising sharply in parts of the country, with some states offering a stark reminder that the pandemic is far from over. Yet again, governors across the country have lifted precautions like mask mandates and capacity limits on businesses. -
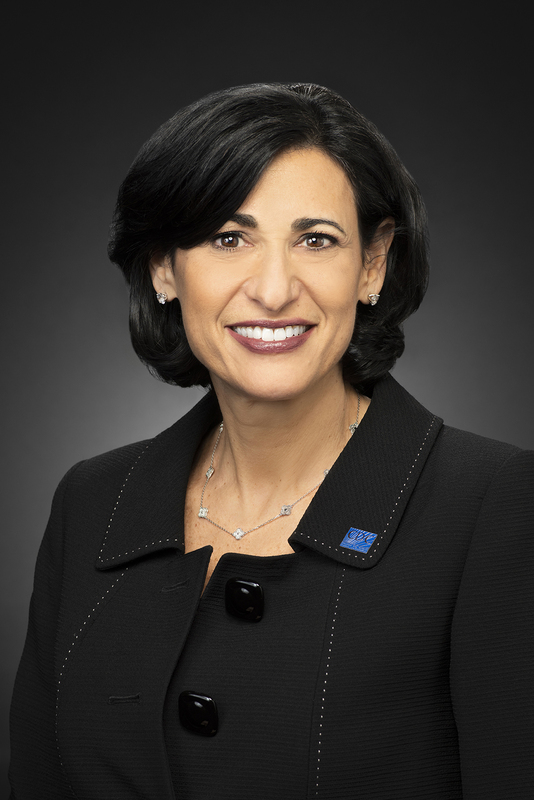 2021-01-19
2021-01-19Incoming CDC Director to Prioritize Communication, COVID-19 Vaccine Rollout
As Rochelle Walensky, MD, MPH, prepares to assume the role of CDC director on January 20, the former professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and infectious disease physician at Massachusetts General Hospital and Brigham Women’s Hospital faces a myriad of challenges wrought by the ongoing coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. January 21st marks the 1-year mark since the first case of COVID-19 was reported in the United States, while current data indicate the country has surpassed 400,000 deaths. In comparison, the 1918 flu pandemic took 675,000 American lives, while the US reported a total of 405,000 fatalities during World War II. Even at the unprecedented speed with which pharmaceutical companies have developed vaccines for COVID-19, rollout has been fragmented at the state level while racial disparities in administration rates are beginning to become apparent. In an effort to improve the national rollout of COVID-19 vaccines, Walensky plans to increase the CDC’s communication to combat any hesitancy in receiving the vaccine, and indicated she wanted to increase media appearances above those made by current director Robert Redfield, MD, who departs with any remaining Trump administration officials Wednesday. She said making sure science-based communication is effectively disseminated to the public in layman’s terms is a top priority. “Science is now conveyed through Twitter. Science is conveyed on social media, on podcasts, and in many different ways. And I think that's critical,” Walensky said during a livestreamed interview with JAMA's Howard Bauchner, MD, the journal's editor-in-chief. When confronting vaccine hesitancy or anti-vaxxer sentiment on social media, “There's just this massive void and the right information, I think, is not getting out there… I want to make sure that the science is conveyed. We have to say it to one another. We have to say it to the public. And then we have to say it in other forms.” Internally, Walensky hopes to bolster the voices of scientists already employed by the CDC. Under the Trump presidency, “they have been diminished. I think they've been muzzled,” Walensky said. “This top tier agency—world renowned—hasn't really been appreciated over the last 4 years, and really markedly over the last year. So I have to fix that.” Although some states have been widely successful in administering the allotment of COVID-19 vaccines they were given, many have reported roadblocks. Part of the Biden administration’s plan to enhance rollout is to expand vaccine allocation to 4 key locations: federally qualified health centers, community vaccination centers (ie, stadiums), mobile units, and pharmacies. “Part of the challenge with COVID-19 was that we had a frail public health infrastructure to start. It wasn't ready to tackle what it was given,” Walensky said. As director, she hopes to bring this reality to Congress’ attention. “We're in this because we had warnings for many, many other public health scares in the last 20 years and we didn't fix our public health infrastructure and our data infrastructure,” in response to those tests. In order to meet President-elect Biden’s goal of 100 million vaccinations in 100 days, the constraints currently faced by federal and state governments need to be mitigated. “We have to titrate our supply and our eligibility so that we somehow hit the sweet spot, wherever it is we are, with how much supply we have and how many people are eligible,” Walensky said. While the CDC set the initial guidelines for vaccine eligibility and revised them this month, the Trump administration left actual rules and distribution processes to states, resulting in wide variation across the country. Some states adopted stricter standards that led to the waste of vaccines, while loose adherence has led to long lines and confused residents. Expanding the population of those eligible to administer the vaccine can also help alleviate these roadblocks. These individuals can include retirees, the Public Health Commissioned Corps, medical military, upper level medical and nursing students, dentists and veterinarians. Increasing both the number of vaccination sites and vaccinators will also help address the equity problems brought to light by the pandemic. “We want to make sure that we can deliver volume, but also volume to the people in places that might be harder to reach.” In a collaborative approach, the federal government will step in at a state-by-state level and offer help based on each state’s unique challenges, Walensky said. -
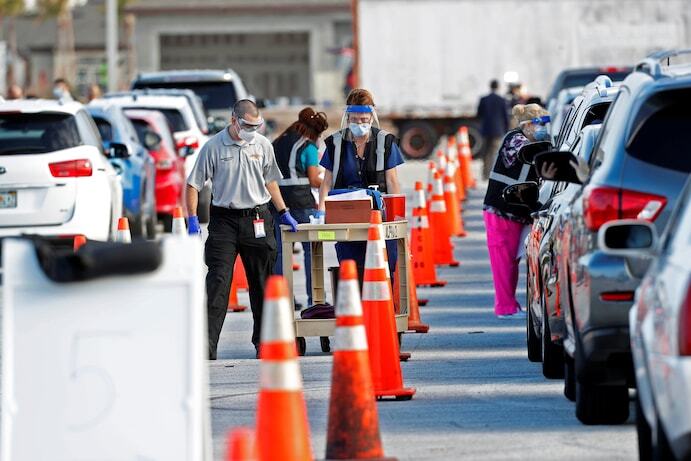 2020-12-31
2020-12-31Trump administration falls far short of vaccination goals as new virus variant looms
