-

--Reflections on the Pandemic Archive--
Looking back over my experience with the “Journal of the Plague Year” COVID-19 archive, my prevailing emotion is gratitude. This opportunity granted me experience that few historians earn, and the remote, asynchronous work schedule allowed me to collaborate with my colleagues in ways that maximized our respective contributions. The breadth and depth of our individual experiences and perspectives tremendously improved our collective process and products.
I spent enough time in the Arizona State Archives last year to recognize such collections as historical treasure chests, but I have now participated in processing an archive’s content and navigating the ethical dilemmas those submissions sometimes create. Archivists and curators are the history profession’s truly unsung heroes, and their work facilitates society’s perception of itself.
My background in police work and public safety drew me to the archive’s existing Law Enforcement collection. In taking on that subset, I succeeded in reshaping the collection’s parameters to now include stories about police and law enforcement. I wanted to diversify the collection to encompass perspective of both the police and the public with whom they interact and serve. While some overlap exists between the Law Enforcement and Social Justice collections, each remains distinct. Through my contacts and writing, I promoted a Call for Submissions to an international audience of law enforcement professionals to reduce their relative silence within the archive.
Within the archive’s content, I recognized that one’s location might shape their pandemic experience, and I created and designed an Arizona-based exhibit to explore that. Further research and discussion with my mentors and colleagues ensured the exhibit illustrated these differences without excluding visitors whose diverse experiences could further enrich the archived and exhibited content. I am proud of my “Arizona’s COVID-19 Pandemics” exhibit, particularly because of its compressed, one-month incubation period. Beyond displaying images, data, and stories representative of the diverse pandemic experiences within the state, the ACP exhibit offers visitors numerous levels of interaction and engagement to became active participants and create their own exhibit experience. Visitors can complete opinion surveys, add a story to the archive, explore additional content related to the displayed pieces, view ever-changing results from pre-defined archival content searches, conduct their own archival search, view collective visitor survey results, and apply to join the staff. The exhibit’s searches will include the archive’s future submissions, which reshapes both the exhibit and the experience visitors may have with it.
A more detailed explanation of my ACP exhibit may be reviewed here: https://covid-19archive.org/s/archive/item/43037
Because of Dr. Kathleen Kole de Peralta and Dr. Mark Tebeau, I stand prepared to join research, curation, and exhibition teams and immediately contribute to their work products.
Despite my gratitude for this experience and the opportunities it presented, I look forward to the day COVID-19 is no longer part of humanity’s daily vernacular.
James Rayroux
22 April 2021
-

While working as a curatorial intern on ASU's 'A Journal of the Plague Year' COVID-19 archive, I created this exhibit on the pandemic experience within the state.
In addition to obvious, overarching realities such as socioeconomic status and immediate access to healthcare systems, I initially believed one of the greatest deciding factors that determined one's experience in Arizona was an individual's residence in either predominantly urban or rural environments. The proposed exhibit had been originally titled "A Tale of Two Arizonas" to pay respect to Charles Dickens and the differing realities experienced here.
To test my proposed hypothesis, I went about finding data, stories, and submissions that substantiated or disputed my premise. Within a short time, I had identified four distinct environmental drivers of personal pandemic experiences; to me, that indicated the existence of many more I hadn't yet found or had overlooked along the way. My evidence suggested a minimum of four pandemic locales: Urban, Rural, Border, and Tribal within the State of Arizona and its fifteen counties. The recorded health data and personal experiences demonstrated the naivete of my initial hypothesis, and I retitled the exhibit: "Arizona's COVID-19 Pandemics."
The Exhibit Background section illustrates the vast dichotomies within Arizona in terms of population density and access to healthcare facilities. Given the virus's respiratory nature, these factors seemed especially relevant to driving diverse local experiences. I chose to include a flyer from the Coconino County Health and Human Services' "Face It! Masks Save Lives" campaign. The flyer included a specific line to "Stay Home When Sick" that seemed to illustrate a different public health paradigm than the broader "stay home" orders from Maricopa and Pima county. This section also features an image of Sedona's red rocks and a portion of The Wave to remind visitors of the wide-open rural areas accessible to all, as well as those with cultural significance to the Native American tribes and limited access to the general public.
The next section asks a short, five-question survey in which visitors may participate.
The Silver Linings piece features a short audio clip of a father and husband discussing some unexpected benefits of the pandemic. Visitors may explore additional Silver Linings stories and submit their own experience.
The Tséhootsooí Medical Center piece seeks to illustrate the different pandemic experience on the state's tribal lands. I hoped to inspire some relevant emotional turmoil for the visitors through the piece's visual presentation. I wanted to create a series of waves with quotes from the medical center's healthcare workers. I hoped visitors' attention would be drawn to the large, bolded key words, and that they would first experience the segments out of sequence because of that. After potentially feeling a sense of chaos, they might settle themselves into a deliberate reading of the texts and find their own order within the experiences provided here. This piece allows further exploration of Native submissions and topics, a review of an additional related news article, and a submission prompt that invites visitors to offer guidance to hospital managers.
The next piece illustrates the differences between mask mandates in communities across Arizona. In addition to hearing an audio clip of interviews with mayors and a public health official, visitors can explore additional submissions related to mask mandates and submit their thoughts on statewide mandates.
The Arizona Department of Health Services provides zip-code specific infection data on its website, and the wide array of known case infections therein further illustrates potential dichotomies across the state. In working to include and represent this data in a consumable way, I encountered inconsistencies with tribal data. The nation's Indian tribes are overseen by Indian Health Services, a federal public health agency, and it does not collect or report data in the same manner as the State of Arizona or its counties. At first glance, the data would seem to suggest that tribal areas had less severe pandemic experiences than the rural and urban areas, which was not objectively true. I wanted to offer the unedited data to visitors, allow them to drawn their own conclusions, and invite them to offer their thoughts on what potential misunderstandings might emanate from these reporting differences. Visitors may also choose to review the foundational data from this piece, as well.
I used the following two sections to offer submission prompts about the visitor's overall pandemic experience as a function of their location, as well as what they might have done if placed in charge of their city, county, or state during this pandemic.
A diverse Search section allows visitors to explore additional topics of interest to them. 23 hyperlinks offer pre-defined search parameters. An Advanced Search link allows self-defined research, and a Join The Staff link connects visitors with opportunities to work within the JOTPY archive.
A final section asks visitors to provide feedback on the exhibit, its content, and the pandemic in general.
Both surveys within the exhibit will display overall results to visitors who participate in them.
Through this process, I found incredible amounts and diversity of data outside the archive that spoke to these generally localized experiences, but not that much yet within the archive explained what Arizonans had experienced outside the state's urban environments. I created a call for submissions and delivered it to fifty rural entities that might help support the effort to collect and preserve more rural Arizona stories. Between all the local libraries, historical societies, museums, small-town mayors, and county health officials to whom I asked for help, I am optimistic the archive will better represent all Arizonans in the coming months and years. Despite the exhibit having been created, I ensured its internal search features would include future submissions and allow the exhibit to remain relevant long after its release.
-