Logistical problems at the heart of the federal government’s faltering rollout of coronavirus vaccines came into sharper view Thursday as the Trump administration fell vastly short of its goal of delivering an initial shot to 20 million people by the end of December. On the final day of a bleak year, only about 2.8 million people had received the shot, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention — the first of two doses needed to provide immunity to the virus. Around 14 million doses had been distributed as of Wednesday, according to Gustave Perna, chief operating officer of Operation Warp Speed, and a total of 20 million doses have been allocated. Though the figures are an underestimate — data collection on vaccinations has lagged — the doses administered so far represent just a small fraction of the ambitious targets outlined by officials from the administration’s Operation Warp Speed program in the fall. “We’d have liked to have seen it run smoothly and have 20 million doses in to people today, by the end of 2020, which was the projection,” Anthony S. Fauci, the government’s leading infectious-disease expert, said in an interview with NBC’s “Today” show on Thursday. “Obviously it didn’t happen, and that’s disappointing.” Nationwide, states and health-care providers continued to grapple with unpredictable timelines for when new vaccine shipments would arrive and in what quantities, while chronically underfunded public health departments struggled to muster the resources to carry out mass injections of front-line workers and vulnerable people. Fauci said that he hoped momentum for vaccinations would build in the first weeks of the new year and bring the country closer to its immunization goals. “But there really has to be more effort in the sense of resources for the locals, namely the states, the cities, the counties, the places where the vaccine is actually going into the arms of individuals,” he said. “We have to support the local groups, the states and the cities to help them get this task done, which is a very prodigious task.” Under the Trump administration’s plan, the federal government supplies vaccines to states but leaves it to state officials to prioritize residents, send doses to providers and get shots into people’s arms. The approach — as well as a litany of logistical problems — has caused a varied distribution effort. Local health departments and hospitals tasked with administering the vaccines have complained that they do not know when shipments will come or if they will receive additional resources, said Oscar Alleyne, and epidemiologist and chief of programs and services for the National Association of County and City Health Officials, which is made up of about 3,000 local health departments. “Some health departments have only received vaccines as recently as this week,” Alleyne told The Washington Post. “I had one health department that told me they had received their vaccines the day after Christmas.” Alleyne compared the communication concerns to those that cropped up during the H1N1 pandemic in 2009, when unclear guidance hampered efforts to get the population vaccinated. “It really boils down to ensuring a very transparent process,” Alleyne said. “There will always be a lag between the doses allocated and those shipped; between those shipped and those administered; and between those administered and those reported to CDC as administered,” Michael J. Pratt, a spokesperson for Operation Warp Speed, said in a statement. “We’re working to make those lags as small as possible.” At the Texas Medical Center, the largest medical complex in the world, the approach has already created logistical challenges. Hospital officials on the campus in south Houston often don’t know exactly when to expect new shipments or precisely how many vials they’ll receive, according to Bill McKeon, the center’s chief executive officer. That leaves the center with just a couple days’ worth of vaccine inventory on hand at a time, he said. “At best, we hear estimates. It’s a day-to-day situation,” McKeon told The Post. “We hear that we may be getting more next week but we’re not sure.” To date, the center has administered the first of the two injections to about 60,000 people, averaging more than 4,000 a day, according to McKeon. That includes some of the center’s 120,000 employees, as well as patients with underlying conditions who are first in line for inoculation. But it’s only a tiny portion of the sprawling metropolitan area the center serves. Until hospital officials can better predict how many vaccine doses they’ll have available week after week, McKeon said, vaccinating more people, faster, will be an uphill battle. “You can’t do scheduling with a couple days of inventory. We wouldn’t put a patient through the process of coming to the hospital, leaving their home, and then say, ‘Sorry we don’t have the inventory,’ ” he said. “We can’t be bold and just say, ‘Let’s do ten thousand a day.’ ” McKeon called on the federal government to take a more active role, possibly offering more large-scale vaccination centers, and relieve pressure on state officials, whom he said were “rowing in the same direction” as providers. There will be a growing need not just for more health-care workers to give the shots, he said, but for people who can perform the administrative work of calling patients, verifying their personal information and signing them up for injections. “I’m not seeing the grand strategies on a national basis, and I’m concerned, because this is a war,” he said. “Every day that we delay on some of those grander strategies we’re going to see losses of life.” As the distribution of vaccines has proceeded in fits and starts, coronavirus deaths and hospitalizations have soared to new heights. More than 125,000 people around the country were in hospital beds battling covid-19, the disease caused by the virus. Hospitalizations have exceeded 100,000 since Dec. 2. The nation on Wednesday also recorded a record 3,862 deaths in a day. The previous record, set on Dec. 17, was 3,406. New daily reported cases were trending upward again, after dipping during the week of Christmas. Family gatherings and spikes in holiday travel make it all but certain that the new year will bring yet another wave of infections. Compounding fears about the accelerating virus spread, a new, more transmissible variant of the coronavirus has cropped up in multiple U.S. states after circulating in the United Kingdom. The presence of the mutated pathogen only added to the need for vaccinations to ramp up quickly, said Scott Gottlieb, former Food and Drug Administration commissioner. “The Covid vaccine could be a tool to help reduce the impact of current wave of epidemic spread,” he tweeted Thursday. “But we’re largely missing the narrow window we had to deploy it rapidly enough to alter the present trajectory of death and disease in January. The new variant makes this more urgent.” Clarification: This story has been updated to cite Operation Warp Speed’s distribution numbers. It has also been updated to note that Operation Warp Speed has allocated 20 million vaccine doses to states. -
 2020-12-14
2020-12-14The U.S. Approves a Vaccine
The Food and Drug Administration authorized Pfizer’s Covid-19 vaccine for emergency use on Friday, clearing the way for millions of highly vulnerable people to begin receiving inoculations within days. The authorization is a turning point in a pandemic that has taken more than 290,000 lives in the United States. With the decision, the United States becomes the sixth country — in addition to Britain, Bahrain, Canada, Saudi Arabia and Mexico — to clear the vaccine. Today, we ask the science and health reporter Donald G. McNeil Jr. what might happen next. -
 2021-11-10
2021-11-10Employee Weekly Covid-19 Test
Since the pandemic and everyone returning back to work a vaccine has been provided for everyone to take the vaccine if they choose to. The vaccine is to help with Covid, if received it can help with less symptoms if one happens to catch Covid. At my place of employment we have received emails from HR that anyone who has not been vaccinated must take a covid weekly test in order to ensure we do not have covid and make sure the campus is a safe place to be and ensure that everyone stays virus free. -
 2020-09-14
2020-09-14Pfizer and BioNTech announce plan to expand Covid-19 vaccine trial
Pfizer and BioNTech are moving to enlarge the Phase 3 trial of their Covid-19 vaccine by 50%, which could allow the companies to collect more safety and efficacy data and to increase the diversity of the study’s participants. The companies said in a press release that they would increase the size of the study to 44,000 participants, up from an initial recruitment goal of 30,000 individuals. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration will have to approve the change before it goes into effect. “The companies continue to expect that a conclusive readout on efficacy is likely by the end of October,” the press release said. The Pfizer and BioNTech study is likely to be among the first in the U.S. to report efficacy data from a Phase 3 trial. Related: AstraZeneca resumes Covid-19 vaccine trials in the U.K. Expanding the trial will likely make it easier for the company to demonstrate whether the vaccine is effective against SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes Covid-19. The companies also said that the change will allow the study to include a more diverse population. The companies said the study will now include adolescents as young as 16, people with stable HIV, and those with hepatitis C or hepatitis B. The companies said that the trial is expected to reach its initial target of 30,000 patients next week. Moderna, which started its trial on the same day as Pfizer, said on Sept. 4 that it is working to increase the diversity of trial participants in its study, “even if those efforts impact the speed of enrollment.” Related: Covid-19 Drugs and Vaccines Tracker The Pfizer/BioNTech study could finish sooner than Moderna’s, even though the two began on the same day, for other reasons, as well. Both vaccines require a second shot; Pfizer’s is given after three weeks, while Moderna’s is given after four. The Pfizer trial also starts to count cases of Covid-19 sooner after participants receive their shots than the Moderna study. But the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine could also prove to be one of the most difficult of the experimental vaccines to distribute, should they prove effective. The vaccine must be kept at a temperature of -70 degrees Celsius. There has been political pressure to move a vaccine quickly, with President Trump saying that one could be available before election day. Last week, several drugmakers, including Pfizer, issued a pledge not to move a vaccine forward sooner than was justified by the results of their clinical trials. -