In this episode, we at the Podcast of the Plague Year were granted the opportunity to record interviews with two organizations assisting refugees that have been relocated to Arizona- RICE and Lutheran Social Services of the Southwest.
Refugees are those who have been forced to flee their country because of a well-founded fear of persecution for reasons of race, religion, nationality, or political opinion. Almost 3 quarters of a million refugees have been resettled in the United States since 2008; they often come with very little resources to begin life anew once resettled. Life for refugees during resettlement comes with hope, but also with struggles to learn a new language, navigate new employment and educational systems and integrate into a new society. It is easy to imagine how a pandemic could intensify already existing struggles.
-

A cursory look into A Journal of the Plague Year reveals that the pandemic is nondiscriminatory, all of are affected. Yet, the reality is that Covid-19 is having more impact on certain populations in American communities. Arizona State University's Center for the Study of Religion and Conflict partnered with the Henry Luce Foundation to provide rapid relief funding to marginalized communities in the southwest. As part of the rapid relief program, the Center for the Study of Religion and Conflict is collaborating with A Journal of the Plague Year and the Walter Cronkite School of Journalism and Mass Communication to raise awareness about the marginalized communities that were assisted via this grant.
By joining this "Southwest Stories" project, we at the Podcast of the Plague Year were granted the opportunity to spotlight one Native American community in Arizona- the White Mountain Apache Tribe.
-
As COVID-19 began to spread across the Southwest in March, lawyers representing incarcerated Arizonans reported “unsanitary conditions,” “inadequate medical staffing and treatment” and a “failure to take strong and sensible precautionary measures” in state prisons.
The combination left prisoners “highly vulnerable to outbreaks,” the attorneys wrote in a letter to the state before asking a federal judge to intervene. The judge did by issuing an order for officials to release more information, but prison advocates say it hasn’t been enough.
Nearly four months later, complaints of insufficient safety measures and subpar medical care continue to plague Arizona prisons. At least 569 prisoners at 13 of the state’s 16 prison complexes had tested positive for COVID-19 as of July 15, according to the Department of Corrections, Rehabilitation and Reentry, and at least 371 staffers have reported positive results.
Justice reform advocates and others with ties to the correctional system worry the state is running out of time to prevent an even more dangerous surge in cases. COVID-19 can spread swiftly in crowded indoor spaces and among individuals with chronic health problems.
-
Amid the COVID-19 pandemic, students are adjusting to their new normal when it comes to online classes, virtual events and social distancing to prevent the spread of the disease.
But for deaf and hard of hearing students in Arizona public schools, as well as for many more enrolled in private schools, these adjustments introduce new barriers to communication and learning. Last year, according to the Arizona Department of Education, 1,622 deaf or hard of hearing students were in public schools.
Sequoia Deaf School, part of the Edkey Inc. charter school group in Mesa, had 52 students enrolled in grades K through 12 for the 2020-21 school year. Its experience navigating the pandemic illustrates some of the challenges deaf students face, such as difficulty reading lips and faces behind masks, the shorter attention spans of young deaf students and the loss of their nurturing school community.
-
PHOENIX – Civil rights marches. Anti-war protests. Rallies against gun violence.
Public demonstrations historically have involved the “mass mobilization of bodies,” according to Tiera Rainey, program director for the Tucson Second Chance Community Bail Fund and an organizer with Black Lives Matter Tucson.
But when the novel coronavirus struck, prompting warnings against crowds and close contact, Arizona’s new reality of social distancing forced organizers to rethink that framework.
-
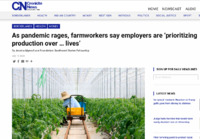
As of early July, 87 workers and 58 family members, 23 of them children, had tested positive for the novel coronavirus that causes COVID-19, according to data compiled by United Farm Workers, a labor union. Many more are awaiting results.
“I don’t want to go back,” Bertha said. She feels she has only two options: Accept the working conditions, or quit.
The pandemic has forced agricultural workers throughout the Southwest to make a similar choice between their health and their incomes. Though industry representatives say farms are doing everything they can do to protect their employees, worker advocates argue a lack of industry protections – and the “invisibility” of much of the work done by day laborers – have made farmworkers especially vulnerable to exploitation.
“It just shows the contradiction in calling somebody an ‘essential worker’ but only for what you need them for, not to care for them as human beings that also are afraid of getting sick,” said Juanita Valdez-Cox, a migrant-rights advocate in Texas.