 2020-07-14
2020-07-14Moderna Phase 1 results show coronavirus vaccine safe, induces immune response
Moderna Inc’s experimental vaccine for COVID-19 showed it was safe and provoked immune responses in all 45 healthy volunteers in an ongoing early-stage study, U.S. researchers reported on Tuesday. Volunteers who got two doses of the vaccine had high levels of virus-killing antibodies that exceeded the average levels seen in people who had recovered from COVID-19, the team reported in the New England Journal of Medicine. No study volunteers experienced a serious side effect, but more than half reported mild or moderate reactions such as fatigue, headache, chills, muscle aches or pain at the injection site. These were more likely to occur after the second dose and in people who got the highest dose. Experts say a vaccine is needed to put an end to the coronavirus pandemic that has sickened millions and caused nearly 575,000 deaths worldwide. Moderna was the first to start human testing of a vaccine for the novel coronavirus on March 16, 66 days after the genetic sequence of the virus was released. Dr. Anthony Fauci, director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, whose researchers developed Moderna’s vaccine candidate, called the results “good news,” noting that the study found no serious adverse events and the vaccine produced “reasonably high” levels of virus-killing or neutralizing antibodies. “If your vaccine can induce a response comparable with natural infection, that’s a winner,” Fauci said in a telephone interview. “That’s why we’re very pleased by the results.” Moderna shares jumped more than 15% in after-hours trading on Tuesday. The U.S. government is supporting Moderna’s vaccine with nearly half a billion dollars and has chosen it as one of the first to enter large-scale human trials. A successful vaccine could be a turning point for Cambridge, Massachusetts-based Moderna, which has never had a licensed product. Moderna’s shot, mRNA-1273, uses ribonucleic acid (RNA) - a chemical messenger that contains instructions for making proteins. When injected into people, the vaccine instructs cells to make proteins that mimic the outer surface of the coronavirus, which the body recognizes as a foreign invader, and mounts an immune response against. The results released Tuesday involved three doses of the vaccine, tested in groups of 15 volunteers aged 18-55 who got two shots, 28 days apart. The groups tested 25, 100 or 250 micrograms of the vaccine. Adverse events after the second dose occurred in seven of the 13 volunteers who got the 25-microgram dose, all 15 participants who received the 100 microgram dose and all 14 who got the 250 microgram dose. In the highest-dose group, three patients had severe reactions such as fever, chills, headache or nausea. One of these had a fever of 103.28 Fahrenheit (39.6 C). “We didn’t see any events that are characterized as serious adverse events,” said lead author Dr Lisa Jackson of Kaiser Permanente Washington Health Research Institute in Seattle, referring to reactions that require hospitalization or result in death. In June, Moderna said it selected the 100-microgram dose for its late-stage study to minimize adverse reactions. At that dose, Moderna said the company is on track to deliver about 500 million doses per year, and possibly up to 1 billion doses per year, starting in 2021, from the company’s internal U.S. manufacturing site and strategic collaboration with Swiss drugmaker Lonza. “It’s a good first step,” said Dr William Schaffner, a vaccine expert at Vanderbilt University Medical Center who was not involved in the study. “There’s nothing here that would inhibit one from going ahead to the Phase 2/Phase 3 trials,” he said. In April, Moderna expanded the Phase 1 trial to include adults over 55, who are more at risk of serious disease, with the aim of enrolling 120 volunteers. Moderna said it will follow study volunteers for a year to look for side effects and check how long immunity lasts. Moderna started its phase 2 trial in May and expects to start a phase 3 trial on July 27. Phase 1 trials aim to ensure a treatment is safe and help determine an effective dose. Phase 2 trials test a treatment in a larger group and get an early read on effectiveness. Phase 3 trials are conducted in a large group of individuals to confirm efficacy and identify rare side effects. Moderna’s Phase 3 trial will be conducted in 30,000 volunteers.
